* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 Preventing Infectious Diseases
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
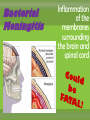
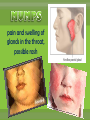
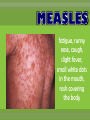
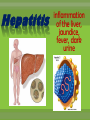
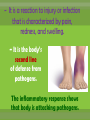
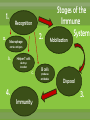
agents that invade the body and cause diseases. List and describe the 5 main pathogens and how they are treated.. single celled organism; can be killed with antibiotics* antibiotics are used to slow or kill the growth of bacteria. You must take all of the prescribed medicine or it can come back! What are some of the more common bacterial infections? Causes severe muscle spasms sore throat, fever, yellow or white specks on the throat headache, thick mucous, feeling pressure in your head Sinus Infection Bacterial Meningitis Inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord Salmonellas affects the digestive system, usually spread by contaminated food Tiny pathogens that survive and replicate only inside living cells; can’t be killed by medication Any medication taken is to treat the symptoms; viruses cannot be cured, they have to run their course. scratchy sore throat, sneezing, runny nose headache, sore muscles, sore throat, fever, vomiting, fatigue and coughing pain and swelling of glands in the throat, possible rash fatigue, runny nose, cough, slight fever, small white dots in the mouth, rash covering the body Fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat & weakness Hepatitis inflammation of the liver, jaundice, fever, dark urine organisms that absorb and use the nutrients of living or dead organisms * Usually treated with an over-the-counter anti-fungal cream single celled; larger than bacteria (Malaria: Spread by mosquito bites*) Good hygiene is the best preventative measure; other medications require prescription Feed off of other living things (Lice, ticks)* prevention best, (don’t share brushes, use medicated shampoo, wear protective clothing in wooded areas, etc… What are the 4 ways infectious diseases can be spread? Domestic and wild What is our body’s first line of defense against disease? Including mucous membranes ~ It is a reaction to injury or infection that is characterized by pain, redness, and swelling. ~ It is the body’s second line of defense from pathogens. The inflammatory response shows that body is attacking pathogens. If a pathogen gets past the physical barriers, what system kicks in to fight the disease from the inside? Your white blood cells produce antibodies that travel through the lymphatic system to fight the pathogens. What are Immunizations? A vaccine (shot) used to help prevent contracting a specific disease. • A small amount of the pathogen is put in the body so the immune system can develop antibodies so if exposed to the same pathogen you can fight it off without getting it. Laws about Immunization… The Texas Department of Health has ruled that students must be current with immunizations in order to attend school unless an exemption has been filed with the school. Reason for Exemptions: • Medical • Unless it is written in the statement that a lifelong condition exists, the exemption statement is valid for only one year from the date signed by the physician. • • • • Religious Too soon after another immunization Immune due to having had the disease Vaccine Shortage What are some things you can do to stay well? Protect yourself Regular Check up Drink water Eat healthy Get enough sleep Vaccines Exercise Reduce stress Avoid contact with sick people Infection Prodromal (Symptoms) The body is able to fight off a disease w/o getting sick. Incubation W/ Immunity W/O Immunity Carrier w/ No symptoms Illness Recovery / Death Body does not fully recover and goes through stages again. 1. a. Recognition 2. Macrophage Stages of the Immune System Mobilization carries antigens b. 4. Helper T cells destroys invaders c. Immunity B cells produces antibodies Disposal 3.