* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 13-15
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Optical fiber wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Fiber Bragg grating wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Optical attached cable wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
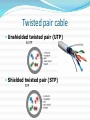
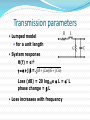
Lecture 13-15: Transmission media Aliazam Abbasfar Outline Transmission media Communications systems Wireline (wired) Telephony (voice, fax, modem, DSL) Ethernet/LAN Cable TV Backplane copper links Wireless (Electromagnetic) Over the air communication Radio and TV broadcast WLAN Cellular Radar Fiber optics High speed long haul data communication High traffic data transfer Transmission media Open wire Twisted pair Coaxial cable Optical fiber Air Open-wire On utility poles share power line routes Interference limited (EMI) Limits the BW too Transposition to reduce interference Early twisting scheme 4 twists per Km Environmental effects Twisted pair cable Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) Shielded twisted pair (STP) Transmission parameters • Lumped model • for a unit length • System response H(f) = e-gL g = a + j b = ( R + jL)(G + jC) Loss (dB) = 20 log10e a L = a’ L phase change = b L • Loss increases with frequency Interference Interference is the main limitation (BW) Twisting reduces interference Shielding further reduces interference Cross talk (X-Talk) Near end cross talk (NEXT) Far end cross talk (FEXT) Cable length Space between pairs NEXT - NEXT and FEXT decreases with frequency f1.5 and f2 FEXT Applications Communication networks Subscriber lines Analog (Voice) Digital (ADSL, HDSL, VDSL) Links (E1,T1) Computer networks LAN Cat Cat Cat Cat 3 4 5 6 < < < < 10 Mbps 100 Mbps 150 Mbps 350 Mbps Coaxial cable Low cross talk Increases with frequency High speed/Long links Long distance communication links Cable TV WAN/MAN Wireline media comparison Medium Freq. range Loss (dB/Km) @ freq Open wire 0-150 KHz 0.03 0.2 1 KHz 200 KHz Twisted pair (Loaded) 0-1 MHz 0.7 (0.2) 1 KHz (3.5 KHz) Cat 6 1-250 MHz 21 60 1 MHz 10 MHz Coax 0-500 MHz 7 10 MHz Optical Fiber Structure 1. Core (8 µm) 2. Cladding (125 µm) 3. Buffer (250 µm) 4. Jacket (400 µm) Optical cable Fiber optics Optical propagation Refraction index ncore > ncladding Fiber types Step index Graded index Single mode Multi mode Optical fiber Loss Absorption Scattering Connectors Low loss : 0.2 dB/Km Color dependent Dispersion Multi modes = different paths Refraction index is frequency (color) dependent High bandwidth ( > 1 GHz) Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) DWDM Data rate > TB/s in a single fiber ! Wireless communication Frequency allocation needed in shared environment To avoid interference Spectrum is a very valuable resource Band allocation to applications Government regulations and policies ITU coordinates between nations Freq band: 3-30KHz Very low freq. (VLF) 30-300KHz Low freq. (LF) 300K-3MHz Medium freq. (MF) 3-30MHz High freq (HF) 30-300MHz Very high freq (VHF) 300M-3G Ultra high freq (UHF) 3-3GHz Super high freq. (SHF) Electromagnetic waves propagations Ground waves travels along the surface of the earth ( freq < 2 MHz) Sky waves reflected by ionosphere Very variable – seasonal Angle and loss of reflection Freq < 30 MHz Line of sight (LOS) No reflection or refraction Non Line of sight Local reflections/refractions Wireless issues Path loss Fading Mobility Interference Satellite systems LEOs Lower power Smaller delay Need many satellites Shift towards LEOs in 1990 Global domination Compete with cellular systems Failed miserably (Iridium ) Big, power hungry mobile terminals Global Positioning System (GPS) Satellite signals used to pinpoint location Popular in cars, cell phones, and navigation devices Natural area for satellite systems is broadcasting Now operate in 12GHz band 100s of TV and radio channels All over the world Reading Carlson Ch. 1 Proakis Ch. 1