* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14: Lifestyle Diseases
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
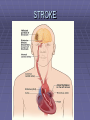
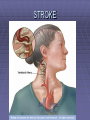
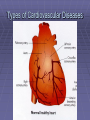
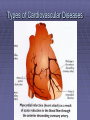
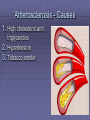
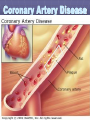
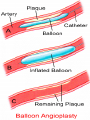
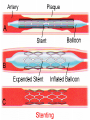
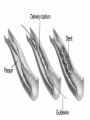
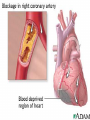
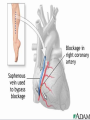
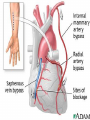
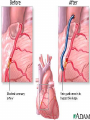
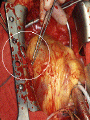
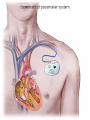
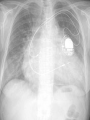
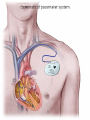
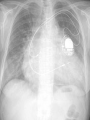
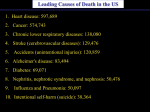
Lifestyle Diseases History and Lifestyle Diseases History: Infectious diseases used to be the main cause of death in the United States. I.D. 60% of a all deaths in 1900 1900 pneumonia, influenza, tuberculosis, and diarrhea/enteritis. Improved hygiene practices, better living conditions, and medical advancements, has slowed infectious disease. History and Lifestyle Diseases 1900s – heart disease and cancer were in the lower top ten in terms of death. Since 1940s – heart disease and cancer have increased 2000 – 1 and 2 causes of death Why the increase? How does this compare to other parts of the world? History and Lifestyle Diseases Today: The top causes of death in the United States are lifestyle diseases. What is a Lifestyle Disease? Lifestyle Diseases are diseases that are caused partly by unhealthy behaviors and/or by other factors such as environment and/or genetics. What Causes Lifestyle Diseases? 1. A person’s lifestyle (their habits, behaviors, and practices) 2. Uncontrollable risk factors like age, gender, and heredity. 3. It is important to understand the risk factors that contribute to lifestyle diseases because the behaviors you choose right now can determine if you develop a lifestyle disease later in life. What Causes Lifestyle Diseases? Controllable Risk Factors: Taking control of the risk factors you can control may greatly reduce your chances of developing a lifestyle disease. 4. Controllable risk factors include habits, behaviors, and practices that you can control: A. diet and body weight B. Your daily levels of physical activity C. Your level of sun exposure D. Smoking and alcohol abuse Diabetes Risk and Obesity 3 3 Relative Risk 2.5 1.73 2 1.5 1.1 1 Risk 1 0.5 0 <23 23-24.4 24.5-26.4 Body Mass Index >26.4 Uncontrollable Risk Factors: Age More older, tougher time protecting against disease. Your chances increase as you age. Gender Certain diseases are more common to the different genders. Males are more likely to develop heart disease. Females are more likely to develop breast cancer. Uncontrollable Risk Factors: Ethnicity African Americans more likely to develop high blood pressure. Mexican Americans have a higher risk for diabetes. Heredity Your genes may predispose you to a certain disease. It does not mean you will get the disease, but you may have to work harder to prevent it. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) diseases and disorders that result from progressive damage to the heart and blood vessels. CVD is the leading cause of death in the U.S. Nearly all people who die from a CVD are over the age of 40. Why does lifestyle matter? Lifestyle decisions that lead to being overweight, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes increases your chances of developing a cardiovascular disease. Types of Cardiovascular Diseases 1. Stroke 2. High blood pressure or hypertension. 3. Heart Attack. 4. Atherosclerosis 5. Coronary artery disease 6. Heart arrythmias 7. Heart failure 8. Heart valve disease 9. Congenital heart disease 10. Heart muscle disease 11. Pericardial disease 12. Aorta Disease STROKE Stroke blood flow to the an area of the brain is interrupted. Results in weakness or paralysis Cause blood clot in one of the arteries of the brain or by a hole in one of the blood vessels that feed the brain. Symptoms of a stoke include: Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg Trouble seeing in one or both eyes Sudden dizziness or loss of coordination Sudden, sever headache with no know cause STROKE STROKE High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) “silent killer” because people do not know they suffer from it until they have a heart attack or stroke. Affect 1 in 4 Americans (source: AMA) can damage the walls of blood vessels. The heart is forced to work harder, causing the heart to weaken. can eventually damage the kidneys and eyes. 120/80 is considered high these days <120/80 is considered normal High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) - Causes Not completely understood 1. Obesity above 25% B.M.I. increases risk 2. Sodium intake 3. Genetics 4. lack of exercise 5. insulin issues 6. drug use 7. Age Types of Cardiovascular Diseases 2. Heart Attack damage and loss of function of an area of the heart muscle. Due to blockage of coronary arteries – supply blood to the heart Myocardial infarction Types of Cardiovascular Diseases Types of Cardiovascular Diseases Heart Attack If a blood clot blocks a coronary artery, blood flow is restricted and heart cells begin to die, the result is a heart attack. Warning signs of a heart attack include: 1. Uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, or pain in the chest that last for more than a few minutes. 2. Pain spreading to shoulder, neck, and arms. 3. Light-headedness, sweating, nausea, and shortness of breath. Atherosclerosis Fatty deposits known as plaque build up on the inside walls of arteries and interfere with blood flow. “hardening” of arteries Plaques can reduce or stop blood flow to certain parts of the body Plaques can break free and release clots in the bloodstream, causing a heart attack or stroke Atherosclerosis Thrombus blood clot Embolus blood clot that breaks off and travels to another part of the body Pulmonary embolism Coumadin prescribed blood thinner Atherosclerosis - Causes 1. High cholesterol and triglycerides 2. Hypertension 3. Tobacco smoke Coronary Artery Disease CA Disease - Treatments 1. Angioplasty balloon is guided to part of the narrowing artery Balloon is inflated to compress the fat and increase blood flow CA Disease - Treatments 2. Stent small metal tube that acts as a scaffold to provide support inside your coronary artery Once in place, the stent expands to the size of the artery and holds it open. Size of an ink pen spring; around 3,000/ piece CA Disease - Treatments 3. Heart bypass blood vessels are used to bypass blocked areas of cardiac vessels Also called coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) CA Disease - Treatments 3. Heart bypass blood vessels can come from your chest, legs, or arms depending on location and size of blockage Heart Arrhythmia Irregular or Abnormal heartbeat Heart pumps less efficiently Normal Heart beats 60 – 100x per minute; 100,000x each day Heart Arrhythmia - Causes 1. Coronary artery disease. 2. Electrolyte imbalances in your blood (such as sodium or potassium). 3. Changes in your heart muscle. 4. Injury from a heart attack. 5. Healing process after heart surgery Heart Arrhythmia - Treatments 1. Medications 2. Lifestyle changes – stop smoking, limit caffeine, etc. 3. Pacemaker send electrical impulses to heart to maintain stable heartrate 4. Surgery