* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biophysical Hazards
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
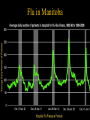
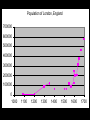
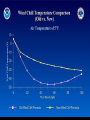
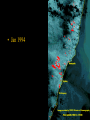
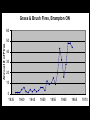
Biophysical Hazards Reading • Smith Ch 10 Biophysical Hazards • “dustbin” category for various assorted hazards – disease – extremes of temperature – wildfire Disease organisms • • • • Microbes: Bacteria, viruses, prions Parasites can affect people directly can affect crops Infectious Disease • Interaction between – population of disease organism – population of host organism – often complex transgenic relationships • Lyme disease Infectious Disease • Endemic: always present • Epidemic: periodically active – Major Epidemics: Pandemics Infectious Disease • Epidemic/endemic depends on size of host population – Too small: tendency toward epidemics – Large enough: tends to be endemic Flu in Manitoba Infectious Disease • Tendency for ecological balance between disease organisms and their hosts • Very deadly diseases – kill their hosts too quickly to spread efficiently – but modern communications can change that … • Fighting flu in Hong Kong Anthropological speculation • Humans evolved in Africa • Human population designed to be naturally regulated by the diseases of Africa • Take humans out of Africa: – Epidemic growth of human population • Humans as an epidemic? Black Death Pandemic 1347-1350 • Bubonic plague • Killed 50 million Europeans in 3 years – 1/3 of European population • Severe social disruption – Weakened the feudal system Black Death Pandemic 1347-1350 • Losses of urban populations: – London: 50% loss – Beijing: 40% loss Population of London, England 700000 600000 500000 400000 300000 200000 100000 0 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1700 Black Death Pandemic 1347-1350 • Western Europe in population crisis by 1347 – war, famine, disease, harvest failure – soil exhaustion • Black Death the latest of a series of calamities • Population took until 1600s to rebuild 1918-19 Influenza Pandemic • WW1: killed 9 million in 4 years • Influenza: killed 25-37 million in 2 years – 16 million killed in India Sydney NSW • Ann Arbor MI Fall 1918 • High River Alberta, Fall 1918 • Potential public enemy #1 Plague in the USA • San Francisco 1909 • New Orleans 1914 • Now endemic in California – transgenic shift from rats to ground squirrels Bubonic Plague in CA Promoting/Discouraging Disease • Increase probability of infection – population builds resistance – example of Tuberculosis in Victorian England • Decrease probability of infection – population does not get the exposure to build resistance – example of Polio Polio in LA, 1950s Biological limits • People suffer irreversible deterioration and death if internal body temperature – falls below 26 degrees C – rises above 40 degrees C Extreme Cold • Windchill, hypothermia – severe high-latitude/high-altitude weather conditions – cold water exposure Extreme temperatures • Cold weather kills fewer than hot weather – easier to keep warm than keep cool – body designed to survive cooling better than overheating The Humidex Chart • US OSHA heat chart Extreme temperatures • Dec 1983 cold snap kills 150 in USA • 1979-80 5000 heat deaths in USA • 1936-75 20,000 died in USA from heat & humidity Extreme temperatures • Kills the elderly, those with compromised circulatory & respiratory systems • Urban areas worse: heat island effect, worse in inner city • Set to worsen with global warming Extreme temperatures • 1955 heat-wave in LA killed 946 people – twice as deadly as 1906 San Francisco earthquake • Toronto Telegram June 1959 Frost Hazards • Bad for agriculture, especially tender crops close to harvest time • Various devices to reduce frost risk • Locate farms to avoid frost The Niagara Fruit Belt • Mainly on the Lake Ontario plain, N of the Escarpment • Cooler temperatures here retard fruit growth, reducing risk of a spring frost • Or make ice wine Wildfire Hazards • Promoted when fuel accumulates (dry vegetation) and meets dry, windy, warm weather October 1871 USA • Wildfire in Michigan & Wisconsin • Follows 14 week drought • Land-clearance fires whipped up by strong winds • Burns 1.7 M hectares • Kills 1500 • World’s greatest wildfire disaster? Ash Wednesday 1983 • • • • Victoria & South Australia 1983 El Nino drought & heatwave Strong winds (70 km/h+) Killed 76, 8000 homeless • Ash Wednesday fires 1983 NSW • 6 firefighters died here Macedon NSW Brushfires, 1983 drought Australia 1983 El Nino drought fires, Australia NSW Fires Dec 1993-Jan 1994 • 1992-3 El Nino • Affected 1 M Hectares • 300+ fires along 1100 km coastline fanned by strong winds • Destroyed 200 buildings • Killed 4 Jan 1994 NSW • Jan 1994 Australian Fires • Burn faster than other people’s fires – 800 Hectares/hour in Australia – 1 Hectare/hour in Northern USA Dandenong NSW 1997 Dandenong NSW 1997 • Engadin NSW 1997 controlled burn Engadin NSW 1997 Pillaga NSW 1997 Lithgow NSW Dec 1997 • Lost home, Sydney NSW Dec 1997 Heathcote NSW Dec 1997 • Mt Martha NSW Jan 1998 Icon in the smoke, Jan 1998 Smoky Sydney Dec 1997 Sussex Inlet NSW Jan ‘02 Toomerong NSW Xmas 2001 Causes of “Wildfires” • Lightning strikes • Human carelessness – rubbish that burning gets out of control – car exhausts, discarded glass containers etc., • Fires maliciously set • Effects of urban growth Grass & Brush Fires, Brampton ON Annual # of Fires 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1935 1940 1945 1950 1955 1960 1965 1970 Fuel Issues • Fire is part of the natural ecology • Controls fuel accumulation • Requires fuel accumulation – tends to be seasonal – Toronto area: • first warm weekend (usually April) New Jersey New Jersey brushfire Northern Quebec Effects of Fire Prevention • May cause fuel to accumulate to dangerous levels • Pre-emptive burns, controlled burns required Some areas fire-prone • Malibu California – Seasonally-dry Chaparral vegetation which burns hot and fast – Seasonally strong Santa Ana winds can whip up fires into a conflagration – Inhabited by the rich, dislike restrictions on their lifestyle – Demand good fire protection • Before & after 1993 canyon fire, Malibu CA • Ventura Co. California 4 July 1985 Arizona wildfires June 2002 El Dorado CO June 2002 • Missionary Ridge fire CO June 02 Oroville CA June 2002 • Smoky skies Valley View CO June ‘02 Hayman CO fire 16hrs old June ‘02 Glenwood CO June ‘02 Sacramento Mtns NM June ‘02 Shaw St Toronto May ‘02 • Windy evening, flames spread through garages at rear Biophysical Hazards • Bit of a mixture • But includes major killers – infectious disease – antibiotics ceasing to be effective