* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE BEAUTIFUL EARTH! (5.2, G3, G4)
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Fauna of Africa wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
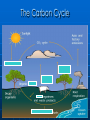
THE BEAUTIFUL EARTH! (5.2, G.3, G.4) By: Monica Gapud 5.2 The Greenhouse Effect Carbon is constantly recycled • Photosynthesis • Combustion of forests • Cellular resp • Fossil fuels The Carbon Cycle The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Sunlight enters atmosphere b/c gases are transparent to light Sunlight reflects off Earth’s surface & back out Some of light energy heat energy & warms the Earth Greenhouse gases retain some heat & trap it in the atmosphere Earth’s natural g. house effect = atmosphere is warmer than space What are the greenhouse gasses? Carbon Methane • Cattle ranching, waste disposal in landfills, production & distrib. of natural gas Oxides of nitrogen • Produced by human activities; burning fossil fuels, organic/commercial fertilizers, industrial processes (prod. of nitric acid) Low concentration = prevents too much heat retention Effects of Global Warming…? Increase in photosynthetic rates Changes in climates, ecosystems Extinction of certain species Melting glaciers Rise in sea level= flooding of coastal areas The Precautionary Principle An ethical theory which says that action should be taken to prevent harm even if there’s not sufficient data to prove that the activity will have severe negative consequences Draw the Carbon Cycle ! G.3 Impact of Humans of Ecosystems Biological diversity; • Richness - # of diff organisms in a part. area • Evenness – how the quantity of each diff. organism compares with the other Simpson diversity index – measures the amount of diversity in a part. area • D = diversity index • N = total # of org. in eco. • n = # of individ. of each species Remember the equation? Time to Calculate ! Did the forest of jungle have more diversity? • Forest: D=4.29 • Jungle: D=6.14 THE JUNGLE HAS MORE DIVERSITY because of its higher # of species Why Conserve Biodiversity? Economic Ecological Ethical Aesthetic Arguments Against Conservation Alien species disrupts communities and outcompete native species reducing biodiversity. Examples? • Kudzu • Zebra Mussels • Prickly Pear Impact of Alien Species Interspecific competition: outcompeting other species Predation: eating another species Species extinction: out-compete extinction of native species Biological control- idea of using a natural predator to control unwanted or invasive species • Purple loosestrife • Red fire ants Biomagnification- process by which chemical substances become more concetrated at each trophic level • DDT Effects of UV Rays Non-lethal skin cancer Lethal skin cancer Mutation of DNA Sunburn Cataracts Reduced biological productivity Ozone layer • “protective sunscreen for planet” • Absorbs UV radiation • Formed in stratosphere when O2 breaks apart & reacts with another oxygen mol. to form ozone CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) • Thinning of ozone layer G.4 Conservation of Biodiversity Indicator species- sensitive to enviro. change • Lichens; sensitive to pollution • Macroinvertabrates; presence or absence can be used to judge water quality Biotic index Nature Reserves • Determinations of size • Edge effect • Corridors Management of Conserv. Areas • Restoration • Recovery of threatened species • Removal of introduced species • Legal protection against development or pollution • Funding & prioritizing In Situ Conservation Methods Placing endangered species in the situation where they belong Goals? • Protect species by maintaining habitat • Defends target species from predators • Removes invasive species • Large area= maintain large pop. • Large pop= maintain genetic diversity Ex Situ Conservation Method Last resort Captive breeding • Increase reprod. output to ensure survival of offspring Artificial insemination Embryo transfer Cryogenics Human raised young Keeping a pedigree • HOWEVER, spread of disease & disadv. in wild Botanical gardens Seed banks