* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8533034_CT
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
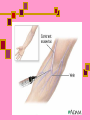
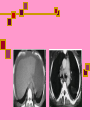
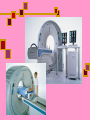
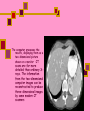
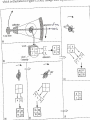
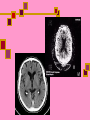
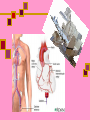
Computed Tomography (CT) & CT Angiography Maral Asmani 8533034 Computed tomographyWhat is it?! Computed Tomography (CT), more commonly known as a CAT scan, is a form of medical diagnostic imaging Joining separate images into one 3-D of graphical cross-section Using X-rays beams that pass through the body to measure how different tissues absorb different amounts of radiation Computed Tomography is commonly used in cancer, cardiovascular disease, infectious disease, trauma and musculoskeletal disorders diagnosis and treatment Computed Tomography as a diagnostic imaging tool has huge potential due to its ability to provide painless, quick and detailed internal images of the body History Tomography is from the Greek word "tomos" meaning "slice" or "section" and graphia meaning "describing". CT was invented in 1972 by British engineer Godfrey Hounsfield of EMI Laboratories, England and by South Africa-born physicist Allan Cormack of Tufts University, Massachusetts. Hounsfield and Cormack were later awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for their contributions to medicine and science. The first clinical CT scanners were installed between 1974 and 1976. The original systems were dedicated to head imaging only, but "whole body" systems with larger patient openings became available in 1976. CT became widely available by about 1980. There are now about 6,000 CT scanners installed in the U.S. and about 30,000 installed worldwide. What are some common uses of the procedure? one of the best tools for studying the chest and abdomen invaluable in diagnosing and treating spinal problems and injuries to the hands, feet and other skeletal structures measure bone mineral density for the detection of osteoporosis quickly identify injuries to the liver, spleen, kidneys or other internal organs in cases of trauma CT scanning can also be used to guide biopsies How should I prepare for the CAT scan? given a gown to wear during the procedure Metal objects including jewelry, eyeglasses, dentures and hairpins may affect the CT images You may be asked not to eat or drink anything for several hours beforehand, especially if a contrast material will be used in your exam Also inform your doctor of any recent illnesses or other medical conditions Women should always inform their physician or technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant Contrast Material They will be given a drink containing gastrografin, an aniseed flavored X-ray dye, 45 minutes before the procedure. This makes the intestines easier to see on the pictures. Sometimes a liquid X-ray dye is injected into the veins during the test. This also makes it easier to see the organs, blood vessels or, for example, a tumor. The injection might be a little uncomfortable, and some people also experience a feeling of warmth in their arm What does the equipment look like? The CT scanner is typically a large machine with a hole, or tunnel, in the center. A moveable examination table slides into and out of this tunnel. In the center of the machine, the x-ray tube and electronic x-ray detectors are located opposite each other on a ring, called a gantry, which rotates around you. The computer that processes the imaging information and monitor are located in a separate room How does a CT scanner work? The X-rays from the beams are detected after they have passed through the body and their strength is measured. Beams that have passed through less dense tissue such as the lungs will be stronger, whereas beams that have passed through denser tissue such as bone will be weaker. A computer can use this information to work out the relative density of the tissues examined. Each set of measurements made by the scanner is, in effect, a cross-section through the body. The computer processes the results, displaying them as a two-dimensional picture shown on a monitor , CT scans are far more detailed than ordinary Xrays. The information from the two-dimensional computer images can be reconstructed to produce three-dimensional images by some modern CT scanners Is a CT scan dangerous? Far more X-rays are involved in a CT scan than in ordinary X-rays, so doctors do not recommend CT scans without a good medical reason. Some patients may experience side effects due to allergic reactions to the liquid dye injected into the veins. In very rare cases, this dye has been known to damage already weakened kidneys. It is important to let the Xray doctors or technicians know if you have any allergies, asthma or kidney trouble, prior to having the X-ray dye injected. Limitations! Not all diseases and medical conditions can be identified by a CT scan. For example, hypertension and diabetes must be tested by blood pressure and blood sugar analysis, respectively. For this reason, CT scans are ineffective as “general check-up” methods and should only be used when a specific condition in a specific region of the body is suspected. CT Heart Scan CT heart scans give doctors a 3-dimensional visual image that provides doctors with detailed information about: heart disease heart disease risk of arterial blockage presence of coronary artery aneurysms Coronary Artery Disease the coronary arteries are responsible for supplying the heart with the necessary amount of oxygen and nutrients. Coronary artery disease occurs when these vessels narrow. Over time, the plaque builds. New cholesterol and fatty deposits surround the existing plaque. Eventually, the arteries harden, leading to a condition called atherosclerosis, Coronary atherosclerosis often has no symptoms, so heart attacks and death may occur suddenly, with little or no warning. plaque buildup narrows the vessel and restricts the flow of blood to the heart. In some cases, the plaque buildup completely blocks the artery. The reduced blood flow means less oxygen goes to the heart. This lack of oxygen can lead to: angina pectoris (Heart pain) myocardial infraction (heart attack) Ways Of Diagnosis….. Unfortunately, it can be difficult for doctors to detect blocked heart arteries. They are small structures in constant motion, and do not appear on x-ray images or regular ultrasound techniques. Doctors typically “guess” the existence of atherosclerosis by assesing risk factors in a patient. Risk factors for atherosclerosis include: Cigarette smoking High cholesterol Diabetes Age (women over 55; men over 45) Family history of heart disease Obesity Other tests exist to predict the existence of blocked arteries, but these tests are not ideal,such tests cannot detect blockages in their earliest stages, when they can still be treated.for example, Resting electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) Signal-averaged electrocardiogram (SAECG) Chest X-ray EB Angiography Exercise stress test ............... Angiography…. Angiography is performed using: x-rays with catheters computed tomography (CT) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Angiography With catheter… Coronary angiography is an X-ray examination of the blood vessels or chambers of the heart. A very small tube (catheter) is inserted into a blood vessel in your upper thigh (groin area) or arm. The tip of the tube is positioned either in the heart or at the beginning of the arteries supplying the heart, and a special fluid (called a contrast medium or dye) is injected. This fluid is visible by X-ray, and the pictures that are obtained are called angiograms. Another name for this test is coronary arteriography. CT Angiography…… A small dose of contrast material may be injected through the IV to determine how long it takes to reach the area under study. Next, the table will then move quickly through the scanner to determine the correct starting position for the scans and a test image will be taken. The table will then move slowly through the machine as the actual CT scanning is performed. As the images are being recorded, an automatic injector machine connected to the IV will continue to inject contrast material at a controlled rate. When the contrast dye is used to visualize veins, the study is called a venogram, and when it is used to visualize arteries, it is known as an arteriogram. How does it compare to standard angiography? With regular angiography, a needle puncture is placed in the groin and contrast material is injected. CT angiography does not require the use of a large vessel for injection and is an outpatient procedure. The complication rates (bleeding, hematoma, emboli) after angiogram are higher compared to CT angiography. Physicians use the procedure to: detect atherosclerosis disease in the carotid artery, Aorta…. detect thrombosis (clots) in veins Detect embolism in pulmonary identify a small aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation…… Benefits of a CT Heart Scan Fast Painless Non-invasive Can detect the buildup of arterial plaque in its early stages, while it is still treatable Sources: www.americaheart.org www.ctcardiac.com www.radiologyinfo.com www.lifescanuk.org.uk www.medscape.com www.patient.co.uk