* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download APES – UNIT 9
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
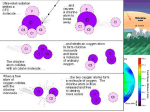
APES – UNIT 9 GLOBAL IMPACT ACID RAIN *a result of pollution released from -burning fossil fuels -smoke stacks -vehicle exhausts -wood burning -smelting metals ACID RAIN COMPOSITION MOSTLY SULFUR OXIDES (SO3) AND NITROGEN OXIDES (NO2) MIXED WITH WATER AND ATMOSPHERIC OXYGEN TO FORM ACIDS SO2 + H2O H2SO3 (sulfurous acid) H2SO3 + ½ O2 H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) OR NO + ½ O2 NO2 (nitrogen dioxide) 2NO2 + H2O HNO2 + HNO3 (nitrous acid and nitric acid) ACID DEPOSITION *ACID RAIN DEPOSITED ON EARTH IS HIGHLY DILUTED *ACID RAIN IS SLIGHLY ACIDIC WITH pH 5.6 – 5.7 because water reacts with the CO2 *note: pH scale is LOGARITHMIC = each whole pH value below 7 is 10X more acidic than the next value ACID RAIN SIGNIFICANCE 1.causes sink holes due to acid dissolving limestone 2.dissolution= dissolves most building structures 3.affect water sources by increasing acidity 4.affects leaves by damaging waxy covering which disrupts leaf gas exchange 5.causes NUTRIENT LEACHING: metals (lead, zinc, copper, aluminum) in soil react with acid rain adding Hydrogen ions which in turn react with minerals (calcium, magnesium, potassium) and prevent them from being absorbed ACID RAIN PREVENTION • • • • SWITCH TO FUELS WITH ZERO OR LOW SULFUR USE SMOKE STACK SCRUBBERS USE CATALYTIC CONVERTERS IN CARS REDUCE IT IN WATER WAYS BY ADDING LARGE AMOUNTS OF SODA ASH (LIME WATER) WHICH RAISES ALKALINITY **CLEAN AIR ACT (1990) = regulates amount of SO2 & Nox that are released form industrial plants which go by the NAAQS (National Ambient Air Quality Standards) http://acidrainmix.weebly.com/uploads/2/5/2/7/25273212/77 1105_orig.jpg ABOUT SMOKE STACK SCRUBBERS GLOBAL WARMING - Caused by Greenhouse gases that absorb infrared radiation which traps the heat and builds up in the atmosphere - Industrial revolution increased levels of greenhouse gases - Greenhouse gases emissions are mostly Anthropogenic (caused by humans) GREENHOUSE GASES and GLOBAL WARMING CO2 = carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels, cellular respiration, decomposition CCl4 = carbon tetrachloride from cleaning solvents CFC= chlorofluorocarbons from air conditioners, refrigerants like Freon HCFC= hydroclorofluorocarbons from foam products and insulator materials CH4 = methane from coal production, natural gas, rice cultivation, trash decomposition N2O = nitrous oxide from fertilizers, livestock waste, burning fossil fuels O3 = ozone from burning fossil fuels GREENHOUSE GASES IMPACTS OF GLOBAL WARMING 1.Acidification= in soil and water affects organisms growth 2.Changes in weather patterns ( hotter temperature higher evaporation higher rainfall El Nino & La Nina) 3.More erosion due to more rainfall 4.Glacier melting rise in sea level flooding increased water flows slows or shuts down Thermohaline Circulation by decreases saline concentration sinking and changing water temperature 5.Loss in Biodiversity from food web disruptions (from deaths, migration patterns altered due to temperature changes) REDUCING CLIMATE CHANGE ***DECREASE GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS HOW: *increase car efficiency *use renewable energy sources *stop deforestation and increase reforestation *use less nitrogen based fertilizers *support protocols to reduce greenhouse gas emissions ****KYOTO ACCORD (1997) = 38 countries agreed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions OZONE OZONE PROTECTS US FROM UV RADIATION UVA = (320 nm - 400 nm) skin tans, safest UVB = (290 nm – 320 nm) causes skin cancer UVC = (10 nm – 290 nm) forms ozone in stratosphere, harmful *OZONE forms in stratosphere by UV radiation reactions: O2 + uv O + O then O + O2 O3 (ozone) OZONE DEPLETION https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OMtZC4FV_zM OZONE LAYER THINNING DUE TO CFC’s: In the Stratosphere, UV decomposes CFC into CL which reacts and destroys ozone CL + O3 ClO + O2 **It takes CFC’s 8 years to reach stratosphere **Hole over Antarctic discovered in 1950’s: Ozone Depletion Effects *increased skin cancer (mutations) *eye cataracts *crop reduction *climate change *kills phytoplankton REDUCE OZONE DEPLETION: by not using Halogen compounds (chlorine, bromine, fluorine) found in refrigerant coolants EX: Freon and Aerosols MONTREAL PROTOCOL (1987) =agreement to phase out CFC’s WATER POLLUTION Due to land runoff with excess nutrients and pollutants POINT SOURCE: directly from source that produces the pollutants NON-POINT SOURCE: indirectly from many sources combined GULF OF MEXICO DEAD ZONE= 5000 sq. miles of Gulf of Mexico where Mississippi River delivers land runoff https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=BqaxdKXO9yc WATER QUALITY TESTS • • • • pH = measures acidity (should be at pH 6 – 8) Hardness = measures concentrations of calcium and magnesium Turbidity = measures density of suspended particles Dissolved Oxygen (DO) = measures amount of oxygen dissolved in water (warm water holds more DO than cold) • Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) = measures rate at which bacteria absorbs oxygen from water WATER QUALITY LEGISLATION CLEAN WATAER ACT (1972) = reduced direct pollutant discharge into waterways OCEAN DUMPING ACT (1972) = unlawful to dump waste into ocean SAFE DRINKING WATER ACT (1974) = monitors safe drinking water supply OIL SPILL PREVENTION ACT (1990) = regulates prevention and response of oil spills CULTURAL EUTROPHICATION *process whereby human activity increases the amount of nutrients that enter the waterways *caused mainly by Nitrates (NO3-) and Phosphates (PO4) from fertilizers, sewage discharge, and animal wastes *these nutrients allow phytoplankton and algae to grow uncontrollably 1.ALGAL BLOOM 2.decreases light penetration 3.kills deeper plants 4.lowers DO concentration 5.kills fish/ other aquatic organisms 6.decomposition uses DO and produces toxins https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qON4FtQAKOs SOLID WASTE/ GARBAGE Includes municipal waste, industrial waste, & hazardous waste ***REDUCE, REUSE, RECYCLE**** PRIMARY RECYCLING= reusing material to make the same product EX. plastic & aluminum SECONDARY RECYCLING= reusing material to make a new product EX. old tires for carpet COMPOSTING: using scraps of food and organic materials in solid waste https://www.youtube. in a decomposition process that makes organic fertilizer com/watch?v=gWNzL Y5Sjyg LANDFILLS https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mA608GJ-EzM LANDFILL REGULATIONS *landfills must not be near geological faults, wetlands, flood plains *landfills must be positioned at least six feet above water table *landfill site must consist of a hole that is lined with geo-membranes or plastic sheets that are reinforced with 2 ft of clay on bottom and sides *landfill waste must be covered with soil to control animal infestation *LEACHATE= the decomposed liquid material that percolates to the bottom of landfill must be piped to the top of the site and collected in leachate ponds ( the methane gas can be used as fuel or burned) LOVE CANAL https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AqWaaBpNUWs *canal near Niagara Falls N.Y. that originally was built to produce power became landfill for hazardous waste was covered became a residential community illnesses occur lawsuits against government *as a result: RCRA (Resource Conservation & Recovery Act) CERCLA (Comprehensive Environmental Response Compensation Liability Act) FISHERY – OCEAN RESOURCE Fishery: industry devoted to catching fish (about 125 million tons of fish are harvested each year – mostly in China) HOW? 1.DRIFTNETS = net floats through water, catches everything in path 2.LONGLINING= long lines with baited hooks 3.BOTTOM TRAWLING= heavy nets scrape ocean floor BY CATCH= refers to the other organisms caught that are NOT target fish EX. Dolphins of Tuna catch OVERFISHING *Overfishing has depleted 50 % of major fish stocks SOLUTION: AQUACULTURE or FISH FARMING raising fish in captivity for harvest EX. Salmon & shrimp PROBLEM: ACCIDENTAL RELEASE *some fish are genetically modified *transmission of new diseases https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tUrGKVJcd9M INVASIVE/ NON-NATIVE SPECIES *species transported to any area where they do NOT naturally live EX: from Marine Ballast *they become pests and crowd out native organisms *they have no natural predators *they out compete native organisms for space and food *they alter the ecological processes of that habitat https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1090CKi_Lzo LOSS OF BIODIVERSITY ACCORDING TO NATURE CONSERVANCY: 1/4 of all mammals and reptiles are endangered 1/8 of all birds are endangered 1/6 of conifers are endangered PROTECT BIODIVERSITY 1. establish breeding programs and reintroduce species 2. protect habitats and create sanctuaries 3. reduce non-native species 4. update laws to protect endangered species https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jWvWf01ObdY LAWS SUPPORTING BIODIVERSITY *MULTIPLE-USE ACT (1960) – manages national forests *CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of wild fauna and flora) (1963)- international agreement between governments to regulate trade of animals & plants *ENDANGERED SPECIES ACT (1973) - to provide conservation programs for endangered species and habitats *ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION ACT (1990) – to develop environmental education programs SUSTAINABILITY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gTamnlXbgqc SUSTAINABILITY= deals with the aspects of human society and preservation of biodiversity and the environment https://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=_5r4loXPyx8 COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS – a technique for deciding whether to make a change or not by: 1st-weighing the benefits of how to use a piece of land/waterway EX: jobs , lumber 2nd-against the cost of using that piece of land/waterway EX: loss of space, CO2, biodiversity