* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3. List differential diagnoses for the neck swelling in this patient
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Mycoplasma pneumoniae wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
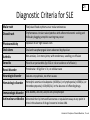
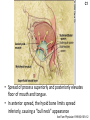
C1 1. Enumerate the classification criteria for SLE C1 Diagnostic Criteria for SLE Malar rash Flat/raised fixed erythema over malar eminences Discoid rash Erythematous circular raised patches with adherent keratotic scaling and follicular plugging; atrophic scarring may occur Photosensitivity Exposure to UV light causes rash Oral ulcers Oral and nasopharyngeal ulcers observed by physician Arthritis Non-erosive, 2 or more joints; with tenderness, swelling, or effusion Serositis Pleuritis or pericarditis (by ECG or rub or evidence of effusion) Renal disorder Proteinuria > 0.5g/d or 3+, or cellular casts Neurologic disorder Seizures or psychosis, no other causes Hematologic disorder Hemolytic anemia or leukopenia (<4000/uL) or lymphopenia (<1500/uL) or thrombocytopenia (<100,000/uL) in the absence of offending drugs Immunologic disorder Anti-dsDNA, anti-Sm, and/or anti-phospholipid Antinuclear antibodies Abnormal titer by immunofluoresence or equivalent assay at any point in time in the absence of drugs known to induce ANA Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 17th ed. C1 2. List differential diagnoses for muscle weakness and elevated creatine kinase C1 Polymyositis • Polymyositis is an uncommon connective tissue disease. It's a type of inflammatory myopathy, which is characterized by muscle inflammation and weakness. • Women between their 30s and 50s • A blood test will let your doctor know if you have elevated levels of muscle enzymes, such as creatine kinase (CK) and aldolase. http://www.medicinenet.com/polymyositis/article.htm C1 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis • Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a rare, progressive neurological disorder in which nerves that control the body's muscle activity deteriorate (degenerate) • ALS is characterized by the presence of extremity (distal) weakness with the presence of upper motor neuron signs. • blood studies (serum creatine kinase may be elevated) http://www.mdguidelines.com/amyotrophic-lateral-sclerosis C1 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus • Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem autoimmune connective tissue disorder with various clinical presentations. • Muscle enzyme levels (creatine kinase, aldolase) may be moderately or severely elevated with lupus myopathy http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1146456-overview C1 3. List differential diagnoses for the neck swelling in this patient C1 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES 1. Diseases with Cervical lymphadenopathy (e.g. Tuberculosis, Lymphoma, Tonsilitis) 2. Ludwig’s angina 3. Upper Respiratory tract Infection esp. Pharyngitis 4. Lymphoma 5. Infectious mononucleosis C1 Cervical Lymphadenopathy • Cervical nodes drain the tongue, external ear, parotid gland, and deeper structures of the neck, including the larynx, thyroid, and trachea. • Inflammation or direct infection of these areas causes subsequent engorgement and hyperplasia of their respective node groups. C1 Ludwig’s Angina • Ludwig's angina, otherwise known as angina ludovici, is a serious, potentially life-threatening cellulitis or connective tissue infection, of the floor of the mouth, usually occurring in adults with concomitant dental infections. • Symptoms: swelling, pain and raising of the tongue, swelling of the neck and the tissues of the submandibular and sublingual spaces; malaise, fever, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) and, in severe cases, stridor or difficulty breathing. • Swelling of the submandibular and/or sublingual spaces are distinctive in that they are hard and classically 'boardlike‘. C1 URT Infection (Pharyngitis) • Pharyngitis is inflammation of the pharynx, which is in the back of the throat, between the tonsils and the voicebox (larynx). • The main symptom is sore throat. • Other symptoms may include: -Fever -Headache -Joint pain and muscle aches -Swollen lymph nodes in the neck C1 Hodgkin’s disease • Hodgkin's disease, also called Hodgkin’s lymphoma, is the result of change or mutation in infection-fighting white blood cells called lymphocytes, which are stored in the lymph glands. This change results in an uncontrolled growth of cancer cells, which develop into malignant tumors in the lymph glands. Hodgkin's disease can also develop in other parts of the lymphatic system, such as the spleen or bone marrow. C1 Infectious Mononucleosis • a generalized infection ,caused by a virus, either the EBV or CMV. • spreads from person to person through intimate contact with the saliva of a person who has mononucleosis (“kissing disease”). • Early flu-like symptoms,classic symptoms develop later and include swollen glands and extreme fatigue C1 Mumps • caused by the mumps virus. Before the development of vaccination and the introduction of a vaccine, it was a common childhood disease worldwide, and is still a significant threat to health in the third world. • Painful swelling of the salivary glands (classically the parotid gland) is the most typical presentation. The disease is generally self-limited, running its course before receding, with no specific treatment apart from controlling the symptoms with painkillers. • May spread to other areas such as the neck and the testicles for males. C1 4. What are some underlying factors and etiologic organisms in Ludwig’s angina? C1 Ludwig’s angina • Ludwig’s angina is a rapidly progressive, potentially fulminant cellulitis • involves the sublingual and submandibular spaces • typically originates from an infected or recently extracted tooth – lower second and third molars C1 • Spread of process superiorly and posteriorly elevates floor of mouth and tongue. • In anterior spread, the hyoid bone limits spread inferiorly, causing a "bull neck" appearance Am Fam Physician 1999;60:109-12 C1 Predisposing factors • • • • • • dental caries recent dental treatment sickle cell disease a compromised immune system trauma tongue piercing Am Fam Physician 1999;60:109-12 C1 Etiologic Organisms Common • Staphylococcus • Streptococcus • Bacteroides Atypical • Pseudomonas • Escherichia coli • Klebsiella • Enterococcus faecalis • Candida • Clostridium Crit Care Clin. 2003;19:55-72 J Emerg Med. 1995;13:499-503 C1 5. Define and distinguish the etiologic organisms in community azquired pneumonia vs hospitalacquired pneumonia C1 Community acquired pneumonia • is a disease in which individuals who have not recently been hospitalized develop an infection of the lungs (pneumonia) • occurs throughout the world and is a leading cause of illness and death. • bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. C1 Most common etiologic organisms… • Infants – caused by Streptococcus agalactiae, also known as Group B Streptococcus or GBS. GBS causes at least 50% of cases of CAP in the first week of life. – Other bacterial causes in the newborn period include Wisteria monocytogenes and tuberculosis. – In cases of viruses herpes simplex virus is the most common and life-threatening, but adenovirus, mumps, and enterovirus can also cause disease C1 • Infants – Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Staphylococcus aureus. – Chlamydia trachomatis-acquired during birth but which does not cause pneumonia until 2–4 weeks later C1 • Adults – Viruses • 20% of CAP cases. • influenza, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, metapneumovirus, and adenovirus C1 • Adults – Streptococcus pneumoniae • common bacterial cause of CAP • "drug resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae" or DRSP older than 65, exposure to children in day care, having alcoholism or other severe underlying disease, or recent treatment with antibiotics should initially be treated with antibiotics effective against DRSP. – Atypical organisms • Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydophila pneumoniae.Legionella pneumophila C1 • Adults – Hemophilus influenzae – Enteric Gram negative bacteria - Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae • residence in a nursing home, serious heart and lung disease, and recent antibiotic use should initially be treated with antibiotics effective against Enteric Gram negative bacteria. C1 Risk Factors • Obstruction • Lung disease • Immune problem C1 Hospital-acquired pneumonia • develops at least 48 hours after hospital admission • microaspirationof bacteria that colonize the oropharynx and upper airways in seriously ill patients • Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) includes: – ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) – postoperative pneumonia – pneumonia that develops in unventilated but otherwise moderately or critically ill hospitalized inpatients – healthcare-associated pneumonia (HCAP) - pneumonia acquired by patients in healthcare facilities such as chronic care facilities, dialysis centers, and infusion centers C1 Risk Factors • • • • • • • mechanical ventilation Old age Decreases filtration of inspired air Other disease states Medications Poor hand-washing Inadequate disinfection of respiratory devices C1 Most common etiologic organisms… • aerobic gram-negative bacilli: – P. aeruginosa – Escherichia coli – Klebsiellapneumoniae – Acinetobacter species • gram-positive cocci – Staphylococcus aureus, particularly methicillinresistant S. aureus (MRSA) C1 • Fungal pathogens: – Candida species – Aspergillusfumigatus • Viral Pathogens: – Influenza – parainfluenza, – adenovirus, – measles, – respiratory syncytial virus