* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11 - Nervous System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
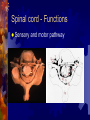
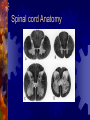
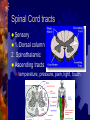
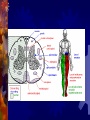
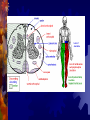
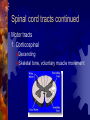
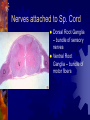
Spinal cord and Peripheral nervous system Spinal cord - Functions Sensory and motor pathway Reflex arc (spinal cord) Reflex center – Sensory receptor Sensory neuron Interneuron (association neuron) Motor neuron (effector) An effector organ Spinal Cord Anatomy Association neuron Motor http://www.bayareapainmedical.com/wspin ecrd.html Matter – “butterfly” interneurons White Matter – myelinated Gray Spinal cord Anatomy Spinal Cord tracts Sensory 1. Dorsal column 2. Spinothalamic Ascending tracts temperature, pressure, pain, light, touch Spinal cord tracts continued Motor tracts 1. Corticospinal Decending Skeletal tone, voluntary muscle movement Nerves attached to Sp. Cord Dorsal Root Ganglia – bundle of sensory nerves Ventral Root Ganglia – bundle of motor fibers Peripheral Nervous system Peripheral Nervous System PNS Somatic Autonomic Nervous systyem sympathtic Nervous system parasympathetic nervous system Somatic Nervous System Includes all nerves in the musculoskeletal system, sense organs Receptor (receives impulse) to Effector (muscle fiber) Autonomic Nervous System Motor neurons that control internal organs (involuntary) Innervate all organs Two divisions of Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic “Fight or flight response” Inhibits digestion Pupils dilate Accelerates heart rate Increase breathing rate. Parasympathetic Normal state Promotes digestion Pupils constrict Normal heartbeat “feed and breed” The Eye: Photoreceptor Lens – refraction and focusing Iris – controls entrance of light into eye Pupil – window into the eye Choroid – blood vessels, absorbs stray light Eye anatomy continued Sclera – white fiborous layer, protection Humors – Aqueous humor – between the cornea an lens Viterous humor – fills large cavity, gelatinous material Eye Anatomy continued Ciliary body – holds lens in place Retina – contains receptors Cones – color vision Rods – black and white vision Optic Nerve Rods and Cones Illustration Eye Anatomy Continued Optic Nerve – picks up impulse Ciliary muscles – controls the shape of the lens Accommodation – Additional focusing power Near object – ciliary muscle contracts, lens becomes round Physiology of sight Focusing – light rays bent by cornea, focus on the retina, refraction and inverted Fields of Vision Illustration Refer to Lab on eye dissection Cross section of head Normal Vision 20/20 at a distance of 20 feet, you can read a certain line (labeled 20) on the chart and that your vision is normal. 20/40 - Nearsightedness (myopic) Farsightedness (hyperopia) Disorders of the Eye: Glaucoma – built up pressure in the eye due to lack of aqueous humor drainage Vision of a person with Glaucoma Cataracts- clouding of the lens