* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Coupled cluster wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Hartree–Fock method wikipedia , lookup
2-Norbornyl cation wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
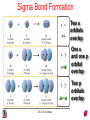
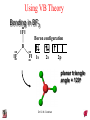
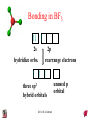
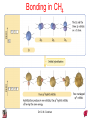
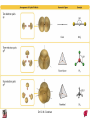
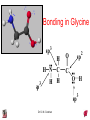
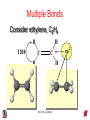
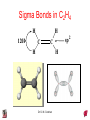
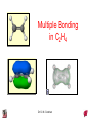
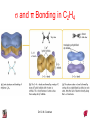
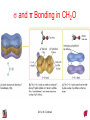
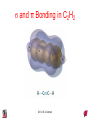
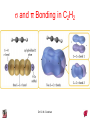
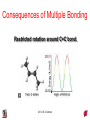
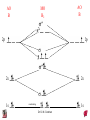
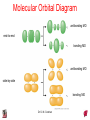
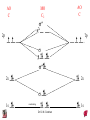
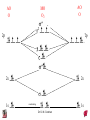
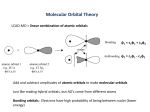
Chapter 10 Bonding and Molecular Structure: Orbital Hybridization and Molecular Orbitals Dr. S. M. Condren Advanced Theories of Chemical Bonding Atomic Orbitals Molecules Dr. S. M. Condren Two Theories of Bonding • MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY — • Robert Mullikan (1896-1986) • valence electrons are delocalized • valence electrons are in orbitals (called molecular orbitals) spread over entire molecule. Dr. S. M. Condren Two Theories of Bonding • VALENCE BOND THEORY — Linus Pauling • valence electrons are localized between atoms (or are lone pairs). • half-filled atomic orbitals overlap to form bonds. Dr. S. M. Condren Sigma Bond Formation by Orbital Overlap Two s orbitals overlap Dr. S. M. Condren Sigma Bond Formation Two s orbitals overlap One s and one p orbital overlap Two p orbitals overlap Dr. S. M. Condren Using VB Theory Bonding in BF3 •• •• F •• •••• F •• B Boron configuration ••• F• 1s •• 2s 2p planar triangle angle = 120o Dr. S. M. Condren Bonding in BF3 • How to account for 3 bonds 120o apart using a spherical s orbital and p orbitals that are 90o apart? • Pauling said to modify VB approach with ORBITAL HYBRIDIZATION • — mix available orbitals to form a new set of orbitals — HYBRID ORBITALS — that will give the maximum overlap, in the correct geometry. Dr. S. M. Condren Bonding in BF3 2p 2s hydridize orbs. rearrange electrons three sp2 hybrid orbitals Dr. S. M. Condren unused p orbital Bonding in BF3 • The three hybrid orbitals are made from 1 s orbital and 2 p orbitals 3 sp2 hybrids. • Now we have 3, half-filled HYBRID orbitals that can be used to form B-F sigma bonds. Dr. S. M. Condren Bonding in BF3 An orbital from each F overlaps one of the sp2 hybrids to form a B-F bond. F F B F Dr. S. M. Condren BF3, Planar Trigonal Dr. S. M. Condren Bonding in CH4 How do we account for 4 C—H sigma bonds 109o apart? Need to use 4 atomic orbitals — s, px, py, and pz — to form 4 new hybrid orbitals pointing in the correct direction. Dr. S. M. Condren 109o Bonding in CH4 Dr. S. M. Condren Bonding in a Tetrahedron — Formation of Hybrid Atomic Orbitals 4 C atomic orbitals hybridize to form four equivalent sp3 hybrid atomic orbitals. Dr. S. M. Condren Dr. S. M. Condren Bonding in Glycine sp 3 H O C H H C •• H N sp 3 sp •• O H •• sp Dr. S. M. Condren 2 3 Orbital Hybridization BONDS SHAPE HYBRID REMAIN 2 linear sp 2 p’s 3 trigonal planar sp2 1p 4 tetrahedral sp3 none Dr. S. M. Condren Multiple Bonds Consider ethylene, C2H4 H H 120Þ C sp C H H Dr. S. M. Condren 2 Sigma Bonds in C2H4 H H 120Þ C sp C H H Dr. S. M. Condren 2 π Bonding in C2H4 The unused p orbital on each C atom contains an electron and this p orbital overlaps the p orbital on the neighboring atom to form the π bond. 2s 2p 3 sp 2 hybrid orbitals p orb. for š bond Dr. S. M. Condren π Bonding in C2H4 The unused p orbital on each C atom contains an electron and this p orbital overlaps the p orbital on the neighboring atom to form the π bond. Dr. S. M. Condren Multiple Bonding in C2H4 Dr. S. M. Condren and π Bonding in C2H4 Dr. S. M. Condren and π Bonding in CH2O Dr. S. M. Condren and π Bonding in C2H2 Dr. S. M. Condren and π Bonding in C2H2 Dr. S. M. Condren Consequences of Multiple Bonding There is restricted rotation around C=C bond. Dr. S. M. Condren Consequences of Multiple Bonding Restricted rotation around C=C bond. Dr. S. M. Condren Diatomic Molecules AO H MO H2 1s AO H 1s ENERGY B => bonding electrons B - AB 2-0 B.O. = ------------ = -------- = 1 2 2 all electrons are paired, thus diamagnetic Dr. S. M. Condren AB => antibonding electrons Diatomic Molecules AO He MO He2 1s AO He 1s ENERGY B - AB 2-2 B.O. = ------------ = -------- = 0 2 2 Dr. S. M. Condren Zero bond order means it does not exist Diatomic Molecules AO He MO He2+ AO He+ 1s 1s ENERGY B - AB 2-1 B.O. = ------------ = -------- = 1/2 2 2 One unpaired electron, thus, paramagnetic Dr. S. M. Condren AO B MO B2 AO B 2p 2p 2s 1s 2s nonbonding 1s Dr. S. M. Condren Molecular Orbital Diagram antibonding MO end-to-end bonding MO antibonding MO side-by-side bonding MO Dr. S. M. Condren AO C MO C2 AO C 2p 2p 2s 1s 2s nonbonding 1s Dr. S. M. Condren AO O MO O2 AO O 2p 2p 2s 1s 2s nonbonding 1s Dr. S. M. Condren Energy Dr. S. M. Condren