* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
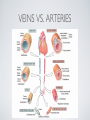
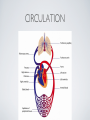
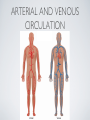
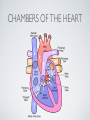
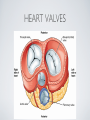
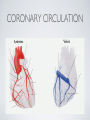
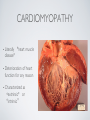
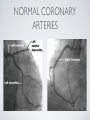
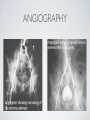
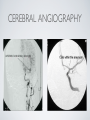
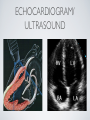
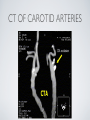
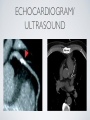
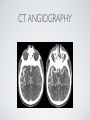
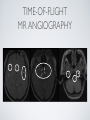
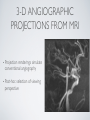
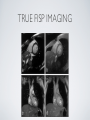
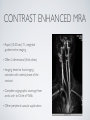
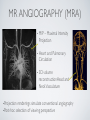
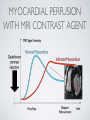
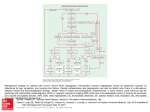
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM BMP 218 November 25, 2014 IMAGING RESOURCE http://www.yale.edu/imaging/ CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE • #1 killer of men and women in the United States • Causes one death every 34 seconds • Causes one death/minute in women (more than uterine or breast cancer) • Kills more Americans than the next 5 leading causes of death combined • Prevalence: • 50 million with hypertension • 13.2 • 5 million with coronary heart disease million with heart failure • 4.8 million with stroke CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM • Organs and tissues which circulate blood throughout the body • Consists of: • Blood • Blood • Heart vessels BLOOD • Only tissue which flows throughout body • Carries • Takes • Essential oxygen & nutrients to body cells waste products back to lungs, kidneys, and liver for disposal part of the immune system • Necessary for fluid & temperature balance • Transports hormonal messages BLOOD CHARACTERISTICS • Fluid = plasma (yellow color) • Components • • Red blood cells (which make blood look red) • White blood cells (fight infection) • Platelets (clotting) Debris (cell fragments, bacteria, etc.) BLOOD VESSELS • Tubes which carry blood through the body • Blood should flow in only ONE DIRECTION • Three types: • Arteries • Veins • Capillaries ARTERIES • Carry blood AWAY from the heart • Thick, muscular walls • NO • Do VALVES NOT have to contain oxygenated blood VEINS • Carry • Thin blood TOWARD the heart walls (little muscle) • HAVE • May VALVES contain oxygenated blood CAPILLARIES • Direct transfer between cells and blood • One-cell thickness between parallel capillaries VEINS VS. ARTERIES ARTERIES • Arteries are covered with a muscle layer • Artery expands as the heart pushes blood • Artery recoils when heart is relaxed • helps • These to keep blood moving features are • measured • can as BLOOD PRESSURE be felt as a PULSE BLOOD PRESSURE • Definition: the pressure of the circulating blood against the walls of the blood vessels • Two systemic blood pressure numbers: • Systolic (when ventricles contract – first #) • • When pulsatile arterial pressure > cuff pressure -> “whoosh” sound with each beat Diastolic (when ventricles relax – second #) • When (continuous) arterial pressure > cuff pressure -> loss of “whoosh” sound VEINS • Little muscle • Blood easily slowed/stopped CIRCULATION ARTERIAL AND VENOUS CIRCULATION HEART • Primary “pump” or ”engine” for the cardiovascular system • Meeting point for the 2 circulatory systems • Right • Left • Has side of heart (pulmonary) side of heart (systemic) both ELECTRICAL and MECHANICAL activity • Electrical activity MUST precede mechanical activity CHAMBERS OF THE HEART HEART VALVES LISTENING TO THE HEART • Closure of the heart valves causes the “lub-dub” sound of the heart • “Lub” • closure • “Dub” • closure (S1 = first heart sound) of mitral and tricuspid valves (S2 = second heart sound) of aortic and pulmonic valves ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION ELECTROCARDIOGRAM CORONARY CIRCULATION CARDIOVASCULAR TESTING • Needs to detect: • • Blood flow abnormalities • peripheral vascular disease (e.g. stroke) • coronary artery disease (e.g. acute myocardial infarction) Structural abnormalities • Cardiomyopathy • Valve problems • Blood clots CARDIOMYOPATHY • Literally “heart muscle disease” • Deterioration of heart function for any reason • Characterized as “extrinsic” or “intrinsic” CARDIOMYOPATHY • Extrinsic Intrinsic • Primary • Primary • most • Drug pathology OUTSIDE the heart often ischemia pathology INSIDE the heart or alcohol toxicity • Infection • Genetic CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING • Radiography • X-ray Angiography (with contrast) • Echocardiography/Ultrasound • Computed Tomography • Electron-Beam • Spiral • MRI CT CT (EBCT) RADIOGRAPHY CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION/ ANGIOGRAPHY • Visualization of arteries/veins via injection of a contrast into the artery/vein of interest • Uses fluoroscopy to obtain images CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY NORMAL CORONARY ARTERIES ANGIOGRAPHY CEREBRAL ANGIOGRAPHY ECHOCARDIOGRAM/ ULTRASOUND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT) • • Spiral (helical) CT • spiral shape of path of x-ray beam during scanning • faster than standard CT • desirable for vascular studies Electron beam tomography (EBCT) • • No moving parts – even faster Usually uses dynamic imaging contrast with contrast • “CT Angiography (CTA)” CT OF CAROTID ARTERIES ECHOCARDIOGRAM/ ULTRASOUND CT ANGIOGRAPHY TIME-OF-FLIGHT MR ANGIOGRAPHY • TOF-MRA • Stationary uses heavily T1-weighted 3D gradient echo MRI spins become “saturated” from repeated pulsing at TR < T1 • Stationary • Blood spins produce hypointense signal flow washes fresh unsaturated spins into the imaging volume TIME-OF-FLIGHT MR ANGIOGRAPHY 3-D ANGIOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS FROM MRI • Projection renderings simulate conventional angiography • Post-hoc selection of viewing perspective TRUE FISP IMAGING HEART CINEMATIC STUDIES MRI CONTRAST REAGENTS AND T1 • Typical contrast reagents are chelates of metals ions having unpaired electron spins • Water molecules must “touch” the agent to enhance T1 relaxation • Molecular structure causes agent to (mostly) stay within vascular system • Large signal enhancement in vascular system CONTRAST ENHANCED MRA • Rapid (10-20 sec) T1-weighted gradient echo imaging • Often 2 dimensional (thick slices) • Imaging timed so that imaging coincides with arterial phase of the contrast • Complete angiographic coverage from arotic arch to Circle of Willis • Other peripheral vascular applications MR ANGIOGRAPHY (MRA) • MIP – Maximal Intensity Projection • Heart and Pulmonary Circulation • 3D volume reconstructionHead and Neck Vasculature • Projection renderings simulate conventional • Post-hoc selection of viewing perspective angiography MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION WITH MRI CONTRAST AGENT