* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fungus & Prions
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Fasciolosis wikipedia , lookup
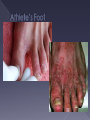
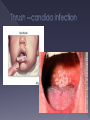
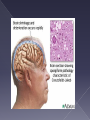
Caused by parasite › Transmitted by mosquito › Once injected into the human, the parasite grows and multiples first in the liver and then the red blood cells. Symptoms appear 710 days after infection Patient will experience: › Fever, chills, sweats, headaches, nausea, body aches, general malaise About 1,500 cases reported every year in the U.S. › From travelers and/or immigrants › Malaria considered eradicated from U.S. in 1950’s. 3.3 billion people diagnosed worldwide › Thrives in tropical and subtropical areas. Multicelled organisms Contain polysaccharide – chitin Reproductive structures – spores Cause disease by interfering with normal organ structure and function or by inflammation or allergy Most pathogenic fungi are molds › Mold common in soil, air, water, dust › Aspergillus mold is most common Recent multistate fungal meningitis outbreak… Picture: (CNN, 2012) Inflammation of the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Many different types: fungal meningitis is NOT contagious but still serious. Symptoms include: › Fever, headache, and stiff neck Normally does not cause disease, but takes advantage of a weakened immune system › “opportunistic” › Ex: Athlete’s foot fungal skin infection Infects about 10% of US population Topical creams prevent new growth, but don’t kill fungi already there Often comes back Prevention Ex: Candida yeast infection › White or yellow curd-like patches (colonies) › Thrives in moist & warm environments: Mouth/throat, Digestive tract/anus, penis, vagina › 75% of women will get a vaginal yeast infection in their lifetime. Prions (Pree – ons) = Proteinaceous Infectious particles Mutated prions cause: › Mad Cow Disease in cows and › Variant Creutzfeld-Jakob Disease (vCJD) in people An infectious agent composed only of protein All known prion diseases affect the structure of the brain or other neural tissues by inducing abnormal folding of normal cellular proteins in the brain Usually progresses rapidly and are currently untreatable and fatal Prions can jump from one species to another, but easier among same species. › “Species barrier” somewhat protective › Cow by-products fed to other cows › In cows: Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy Symptoms › Loss of coordination › Dementia › Brain full of holes (sponge) › Death Mad cow disease 1st identified in 1980s in Britain 217 people from 11 countries have contracted or died from vCJD to date (CDC) › 170 in United Kingdom › 25 in France › 3 in U.S. – believed exposed in UK in 1980s CDC: “The risk of getting mad cow disease from eating beef from European cattle is about 1 in 10 billion” CDC: “The risk to human health from BSE in the United States is extremely low” While the risk is small, it takes 10-20 years from infection to the onset of disease – so who really knows the risk?? (10/2003) (2007) USDA budget for 2007: cut back on cattle testing Less than ½ of 1% (0.006) tested! Public health control measures to keep infected meat out of the human food chain. › No downer cows (12/2003) › No cows fed to cows (1997) › Prohibition of certain cow parts in the human food supply (2006) Ground beef a source?