* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture 36 - waves in 3 dimensions, optical devices
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Fourier optics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Photonic laser thruster wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
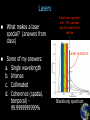
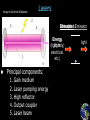
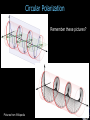
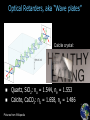
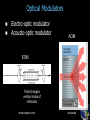
Announcements 11/22/10 Prayer No office hours tomorrow (neither TA nor I), even though we do have class. Exam 3 starts Tuesday after the break. Lab 10 (final lab) going on right now. Due the Tuesday after the break. Reading quiz Which of the following is NOT true of the wave vector? a. Its magnitude is equal to 2p/l. b. In a plane wave it points in the same direction everywhere in space. c. In a spherical wave it points in the same direction everywhere in space. d. It tells us which way the wave is going. e. In one dimension it reduces to the wave number k. Waves in 3-dimensions Plane waves a. polarization Wave vector a. direction of wave Spherical waves Student-designed problem What direction do you want the wave to be traveling in? What direction do you want the wave to be oscillating in? What wavelength do you want the wave to have? What do you want the wave’s amplitude to be? What frequency (or velocity) do you want the wave to have? What do you want the overall phase of the wave to be? Lasers What makes a laser special? (answers from class) Some of my answers: a. Single wavelength b. Intense c. Collimated d. Coherence (spatial, temporal) 99.9999999999% Actual laser spectrum over 100 narrower than the width of the red line Laser spectrum Blackbody spectrum Image & list from Wikipedia Lasers Stimulated Emission Emission Absorption Energy (light only) (light, electrical, etc.) Principal components: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Gain medium Laser pumping energy High reflector Output coupler Laser beam light Green laser pointer 1. Gain medium 2. Laser pumping energy 3. High reflector 4. Output coupler 5. Laser beam More Wikipedia More Wikipedia Circular Polarization Remember these pictures? Pictures from Wikipedia Optical Retarders, aka “Wave plates” Calcite crystal: Quartz, SiO2: no = 1.544, ne = 1.553 Calcite, CaCO3: no = 1.658, ne = 1.486 Pictures from Wikipedia Optical Modulators Electro-optic modulator Acousto-optic modulator AOM EOM Field changes vertical index of refraction www.newport.com wikipedia That’s All! (for optics) Survey (right now) about exam 3 review session times for Monday next week