* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
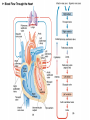
Download Q = HR x SV
Survey
Document related concepts
Circulatory system wikipedia , lookup
Weight training wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Management of atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Neurobiological effects of physical exercise wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
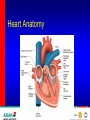
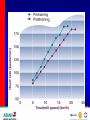
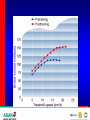
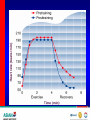
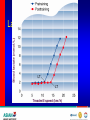
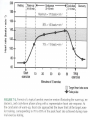
Optimizing heart rate during exericise Dr. Aashish Contractor HOD: Preventive Cardiology and Rehab, Asian Heart Inst. Medical Director, Standard Chartered Mumbai Marathon What is Exercise Physiology? Definitions • Physiology: is a branch of biological • science concerned with the function of organisms and their parts. Exercise physiology is a branch of physiology that deals with the functioning of the body during exercise. Heart Anatomy Cardiac Output The amount of blood pumped by the heart each minute • • Product of heart rate and stroke volume Q = HR x SV Heart rate = number of beats per minute Stroke volume = amount of blood ejected in each beat 75 bpm x 70 mls/ beat = 5000 mls or 5 liters/min Transition From Rest Exercise and Exercise Recovery • Rapid increase in HR, SV, cardiac • • output Plateau in submaximal (below lactate threshold) exercise Recovery depends on: Duration and intensity of exercise Training state of subject Cardiovascular Response to Endurance Training • Maximum cardiac output increases • Maximum stroke volume increases • Maximum heart rate does not change Lactate Threshold Cardiovascular Conditioning FITT Frequency Intensity Type Time Exercise Programming Components Cardiovascular • Frequency- 3-5 days/week • Intensity- 55/65% - 90% HR max • • 40/50% - 85% VO2R or HRR Duration- 20-60 min of continuous or intermittent (minimum 10 min bouts) Mode- uses large muscle groups, maintained continuously, and rhythmical in nature Intensity • • • Intensity refers to how hard the body is working during exercise. Needs to be sufficient to overload the body in order to achieve a training effect. Common ways for deciding the intensity would be by using Age predicted formula Karvonen formula Functional capacity (MET system) • Age predicted formula : HRmax = 220 – Age • Karvonen method : Using Heart Rate Reserve (HRR) to calculate intensity HRR = MHR – RHR Target HR intensity = Target % HRR + RHR Guidelines for choosing intensity • To experience benefits of cardiovascular exercise one must work at an intensity of 50 % - 85 % of VO2max (MET system) 50 % - 85 % of HRR method 60 % - 90 % of HRmax Monitoring Intensity • Heart rate method • RPE scale • Talk test method Heart Rate Depending on the person’s level of fitness, calculate the Target heart rate intensity range by using the Age predicted formula or the Karvonen method and accordingly ask the client to maintain his exercise intensity in that range. Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) • Indicates a quantitative feeling of fatigue • Used to regulate exercise intensity Borg RPE Scale • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 14 16 17 18 19 20 very , very light very light fairly light somewhat hard hard very hard very, very hard Talk Test • This simple test indicates if an individual is working at an appropriate intensity by whether or not he or she can converse while exercising. Breathing should be rhythmical and comfortable. If the person is gasping for breath between words then exercise intensity is too high.