* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download period
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
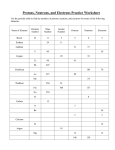
Patterns and the Periodic Table Featuring the Return of Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams and the Periodic Table SNC2D The Periodic Table • Designed by Mendeleev in 1869 • Organizes matter based on its properties and atomic number • Allowed for the prediction of then unknown elements Periods and Families • The rows in the periodic table are known as periods. • The columns in the periodic table are known as groups. • Groups tend to have similar properties. • Major groups (multiple columns): – Metals – Non metals – Metalloids • Single column groups: – – – – Alkali metals Alkali earth metals Halogens Noble gases Properties Compared • Metals – – – – – Nickel (Ni) Solid Shiny Malleable Conductor • Non-Metals – – – – – Sulphur (S) Solid, liquid, or gas Dull Brittle Insulator Atomic Theory of Matter • Dalton brings back Democritus’ idea of the atom as an indivisible particle. • Dalton gives us the “billiard ball” model. Subatomic Particles • Atomic theory is revised as subatomic particles are discovered. – Electrons and Protons • “Raisin Bun” model • Saturn/solar system model – Neutrons • Bohr – Rutherford model Modern View of the Atom • Protons, neutrons, electrons • Mass measured in atomic mass units (amu) which is equal to 1.66 x 10-24g Subatomic Charge Particle Symbol Mass (amu) Electron 1- e- 1/2000 Proton 1+ p+ 1 Neutron 0 n0 1 The Bohr-Rutherford Model -used to show the arrangement Helium Atom of electrons in the atom • 2 positive protons in nucleus • 2 neutral neutrons in nucleus • 2 negatively charged electrons in the first energy level – 2-8-8-2 are the number of electrons in each energy level for the first 20 elements How to Draw a Bohr Diagram • Find your element on the periodic table. Si Element 14 has the symbol Si and 14 electrons • Determine number of electrons, which for a neutral atom is equal to the number of _________, which is equal to the ________________ Si • Place the element symbol in the middle. • Draw in the energy levels – (determine which period (row) your element is in) • Add electrons following the 2-8-8-2 Check your work: Count your pattern for the first 20 elements electrons per shell and your total electrons! Standard Atomic Notation (for a neutral atom) Atomic symbol Mass number 28 14 Atomic number Si Number of protons Atomic number (14) 14 p+ Number of electrons (for neutral atom) Atomic number (14) 14 e- Number of neutrons Mass number – Atomic number (28-14=14) 14 n0 How to Draw a Bohr-Rutherford Diagram • Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons Element 14 has 14 electrons, 14 protons, and 14 neutrons • Place the number of protons and neutrons for the element in the middle • Draw in the energy levels • Add electrons following the 2-8-8-2 pattern for the first 20 elements 14 p+ 14 n0 Homework 1. 2. Refer to the periodic table to name and write the symbols for the following elements: [K] a. b. c. d. e. f. A halogen of the second period The alkaline earth metal in the fifth period The noble gas with the smallest atomic number The non-metal in the fifth period with seven outermost electrons The alkali metal of the fourth period The metal of the third period with three outermost electrons g. The unreactive gas of the second period. Try drawing Bohr-Rutherford diagrams for each of the following elements: [C] [I] a) O b) Al c) Ne d) K 3. Imagine that a chemist discovers a new element with atomic number 119. [I] a) b) c) Use the periodic table to predict what chemical family this element would belong to. How many outer electrons would an atom of this element have? Predict one physical property and one chemical property of this element. 4. Why are atoms electrically neutral? [K] Lewis Dot Diagrams The electrons in the outermost shell are called ? Lewis Dot Diagrams The electrons in the outermost shell are called valence electrons . Lewis Dot Diagrams The electrons in the outermost shell are called valence electrons . Lewis Dot Diagrams are abbreviated Bohr Diagrams that show just these outermost electrons, e.g.: Valence Electrons and Families Note that both hydrogen (H) and potassium (K) have just ? electron in their outermost shell. Note also that these elements are both found in the ? column of the periodic table. This is not a coincidence! Valence Electrons and Families Note that both hydrogen (H) and potassium (K) have just 1 electron in their outermost shell. Note also that these elements are both found in the ? column of the periodic table. This is not a coincidence! Valence Electrons and Families Note that both hydrogen (H) and potassium (K) have just 1 electron in their outermost shell. Note also that these elements are both found in the 1st column of the periodic table. This is not a coincidence! Valence Electrons and Groups All elements in the same group (column) have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell (ref. p. 150) It is these electrons that determine the behavior of the element (chemical properties), including how it reacts with other elements – and how it forms ions. Homework 1. For each of the elements that you drew a Bohr-Rutherford diagram in question 2, draw its Lewis Structure. [C] [I] a) O b) Al c) Ne d) K 1. Which of the above elements would you expect to be the most reactive and why? [K] 1. Which of the above elements would you expect to be the least reactive and why? [K] Credits • • • • • • • • http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:IUPAC_Periodic_Table.PNG http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Atomic_size_periodic_table.svg http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Periodic_table_fluorine.svg http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nickel_kugeln.jpg http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Sulphur2.jpg http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Radiosity.png?uselang=en-gb http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bohr_model.jpg http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Helium-Bohr.svg