* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Surgical Complications
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
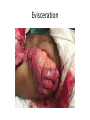
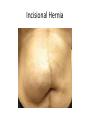
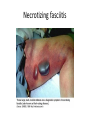
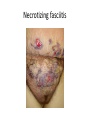
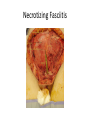
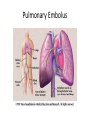
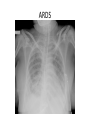
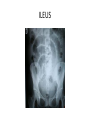
Surgical Complications Rajan Thakkar Surgical Complications • • • • • • • • • Wound Thermal Regulation Postoperative Fever Pulmonary Cardiac Renal Gastrointestinal Metabolic Neurological Surgical Complications • • • • • Primary disease Operation Unrelated factors Complications leading to other complications Prevention Wound Complications • • • • • Dehiscence Seroma Hematoma Infection Incisional Hernia Wound Dehiscence • • • • • • Separation of facial layers Serosanguinous drainage Technical Complication Risk Factors Mortality approaches 30% Evisceration Evisceration Incisional Hernia Seroma • Collection of liquefied fat, serum and lymphatic fluid under the incision • Benign • No erythema or tenderness • Mastectomy, axillary and groin dissections • Treatment Hematoma • Abnormal collection of blood – Discoloration of the wound edges (purple/blue) – Blood leaks through skin sutures • Imperfect hemostasis • Potential for secondary infection • Neck hematomas can be dangerous Wound Infection • • • • • • • • Major problem Superficial Deep Organ space Most commonly occur 4-6 days post-op Erythema, tender, edema 2.5% of abdominal incisions Staphylococcus aureus Wound Infection • Necrotizing fasciitis – Bacterial infection of underlying fascia – Classically Streptococcus, most often polymicrobial with anaerobes/GNR – Surgical debridement and IV antibiotics • Clostridial Myosistis – Clostridial muscle infection (myonecrosis and gas gangrene) – Clostridium perfringens – Surgical debridement and IV antibiotics Necrotizing fasciitis Necrotizing fasciitis Necrotizing Fasciitis Complications of Thermal Regulation • Hypothermia • Malignant Hyperthermia Hypothermia • • • • Drop in body temperature of 2 degrees C Causes Body’s Response Temperature below 35 C – Coagulopathic – Platelet dysfunction • • • • Mild - 32 – 35C = 90-95F Mod – 28 – 32C = 82–90F Severe – 25 – 28C = 77-82F Extreme Malignant Hyperthermia • • • • • Rare; autosomal dominant Fever, tachycardia, rigidity, cyanosis First sign is increased end tidal CO2 Often within 30 minutes Treatment: Dantrolene, correct electrolytes, cooling blanket Postoperative Fever • The Six W’s – – – – – – • Wind: pneumonia Wound: infections Water: UTI Walking: DVT (possible PE) Waste: abscess Wonder Drug: medication Noninfectious – Within the first 48-72 hours • Infectious – Fevers POD 3-8 – Standard work up includes • • • • • Blood cultures UA and Urine Cultures CXR Sputum cultures Tylenol/Motrin Pulmonary Complications • Atelectasis – Peripheral alveolar collapse due to shallow tidal breaths – Most common cause of fever within 48 hours of surgery – Incentive spirometry • Aspiration Pneumonitis – Reduced by pre-op fasting, protonix, cricoid pressure • Nosocomial Pneumonia • Pulmonary edema – CHF – ARDS • Pulmonary embolus – 500,000 per year – 1 in 5 are fatal – Prevention Pulmonary Embolus ARDS Cardiac complications • Hypertension • Ischemia/Infarction – Leading cause of death in any surgical patient – Key to treatment: prevention – MONA • Arrhythmias – >30 seconds of abnormal cardiac activity – Key to treatment is to correct underlying medical condition Renal Complications • Urinary retention – Inability to evacuate a urine-filled bladder – Commonly a reversible abnormality – Perianal and Hernia repairs • Acute Renal Failure – Pre-renal – Intrinsic – Post-renal Gastrointestinal Complications • • • • • • Postoperative ileus GI Bleeding Pseudomembranous colitis Ischemic Colitis Anastomotic Leak Enterocutaneous fistula Postoperative Ileus • Lack of function without definitive obstruction • Prolonged by extensive operative manipulation, SB injury, narcotic use, abscess and pancreatitis • Must be distinguished from SBO • Flat and Upright abdominal film – Ileus: dilated bowel throughout, air in colon and rectum – SBO: air fluid levels, no colonic or rectal air ILEUS SBO Gastrointestinal Complications • GI Bleeding – From Any source (get a detailed history) – Gastric “stress” ulcers (Curling’s Ulcer) • Uncommon with invention of H2Blockers and PPIs • Pseudomembranous colitis – Superinfection with C difficile – Alteration of intestinal flora by perioperative antibiotics – Toxic colitis is a surgical emergency (mortality of 20-30%) • Ischemic Colitis – Bowel affected helps determine cause – Surgical devascularization, hypercoagulable states, hypovolemia and emboli • Anastomotic leak • Enterocutaneous fistula – The most complex and challenging surgical complication C diff colitis C diff colitis Anastomotic leak in GBP Metabolic Complications • Adrenal Insufficiency – Uncommon but potentially lethal – Sudden cardiovascular collapse • Hypotension, fever, confusion, abdominal pain – “Stim” test, administration of hydrocortisone • Baseline serum cortisol, 30 min, 60 min • Hyper/Hypothyroidism • SIADH – Continued ADH secretion despite hyponatremia – Neurosurgical procedures, trauma stroke, drugs (ACEI, NSAIDs) Neurologic Complications • • • • Beware the drugs you will be prescribing Delirium, Dementia and Psychosis Seizure Disorders Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attacks