* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria/Virses
Viral phylodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Social history of viruses wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Human papillomavirus infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
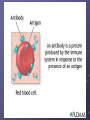
Bacteria: Bacteria are: Prokaryotes no membrane bound organelles Like nucleus, chloroplasts or mitochondria Bacteria: Genetic material floats around in the cytoplasm Movement possible with structures called: flagella, or cilia Bacteria: two kingdoms of bacteria Archaebacteria : harsh environments, harsh environments, create endospores thick walled cell Oldest organisms, Eubacteria All the same characteristics of Archaebacteria except living in harsh environments Cell Structure: 3 general shapes: rod-like , spherical, spiral Reproduce asexually by binary fission Sexual reproduction: Some can reproduce sexually by conjugation (2 organisms get together and exchange genetic material) Bacteria Can be an autotroph or Heterotroph Play positive role in society: Fuel production Food production Medicines Environmental recycling Bacteria .Causes many infectious diseases .Can be treated successfully with antibiotics Staphylococcus aureus, the most prevalent pathogen of humans, may cause up to one third of all bacterial diseases ranging from boils and pimples to food poisoning Infectious diseases: STD’s Most STD’s ( sexually transmitted diseases) are bacterial What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common (STD) caused by the bacterium, Chlamydia trachomatis, which can damage a woman's reproductive organs. symptoms of Chlamydia are usually mild or absent, serious complications that cause irreversible damage, including infertility, can occur "silently" before a woman ever recognizes a problem. Colorized micrograph of gonorrhea cells Syphilis Spirochetes on Head of Sperm Viruses Dead or alive? Viral structure Viruses are not cells. Basic structure: Protein coat Nucleic acid core (RNA or DNA) Lipoprotein coat (second coat – only in enveloped viruses) Contains genetic material Are viruses alive? Only 1 characteristic of life: reproduction Can only reproduce inside a host cell! What is human papilloma virus (HPV)? What is human papilloma virus (HPV)? Human papilloma virus (HPV) is one of the most common (STDs). Sexually Transmitted Diseases HPV: HPV is estimated to be the most common sexually transmitted infection in the US Most sexually active men and women will probably acquire genital HPV infection at some point in their lives. The American Social Health Association reported estimates that about 75-80% of sexually active Americans will be infected with HPV at some point in their lifetime. HPV: can be spread through skin-to-skin contact. many different types of HPV. Some types cause genital warts & are called low-risk, some types can lead to cervical cancer and are called high-risk. There is no known cure for HPV, there is a vaccine that can protect against some types of the virus. condoms may not protect sexual partners from contracting genital HPV infections!!!! WHY???? Herpes Virus: Herpes Herpes, whether genital herpes or cold sores (fever blisters) are caused by an infection with the herpes simplex virus. Genital herpes, for example, affects more than one in five adolescents and adults With genital herpes, tender ulcers will generally appear around the genitals or rectum. Herpes Cont. The herpes virus can be spread by direct contact with the sore or indirect contact through sharing items such as utensils, towels, or drinks. HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus HIV Infection occurs by the transfer of blood, semen, vaginal fluid, pre-ejaculate, or breast milk, bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected immune cells. The 4 routes of transmission are unprotected sexual intercourse, contaminated needles, breast milk, and transmission from an infected mother to her baby at birth How does our body fight these invaders? Immune System Immune System Terminology: Pathogen – organism which causes the disease Toxin – poison that travels through the body interfering with normal processes antibodies – molecules that fit to an invading foreign body signally WBC’s for destruction The Immune System Purpose: to remove infectious diseases and other pathogens from the human body Immune System Major Organs and Their Functions 1st line of Defense: Skin – also called the Integumentary system, acts as a barrier 2nd line of Defense: Mucous and Chemicals traps or kills the pathogen 3rd line of Defense: White Blood Cells – recognize disease agents (antigensmarker) and create antibodies ( to tag and remove these antigens WBC’s Cont. Part of your blood Made of many types Phagocytes are the WBC type that actually eats and destroys these antigens Ex. macrophage macrophage Lymph Nodes Lymph Nodes – help restore fluid lost by the blood and return it to the circulatory system