* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Data Communication & Network
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical fiber wikipedia , lookup
Optical attached cable wikipedia , lookup
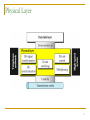
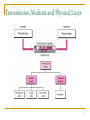
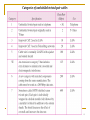
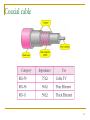
Computer Communication & Networks Lecture 8 Physical Layer: Transmission Media http://web.uettaxila.edu.pk/CMS/coeCCNbsSp09/index.asp Waleed Ejaz [email protected] 1 Physical Layer 2 Physical Layer Topics to Cover Signals Digital Transmission Analog Transmission Multiplexing Transmission Media 3 Transmission Medium and Physical Layer 4 Twisted-pair Cable 5 Categories of unshielded twisted-pair cables 6 Twisted Pair Cable (a) Category 3 UTP (b) Category 5 UTP 7 UTP connector 8 Twisted Pair Cables (Example) ADSL Ethernet networks - 10BASE-T - 100BASE-TX - 1000BASE-T - 1000BASE-TX (Cat5e (enhanced)) 9 UTP Performance 10 Twisted Pair Cable (Pros & Cons) Pros: easy to understand mass production - low cost most widely used medium Cons: prone to electromagnetic interference in power plants, airport buildings, military facilities, cars… Note: In-building networks at our university are almost all twisted pair 11 Coaxial cable 12 BNC connectors 13 Performance Coaxial Cable 14 Bending of light ray 15 Optical fiber 16 Propagation Modes 17 Modes 18 Fiber types 19 Fiber construction 20 Fiber-optic Cable Connectors 21 Performance Optical Fiber 22 Optical Fiber (Pros & Cons) Pros: Low attenuation Large bandwidth Cons: Relatively “new” technology “Expensive” 23 Comparing optical fiber to UTP Pros: Immune to electro-magnetic interference no crosstalk Reduced need for error detection and correction Enables longer link distances Attenuation unaffected by transmission rate Easier network upgrade Can combine different services: telephony, TV, internet… Cons: Optical components have higher cost Expensive deploying protocols 24 Unguided Media: Wireless Unguided media transport electromagnetic waves without using a physical conductor. This type of communication is often referred to as wireless communication. 25 Wireless Modern wireless digital communication began in the Hawaiian Islands What is “the best” frequency to use for communication? 26 Propagation Methods 27 Bands 28 Wireless Transmission Waves 29 Omni directional Antenna 30 Note Radio waves are used for multicast communications, such as radio and television, and paging systems. 31 Unidirectional Antennas 32 Note Microwaves are used for unicast communication such as cellular telephones, satellite networks, and wireless LANs. 33 Note Infrared signals can be used for shortrange communication in a closed area using line-of-sight propagation. 34 Readings Chapter 7 (B.A Forouzan) Section 7.1, 7.2 35 36