* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Atomic Model
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
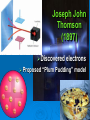
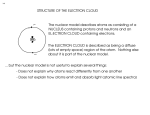
The Atomic Model Define: Atom An atom is the smallest component of an element that retains the characteristics of the element What atoms are made of ? If you broke apart any one atom, it would be made of three parts- and it wouldn’t be the atom anymore. Atoms are made from three different sub-atomic particles: • Proton • Neutron s • Electron A brief history of Atoms 460 B.C. Democritus: pounded stuff into itty-bitty pieces 1808 Dalton: small solid spheres 1898 Thompson: atoms eject tiny negative particles!!!! 1904 Thompson: Plum pudding model 1910 Rutherford: Gold foil expt 1913 Bohr: Electrons in ORBITS! Modern Theory (Wave Theory): electrons are wavelike, NOT arranged in neat orbits, but can be discussed only by the probability of where they are. (Electron Cloud) Democritus (460 – 370 BC) Eventually reach matter that cannot be divided: which he called an “atom”. John Dalton (17661844) Elements combine in certain ratios 1803: Dalton proposes “Atomic Theory” All Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element possess unique characteristics and mass Atoms of different elements can join to form compounds. Joseph John Thomson (1897) Discovered Proposed electrons “Plum Pudding” model Rutherford Discovered the nucleus According to his model, an atom is mostly empty space. Stadium Analogy If a football is placed on the 50 yard line (in the middle) of a football field then the outer seats are the edge of the electron cloud and the football is the nucleus. Everything in the stadium (atom) other than the football is empty space. Niels Bohr Proposed that each electron is in a specific energy level. Bohr’s model is also called the “planetary model” Bohr Model Write the number of protons and neutrons in the center Up to 2 electrons on the inner ring, and up to eight on the second ring. The third ring can have up to 16 electrons. P= N= Cloud Model Erwin Schrödinger The cloud model represents a sort of history of where the electron has probably been and where it is likely to be going. It utilizes Heisenberg’s uncertainty Principle The structure of an atom Bohr Model Schrödinger Model “Planetary Model” “Electron Cloud Model” Lewis Dot Model Dots are drawn for each OUTER electron Not all electrons are drawn Valence Electrons Electrons located on the outermost energy level. Use the columns on periodic table!!! Dmitri Mendeleev Russian scientist/professor Citations History of the Atom Timeline: http://cstlcsm.semo.edu/mcgowan/ch181/atomhist.htm