* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Environmental Protection
Fossil fuel phase-out wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Energiewende in Germany wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
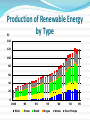
Eralp TÜZÜNER Merve AVŞAROĞLU Şeyma GÜNGÖR What is Environmental Protection? Environmental Protection is a practice of protecting the environment on individual,governmental and organizational level for the benefits for humanity and natural environment ?=The usage of fossil fuels,deforestation,high carbondioxide emission, and etc. Main Priority for Environmental Protection; Combating climate change. Preserving bio-diversity Reducing health problems from pollution Unconscious usage of Fossil Fuels What is Climate Change? “Climate Change” effects more than just a change in the weather, it refers to seasonal changes over a long period of time. Earth is getting Warmer Why Environmental Protection important? The world renew itself but it takes a long time The quality of air decreases We haven’t got any land for living Water quality declines Ecosystem affected badly Limited Resources What is the role of European Union in Environmental Protection? Big Conferences, Treaties about E.P. Single European Act: basic law came. however did not mention about the sustainability. 2. 1992 Maastcriht Treaty: given the status field of environmental policy, and "sustainable development" concept was officially formed in EU law. 3. 1997 Treaty of Amsterdam:The concept of sustainable development has become one of the main objectives of the EU. 4. 2000 Treaty of Nice: The place of environmental protection explicitly stressed in new European order 5. Environmental Action Plans was completed in1973 to the present.6th Environmental Action Plan was prepared in2002 1. What the EU is doing? European Union has; highest environmental standarts in the world. European Union make many investments in this topic. Since the 1990s, many studies done on climate change EU governments have also set aside more than €2.7 billion for investments in emission-saving projects European Climate Change Programme Launched in 2000 Apply to all applications in the Kyoto protocol Strategy;to limit carbon dioxide (CO2) Improve energy efficiency Emissions Trading Scheme Launched in 2005 Works on “cap and trade” gives a financial incentive to reduce emissions by establishing a market-based trading system the 27 EU Member States plus Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway Johannesburg Renewable Energy Coalition Agreed by Heads of State at the 2002 World Summit for Sustainable Development (WSSD) There were 66 founding members JREC Members focus on international, regional, and national political initiatives that help fostering an enabling policies for the promotion renewable energy. JREC supported by community, International companies, NGOs The "20-20-20" targets A reduction in EU greenhouse gas emissions of at least 20% below 1990 levels 20% of EU energy consumption to come from renewable resources A 20% reduction in primary energy use compared with projected levels, to be achieved by improving energy efficiency. Indicators Wind, Solar, Hydro Energy sources and; air pollution What is Renewable Energy? Renewable Energy Solar energy Wind energy Hydro energy Solar Energy Solar panel Photovoltaic (PV) cells Advantages of solar energy Infiniteness No environmental pollution Easily affordable Decrease in bills Disadvantages of solar energy Cost Days with no sunlight Wind energy Wind turbines Advantages of Wind Energy Infiniteness No environmental pollution Undisturbed agricultural activities Disadvantages of Wind Energy Cost Days with no wind Large wind farms Noise Harmful for animals Hydro Energy Hydro energy dams Advantages of Hydro Energy Control Continuity No environmental pollution Disadvantages of Hydro Energy Cost Habitat to be disturbed Need for certain amount of water Air Pollution What is greenhouse effect? Causes of greenhouse effect Fuel Deforestation Industrial gases Overpopulation Impacts of greenhouse effect Climate change Natural disasters Shortage of food supply Potential solution Decrease in “carbon footprint” Comparison of Some Countries DENMARK SWEDEN POLAND MALTA TURKEY DENMARK Denmark is one of the most efficient users of renewable energy compared with the other EU Member States and OECD countries Wave Power BIOMASS WİND POWER Production of Renewable Energy by Type PJ 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 1980 Wind '85 Straw '90 Wood '95 Biogas '00 Waste '05 Heat Pumps '09 Today, Denmark is a world leader in wind turbine production and has a very big wind power..!! Now in Denmark, Renewable energy covers 14 % of gross energy consumption and over 28 % of the electricity generated. (Danish Energy Athority Report, 2010) 20 % of Denmark electricity generation comes from wind power. Denmark have failed to reduce their own emissions. Sweden Sweden has the greatest renewable energy in all European countries. Sweden has set their target at 50 percent renwable energy by 2020, In 2009, 47,7 percent of Sweden’s total energy supplied was renewable energy. Hydro power Biofules Sweeden has set their target at 50% renewable energy by 2020 Share in total EU-15 GHG emissions 2005 1.6 % Kyoto target (absolute) 75.2 Mt Kyoto target (% from base year) + 4.0 % Change base year to 2005 – 7.4 % Change 2004–05 – 3.9 % Change base year to 2010 with existing measures – 2.7 % GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSION http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications /eea_report_2007_5/Sweden.pdf POLAND Nature has bestowed Poland generously renewable resources. Wind and Solar energy, are used more and more frequently, their growing popularity supported by great advances in technology. However, Biomass is now the largest source of clean power in Poland, 15 % share of RES on the final consumption of energy in 2020. Poland supports renwable energy in everywhere and every time. the National Environmental Protection and Water Management Fund and provincial, district and commune environmental protection and water management funds. Poland’s GHG emissions were 32.0 % below base-year (1988) levels and 0.6 % above those in 2004 in 2005. Poland’s GHG emissions were 32.0 % below base-year (1988) levels and 0.6 % above those in 2004 in 2005. MALTA Malta is totally dependent upon imported fossil fuels for its energy needs. Renewable energy could be used effective in the island however it cost very high. It is the worst for renewable energy uses in European cuntries. Its aim is to catch the 10% for 20 20 20 target. Wind and solar energy is high. CO2 emissions (kt) in Malta Carbon dioxide emissions are stemming from the burning of fossil fuels and the manufacture of cement. They include carbon dioxide produced during consumption of solid, liquid, and gas fuels and gas flaring. Malta is a small, island economy in the Mediterranean. Malta is dependent on foreign trade (serving as a freight trans-shipment point), manufacturing (electronics and textiles), tourism and financial services. TURKEY Today, Turkey’s economy is mainly dependent on oil,and natural gas. On the other hand, it is a rich country for the renewable energ resources It has the 8% of the geothermal energy potential in the world. The aim is : to decrease of 3% in the country's energy dependence ANY QUESTIONS?