* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
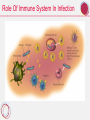
Chapter 16 Infectious Illnesses Elizabeth Lytle, MPH, BSN, RN Los Altos School District Topics Of Focus For This Chapter Infectious Disease Causes and spread Common infectious diseases Infection Process and immune response Prevention Colds and flu Disorders Immune system disorders Agents Of Infection Viruses Require our cells to reproduce Viral diseases: flu, herpes, hepatitis, HIV Fungi, Protozoa and Parasitic Worms Fungi release enzymes to digest cells (athlete’s foot) Protozoa release enzymes and toxins to destroy cells (giardiasis) Worms attack certain tissues or organs and compete with host for nutrients (schistosomiasis) Agents Of Infection Bacteria Release enzymes to digest body cell or create toxins Bacterial Diseases: tuberculosis, scarlet fever, gonorrhea, diphtheria, tetanus Four Vectors That Spread Infections Vector Method 1. People Touch, sexual contact, in air Animals & 2. Insects Touch, ingestion, and bites 3. Food Eating infected food 4. Water Inadequate water purification Process of Infection Prodromal Period • Time between invasion and symptoms Incubation • Highly contagious • Illness surfaces • Body’s forces gain advantage • Destroys invader and heals Recovery Role Of Immune System In Infection Increased blood supply brings oxygen & nutrients White Blood Cells Invader reaches bloodstream Inflammation Make antibodies Systemic Disease Attempt to kill invader B Cells T Cells Immune System’s Role In Infection Fight infection and clean up Allergies Are An Immune Disorder Defined Immune Process Hypersensitivity to substance in environment or diet Reacts as if defending against germ Creates IgE antibody to substance IgE causes histamine release when substance is encountered Oral medication Treatment Nasal spray Immunotherapy Autoimmune Disorders Immune Process Impact Immune system attacks body’s cells, tissues or organs Affect 3 times as many women as men Top 10 killer and disabler of Americans Addison’s disease Examples Crohn’s disease Lupus erythematosus Multiple sclerosis Prevention of Cold 1. Avoid people with colds Sneeze and cough into tissue, then throw 2. it away 3. Clean surfaces with disinfectant 4. Don’t touch nose, eyes or mouth 5. Wash hands often with soap and water 6. Dry hands thoroughly Prevention of Influenza 1. Get vaccinated 2. Reduce time in crowded settings 3. Improve airflow in living space 4. Do not share eating dishes and utensils 5. Wash hands often with soap and water 6. Avoid touching your eyes, nose or mouth 7. Stay in good general health Meningitis Disease Attacks membranes around brain and spinal cord Droplet transmission Transmitted Sharing drinks, silverware, cigarettes, kissing, sneezing, coughing Vaccine protects against 4 of 5 strains Treatment If disease is contracted, emergency medical care required Hepatitis A, B and C Disease Attacks the liver A – poor sanitation B – blood and bodily fluids incl. sweat Transmitted C – blood, illegal drug use, tattoos, body piercings Interferon for Hepatitis C Treatment Rest and high protein diet Avoidance of alcohol and drugs that stress liver Mononucleosis and Epstein-Barr Virus Disease Virus in herpes family; Epstein-Barr can cause mononucleosis in adolescents or young adulthood Transmitted Kissing or other close contact Rest as needed Treatment Avoid physical activity that could rupture the spleen Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Disease Complex disorder causing profound fatigue that does not improve with bed rest and may get worse with activity No known cure Treatment Combination of therapies can relieve symptoms Herpes Gladiatorum Disease Cluster of blisters on face, trunk or extremities Skin to skin contact Transmitted Most common among wrestlers, judo players No treatment Treatment Avoid contact with others when lesions are present Group A and B Strep Infection Disease Sore throat Antibiotics Untreated infection can cause rheumatic fever Treatment Untreated strep infection can cause shock syndrome requiring emergency medical treatment Toxic Shock Syndrome Disease Associated with use of tampons. Caused by staph and strep bacteria releasing toxins into bloodstream Antibiotics If shock occurs: Treatment • Hospitalization • IV fluids and medications to raise blood pressure • Powerful antibiotics MRSA—The Superbug Disease Bacterial infection resistant to antibiotics methicillin and penicillin Enter body through scrape, burn or Transmitted surgical incision Through touch Treatment Appropriate antibiotics Insect- and Animal-Borne Infections Lyme Disease West Nile Virus Avian Influenza Spread through ticks Treated with antibiotics Spread by infected mosquito No specific treatment Virus spread from bird to human through contact No specific treatment SARS Virus Disease Acute respiratory syndrome often resulting in pneumonia Close face-to-face contact Transmitted Droplet from cough or sneeze Treatment No specific treatment Disease Spread Through Bioterrorism Anthrax Small Pox Spread through exposure to spores Inoculation prevents infection No treatment Muscle paralyzing disease Botulism Treatment is anti-toxin Spread through blood or body fluids Tularemia of infected animal, bite of infected animal, contaminated water or air Common Reproductive Tract Infections Bacterial Vaginitis Spread through sexual contact Treatment is antibiotic Spread through sexual contact Yeast Infection Also caused by chemical imbalance of vagina Treatment is antifungal medication Trichomoniasis Spread through sexual contact Treatment is antibiotic Urinary Tract Infections Usually caused by bacteria Disease Untreated, can lead to bladder or kidney infection and failure Pregnancy Bike riding Bubble bath, douches, diaphragm Risk Factors Urinary stones Enlargement of prostate Vaginitis Treatment Antibiotics Tips to Protect Your Health • WASH YOUR HANDS!!!! • SNEEZE INTO YOUR ELBOW OR USE A TISSUE • DON’T COME TO SCHOOL OR GO TO WORK WHEN SICK • DON’T SHARE THINGS Ted Talk Nathan Wolfe: The jungle search for viruses http://www.ted.com/talks/nathan_wolfe_hunts_for _the_next_aids.html