* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development in a time of climate change
Survey
Document related concepts
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
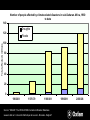
Development in a time of climate change: Putting women at the heart of solutions Kate Raworth, Oxfam Great Britain Charles King, Liberia Finance and Trust Corporation Anyaa Vohiri, Fauna and Flora International Heather Grady, Realising Rights 1. Why is gender relevant to climate change? 2. How will climate change affect rural West Africa? 3. Development in a time of climate change: - Stopping deforestation - Getting clean energy to communities - Adapting agriculture to climate impact What does this family need to get out of poverty? What does this family need to get out of poverty? Physical Financial Social Human Natural Women and men have: - different roles in the household - different resources to deliver them with. P P resources roles roles S F H N F S H N Men provide food and cash from farming by: - Growing cash crops to sell - Growing food to eat or sell i And they provide cash through: - Small-scale manufacturing - Trading goods - Selling labour i Rural women produce much of the family’s food • on marginal lands • without irrigation • using saved seeds • with no formal training • without access to credit They provide the household water And the household fuel supply They cook, clean and care for the sick while caring for children at the same time. while caring for children at the same time… …all for no payment. Women and men have: - different roles in the household - different resources to deliver them with. P P resources roles roles S F H N F S H N Men’s physical resources: Bodily strength Inherit crop land House Livestock, Stored food Machinery Transport Women’s physical resources: Few belongings, but: Bodily strength Children Common, marginal land Stored food Some tools? Forced to sell sex? Men’s human resources: More likely to be educated and to benefit from agricultural training services Women’s human resources: Less likely to be educated Far less likely to get training for agriculture or other livelihood opportunities Men’s financial resources: Women’s financial resources: Minimal savings Micro-credit Schemes Limited access to selling in markets Men’s natural resources: better land more likely to have irrigation and tools to cope with climate uncertainty Women’s natural resources: Poor quality land. Few tools. Rain-fed agriculture Wild crops for extra food & medicine Wells and rivers for water Bush and forest for fuel Men’s social resources: Networks: Voice in village committees More access to official power Norms: Mobility, independence Authority,may use violence Controls divorce decisions. Women’s social resources: Networks: women’s groups, cooperatives Norms: Less mobility and independence Household roles are assumed to be hers Women and men have: - different roles in the household - different resources to deliver them with. P P resources roles roles S F H N F S H N One household? P P resources roles roles S F H N S F H N Women invest more in their children Income in women’s hands goes further towards children’s nutrition, education, health and well-being. In sub-Saharan Africa, if women had equal access to land, seed and fertilizer, then agricultural productivity would rise by up to 20%. An educated woman is 50% more likely to have her children immunised. In Africa, children whose mothers got at least 5 years of education are 40% more likely to live beyond the age of five. Over to you… Is this story true for rural women and men in Liberia? Which differences between women and men are the greatest challenge? What role does climate change have in Africa? Average temperature of Earth’s surface, 0C Who has produced CO2 emissions to date? But who is already bearing the worst impacts? Number of people affected by climate-related disasters in sub-Saharan Africa, 1960 to date 140 Droughts Total affected (millions) 120 Floods 100 80 60 40 20 0 1960-69 1970-79 1980-89 Source: "EM-DAT: The OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database www.em-dat.net - Université Catholique de Louvain - Brussels - Belgium" 1990-99 2000-06 “…climate change will negatively impact on the full range of human and economic development in Africa: reducing people’s ability to feed themselves; threatening people’s health; reducing livelihood opportunities and economic growth prospects” Dr. Anthony Nyong, Coordinating Lead Author, Africa Chapter, IPCC 4th Assessment Working Group Two Expected climate change in West Africa Uncertainty in models and data but… Temperatures: rising Sea level: rising More or less rain? Less predictability of rainfall Expected climate impacts in West Africa Agriculture: much shorter growing season in some areas, with serious impacts on food security Livestock: animals likely to suffer from heat stress, drought and spreading disease Water resources: likely increase in water stress Coastal settlements: low-lying lands will be inundated, threatening coastal cities across the region Health: increased diarrhoea and malnutrition, likely impacts of malaria, dengue, cholera Social change: risk of land conflicts, mass migration, more frequent humanitarian crises African agriculture coming under stress UNDP 2006 Expected climate impacts for rural communities in Liberia: • How will women’s and men’s roles be affected? • How will women’s and men’s resources be affected? • What social and economic pressures could there be? Development in a time of climate change: 3 challenges for gender equality 1. How can we stop deforestation – and ensure that women benefit? 2. How can we get clean energy to rural communities – and ensure that women benefit? 3. How can we adapt agriculture to cope with climate impacts – and ensure that women benefit? 1. Stopping deforestation •How can we stop deforestation in Africa? •Will women benefit or lose out? Logging in Congo DRC 2. Getting clean energy to communities Solar panels for electricity Wind power, Kenya How can clean energy most benefit rural women? Wind power, Kenya Constructing biogas plant, Rwanda 3. Adapting agriculture to climate impacts Conservation tillage Extending irrigation How can communities adapt to climate change? What role must women play? Drought-tolerant crops