* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint プレゼンテーション
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
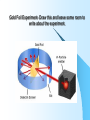
Chapter 3: Atoms, the Building Blocks of Matter Atomic Theory has Evolved! Leave a couple of lines! Law of Conservation of Mass Mass is neither created nor destroyed during an ordinary chemical reaction or physical change. Remember the Candle Lab: C25H52 + O2 + E CO2 + H2O + C + E Draw a picture and explain why it happens? Leave about a half a page for an activity… Pioneers of the Atomic Theory Chapter 3 Observant people have been looking at matter and pondering why different phenomenon occur for hundreds of years. Early PhilosophersAristotle and Democritus Didn’t agree!! Dead Dude #1- Democritus Ancient philosopher- 460BC Matter is made of indivisible particles. Atomos means “that which cannot be further broken down” Shortcomings It is a conceptual definition, not based on science. Doesn’t talk about subatomic particles. Dead Dude#2- Dalton Explained the Laws John Dalton (early 1800s) Atom is a solid, indestructible mass (like a billiard ball) All Atomic Theory builds on Dalton’s Law All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass and properties Atoms of each element are different. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. 4. Compounds consist of atoms of different elements combined together. Compounds have constant composition (fixed ratio of atoms). 5 Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of those atoms. 1. Dead Dude #3 J.J Thomson- 1850 A ball of positive mass containing a number of electrons that are embedded. Getting the idea that there are protons and electrons (nucleus). Shortcomings Doesn’t explain the existence of electrons outside the nucleus or their importance in bonding. No neutrons- can’t explain radioactivity or the existence of isotopes. What did experiments with the cathode ray tubes teach us? Late 1800’s Discovery of and experiments using the cathode ray tube led to our understanding of the electron. Millikan Oil Drop Experiment Henri Becquerel- 1897 Researched newly discovered Xrays (Phosphorescence). Accidently discovered that uranium emits radiation that could be measured using photographic plates. Discovered Radioactivityelectrically charged particles. The Dr’s Curie- 1898 Discovered new elements- Polonium and Radium. Very unstable elements that give off energy. This led to an understanding of Alpha, Beta and Gamma particles. Dead Dude #4 Rutherford Model- 1905 – Mass of the atom is concentrated in the center of a positively charged region called the nucleus. – The Planetary Model Gold Foil Experiment- Draw this and leave some room to write about the experiment. Shortcomings Doesn’t place the electrons. Doesn’t include neutrons. Bohr Model-1920 Believed that electrons traveled in precise orbits around the nucleus of an atom Schrodinger Quantum Mechanical Model. Describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons and other very small particles The nucleus is at the center of the atom and the electrons are in the electron cloud.