* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
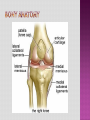
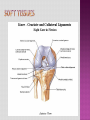
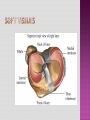
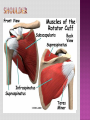
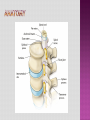
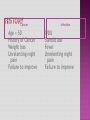
Programme for today: 13.30 Intros: Us, You, specialities? 13.45 Knees 14.15 Shoulder /1 14.30 Break 14.45 Shoulder /2 15.00 Back 15.30 Q&A, other examinations 16.00 Close MSK consult common in primary care Accurate dx is therapeutically important Possible with careful history and clinical examination A referred cause is common Accurate diagnosis and physiotherapy will prevent chronic pain, prolonged symptoms and functional disability. History Look Feel Move History of trauma Nature of symptoms/ Effect on activities Pain, instability, swelling Duration of symptoms History of arthropathy Gout, rheumatoid, psoriatic History of immunocompromise Steroids, diabetes Scars of surgery Deformity Swelling Muscle wasting Skin changes erythema/psoriasis/eczema Bone/muscle contours Comparison to unaffected side Joint temperature Effusion Bony prominences Area of tenderness along joint margin Crepitus Pulses Range of movement Active and Passive Stress tests Special tests Neurological Examination Anatomy Case study Differential Diagnosis Examination 28 Year old, football injury 4/12 ago, heard pop/snap in R knee and immediate swelling/pain. Eased with ice and rest within a week. Improved by 75% at first appointment and after full compliance with rehab, better but unable to fully extend knee (-10 degree). Agg: nothing really, just “discomfort” when getting into a car and occasional “weak” knee when playing football Ease: short-term discomfort 24: activity dependent Sleep: OK DH: nil SH: computer programmer, football 5xweek slim tall, good quads definition Trauma- bony soft tissue Degenerative Inflammatory Tumour Infection Referred Answer: full ACL rupture. Was fully functional apart from his high level sports. Was given the option for surgical intervention - age+sporting interest key factors, surgery not for everyone Look Feel Move Special Tests 3 Bones Humerus Scapula Clavicle 3 Joints Glenohumeral Acromioclavicular Sternoclavicular 1 “Articulation” Scapulothoracic BREAK 54 Year old male chopping wood in Jan, felt ache in L shoulder a few days later. The heaviness/achiness has not fully resolved. Symptoms ISQ 5/12 down the line. Agg: nothing in particular Ease: nothing 24h: worse during the night Sleep: disturbed DH: meds for gout SH: lorry driver barrel chest, rounded shoulders What is the differential diagnosis? Rotator cuff disorders cuff tendinopathy, calcific tendonitis, subacromial bursitis, impingement, cuff tears Glenohumeral jt. Problems adhesive capsulitis, osteoarthritis ACJ Problems Traumatic Dislocation Infections Pain arising from the shoulder jt Referred Pain Neck pain, myocardial pain, referred diaphragmatic pain Polymyalgia Rheumatica Malignancy Apical lung tumors, metastases Pain arising from elsewhere Answer: Cx radiculopathy + neural tension pain. Amitriptyline for sleep, rehab involved posture, Tx extension exc, Cx traction and retraction Look Feel Move Special Tests 61 Year old cashier I/M LBP over many years, constant in the last 3/12. CE, B+B, SA , bilat P+N/numbness clear Agg: working at till, walking to town Ease: movement if stationery, rest if mobile 24h: stiff in morning, eases with movement Sleep: aware of pain if awake slouched posture SH: married, 3 children at home, part-time work, main carer for mum What is the differential diagnosis? • Mechanical low back pain (97%) Lumbar strain or sprain (≥ 70%) Degenerative disk or facet process (10%) Herniated disk (4%) Osteoporotic compression fracture (4%) Spinal stenosis (3%) Pain better when spine is flexed or when seated, Spondylolisthesis (2%) • • • • Nonmechanical spinal conditions (1%) Neoplasia (0.7%) Inflammatory arthritis (0.3%) Infection (0.01%) • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Nonspinal/visceral disease (2%) Pelvic organs—prostatitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis Lower abdominal symptoms common Renal organs—nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis Aortic aneurysm - pulsatile abdominal mass Gastrointestinal system—pancreatitis, cholecystitis, Shingles - Unilateral, dermatomal pain; distinctive rash Answer: Disc degenerative changes, back exc, core work Look Feel Move Special tests Other examinations... Cancer Age > 50 History of Cancer Weight loss Unrelenting night pain Failure to improve Infection IVDU Steroid use Fever Unrelenting night pain Failure to improve Fracture Age >50 Trauma Steroid use Osteoporosis Cauda Equina Syndrome Saddle anesthesia Sphincter dysfunction Loss of sphincter control Major motor weakness