* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How can you prevent the spread of diseases caused by microbes?
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
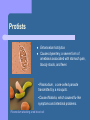
Coming Soon to a Person Near You! Understanding Microbes and Disease By: Essential Question: How can science help us to understand the world around us? Rationale Microbes are a part of our lives every day. Some of them are good for us, some of them are harmful, and some of them are deadly. We need to understand the role microbes play in our lives and how to prevent diseases that are associated with them. Many microbes in our world cause sickness and disease in animals and plants. Some Microbes in Our World Entamoeba Protists histolytica Streptococcus Bacteria AIDS Virus Protists Entamoeba histolytica Causes dysentery, a severe form of amebiasis associated with stomach pain, bloody stools, and fever. •Plasmodium, a one-celled parasite transmitted by a mosquito. •Causes Malaria, which causes flu-like symptoms and intestinal problems. Plasmodium attacking a red blood cell Bacteria Streptococcus Bacterium Causes the strep throat, a painful sore throat and fever. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Causes Tuberculosis, a highly contagious respiratory disease. Viruses Retroviridae - HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) Causes Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), which is a deadly disease that attacks the human immune system. Orthomyxoviridae – Influenza Virus Causes the flu, which is a respiratory infection that often causes the infected person to have a fever, headache, and body aches. How disease spreads! Pathogen- any microbe that causes disease Infectious disease- a disease caused by a pathogen Contagion- a pathogen that can be passed from one organism to another Non-infectious disease- a disease that cannot be spread from organism to organism (may be genetic) Mutagen- anything that causes changes (mutations) in your DNA. – A virus can be a mutagen, because it inserts its own genes into the host DNA. Vector vs. Carrier Vectors- an organism that helps spread a disease, but is not infected with the disease Carrier- an organism, usually a human, that is infected with a disease and can transmit it, but shows no symptoms. How can you prevent the spread of diseases caused by microbes? Top 5 ways to help prevent the spread of disease: #5 - Use antibiotics correctly. #4 - Get immunized. #3 - Use care when preparing and handling food. #2 – Keep surfaces clean and disinfected. And, #1 - Wash your hands. Immunity Types of Immunity– Active Immunity- obtained by exposure to the pathogen. (Having the disease or receiving a vaccine). – Stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies Antibodies are chemical substances that help destroy pathogens Passive Immunity- transferring antibodies made in one organism to another organism. Antimicrobials vs. Antibiotics How are they different? – Antimicrobial products are designed to kill microbes before they enter your body. – In soaps, cleaning products, children’s toys, caulks, and grouts used around showers. Antibiotics are drugs that kill bacteria or prevent their reproduction internally (even those used to kill bacteria in cuts and scrapes) Concerns – Overuse of these products leads to development of resistant forms of the various microbes. Biotechnology and Medicine What is biotechnology? – The use of living organisms or parts of organisms to produce products used by people (medications and foods). Examples: – – Bacteria are used to produce large quantities of certain drugs rapidly, because of their rapid reproduction ( insulin, growth hormone, blood pressure medicines, interferon: which treats influenza) Viruses are used to make vaccines. They are also used to transmit “piggyback vaccines” which treat genetic disorders by inserting the DNA sequence that is missing by using a harmless virus. Biotechnology and Agriculture Scientists are seeking ways to alter crops to make them resistant to disease, herbicides, and frost. Food crops are manipulated to taste better and provide better nutrition. Scientists developed a type of tomato that can stay on the vine longer to ripen without rotting before going to market. North Carolina and Biotechnology Largest firm is the North Carolina Biotechnology Center in Research Triangle Park. – Provides economic benefits by creating jobs and conducting research so farmers can increase crop production. Ethics and Biotechnology Safety of genetically modified crops Is it appropriate to alter genetic material of a living thing? Resources: AIDS Pathology http://medstat.med.utah.edu/WebPath/TUTORIAL/AIDS/AIDS001.html – I obtained images of viruses from this site. The Big Picture Book of Viruses http://www.virology.net/Big_Virology/BVHomePage.html – I obtained images of influenza virus and HIV. Flu – NIAID Fact Sheet http://www.niaid.nih.gov/factsheets/flu.htm – I obtained information about influenze from this site. Handwashing – CDC – An Ounce of Prevention: Keeps the Germs Away http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/op/handwashing.htm – I obtained the video on hand washing from this site. Resources, continued Malaria Brochure http://www.niaid.nih.gov/publications/malaria/ Epidemic – The World of Infectious Diseases http://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/epidemic/index.htm l Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute – Press Release on DNA of the tissue destroyer Genome clues to Amoebic Dysentery http://www.sanger.ac.uk/Info/Press/2005/050223.shtml – I obtained an image and content information about Etamoeba Hystolytica.