* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ID Amebiasis
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Inflammatory bowel disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Ulcerative colitis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
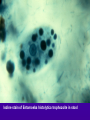
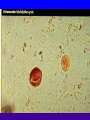
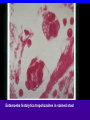
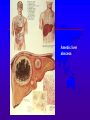
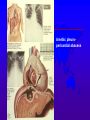
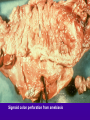
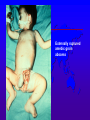
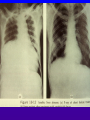
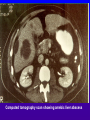
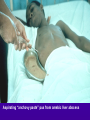
Amebiasis AMEBIASIS Incidence Possibly 10 % of world's population infected Prevalence in tropical countries : 30 % Prevalence in U.S.A. : 1 to 5 % Man is primary reservoir Prevalence in U.S. homosexual population : 25 % Reported epidemic in Grand Junction Colorado from chiropractic "colonic therapy" irrigation AMEBIASIS Pathophysiology Two life cycle forms (as for Giardia) : –Trophozoite : causes illness –Cysts : passed in stool, are infectious Transmission by fecal-oral route Most infections are asymptomatic Attack rates 5 to 30 % Cysts can remain viable for months in moist environment Cysts sensitive to chlorination, dessication, boiling Iodine stain of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite in stool Entamoeba histolytica tropohozoites in stained stool Life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica AMEBIASIS Pathology Main pathology is in colon –Initial mucosal inflammation –Then mucosal erosions, then ulcers Extraintestinal spread is hematogenous Large abscesses can develop in : –Liver –Lung –Brain –Other tissues Amebic liver abscess Amebic pleuropericardial abscess AMEBIASIS Symptoms Incubation period variable, but often 5 to 10 days Crampy abdominal pain Dysentery +/- weight loss +/- anorexia, nausea Focal symptoms if complications develop AMEBIASIS Complications Fatality rate for amebic dysentery is 2 % Overall complication rate is 3 to 4 % –Colon perforation –Toxic megacolon –Ameboma (abd. mass, bowel obstruction) –Liver abscess - may rupture into pleural or pericardial space –Brain abscess May cause 40,000 to 75,000 deaths annually (2nd or 3rd parasitic cause of death in the world after malaria +/- leishmaniasis ) Sigmoid colon perforation from amebiasis Externally ruptured amebic groin abscess AMEBIASIS Diagnosis Fresh stool or colon mucus shows cysts or trophozoites Often 3 or more stool exams required Serologic tests important to distinguish amebiasis from ulcerative colitis Sigmoidoscopy useful to inspect ulcers and obtain stool or mucus for culture & stain Abd. CT needed if liver abscess suspected Computed tomography scan showing amebic liver abscess Aspirating “anchovy paste” pus from amebic liver abscess AMEBIASIS Treatment Two general classes of meds used: –Tissue amebacides : combat invasive amebiasis in bowel & liver Metronidazole Emetine, dehydroemetine Chloroquine –Lumenal drugs : kill amebas within colon Iodoquinol Paramomycin Diloxanide AMEBIASIS Treatment of Asymptomatic Carriers Recommended for: –Food handlers (always) –All cases in low incidence regions ( U.S.A., Europe) –Not always recommended for asymptomatic cases in high incidence tropical countries AMEBIASIS : Treatment Regimens for Asymptomatic Carriers Iodoquinol –650 mg tid x 10 days (40 mg / kg / day ) –Side effects mild : nausea, emesis, rash Paramomycin –500 mg tid x 7 to 10 days (30 mg / kg / day) –OK in pregnancy Diloxanide furoate (Furamide) –500 mg tid x 10 days (20 mg / kg / day) –Only available in U.S.A. by calling CDC in Atlanta AMEBIASIS : Treatment of Invasive Disease Metronidazole 750 mg tid x 10 days, followed by iodoquinol 650 mg tid x 20 days (or paramomycin 25 to 30 mg / kg / day in 3 divided doses x 7 days) Dehydroemetine one to 1.5 mg / kg / day (max. 90 mg / day) IM up to 5 days following iodoquinol Tetracycline 500 mg qid x 10 days (indirect amoebacidal action) Chloroquine phosphate : 2nd line agent for extralumenal infection ; 1gram / day, then 500 mg / day x 2 to 3 weeks