* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Procedure - El Camino College
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
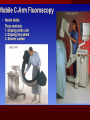
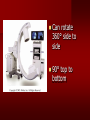
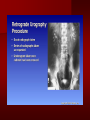
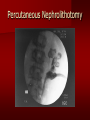
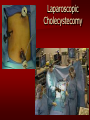
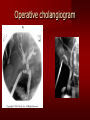
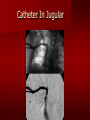
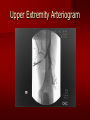
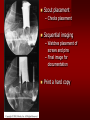
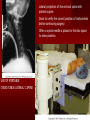
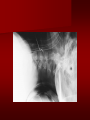
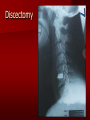
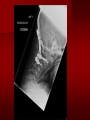
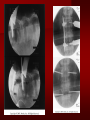
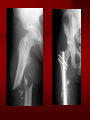
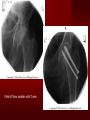
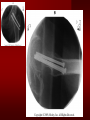
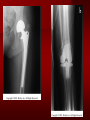
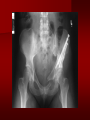
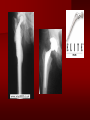
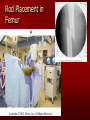
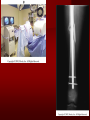
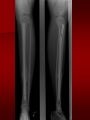
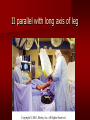
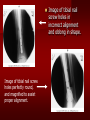
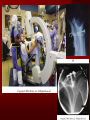
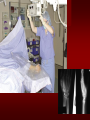
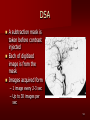
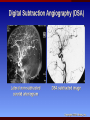
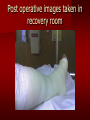
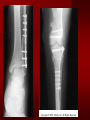
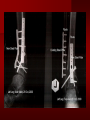
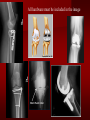
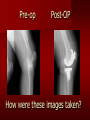
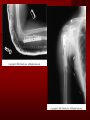
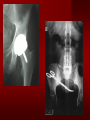
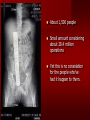
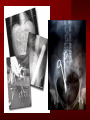
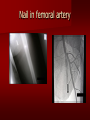
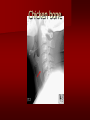
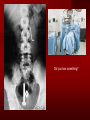
PORTABLE OR applications and Considerations Week 13 RTEC 124 CAUTION: SOME IMAGES MAY BE DISTURBING BUT AS HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS THIS IS WHAT YOU MAY EXPERIENCE Who are these people? Importance of maintaining a sterile field…. Your role as an RT STERILE IN OR Must change clothing Wear a “cover gown” when leaving Masks, hair cover, and shoe covers Change when you leave the OR room DO NOT TAKE HOSP SCRUBS HOME!! The Operating Room Team…you are part of it! What to expect… From your point of view do not touch sterile field Surgical Radiography Imaging is commonly used in surgical procedures But the surgeon already has the patient’s body open, right? Sometimes it is used as a guide Must cover equipment in sterile drapes when it may come into contact with patient , instruments, or surgeons hands Sterile trays The sterile incision covered for portable Instruments away from portable Never use portable over sterile field USE CAUTION! Exchange the IR into the sterile drape SURGERY Sterile procedures must be followed – Not to contaminate surgical site – Don’t touch anything BLUE or GREEN – Be careful not to run into trays, etc IMAGING IN THE OR Moblie Radiographic Mobile C-arm – fluoroscopic Dedicated room – Cystography – Radiography room UNLIKE PORTABLE EXAMS ON THE UNITS Equipment in the OR must be covered – Must be cleaned before bringing into room Protects patient – Prevents contamination of sterile field and instruments C- ARM Mobile Fluoro Can rotate 360° side to side 90° top to bottom C-Arm FLUOROSCOPY Tube at one end and I.I. at other end TV Monitor control cart separate from unit Uses Digital Fluoroscopy Last Image Hold Image Enhancement Save for hard copies from disk and video Photographic Magnification Subtraction Static (pulsed) and continuous fluoroscopy Set up room in advance if possible Fluoroscan Hand surgery table Never use IR as a table – Blood – Fluids – Water Some tables have a gap – Allows for cassette placement without contaminating sterile field Tables without gap Slide cassette at top with help of anesthesiologist Considerations before procedure Find out where surgeon wants you to go Be careful not to contaminate Plug in C-arm and test it – Marker check on II if possible – Guard FOOT Switch Park portable equipment in corner –out of the way Orient anatomy using markers Mobile Radiography Considerations If surgery is already in progress – Before entering, park machine outside of room – Survey room to get lay-out – Rearrange equipment/furniture if necessary Place cassette in a STERILE WRAP PATIENT CONSIDERATIONS DURING SURGERY Patient may not always be “unconscious” – Pain management – Twilight state Always treat patient with respect and courtesy – They may be hearing everything USING C-ARM vs PORTABLE C-ARM Faster- instant image More radiation Portable Must have accurate technique Processing needed – Longer Smaller field of view Larger field of view Various Imaging Procedure in Operating Room SURGERY - Common Procedures Ortho (Bone) Work Pinning/ Rod / Screw placement Fracture realignment Organs / Vessels with contrast Arteries / Veins in the extremities Cholangiograms = ducts Urography Pacemaker and Line Placements etc TECHNIQUE CONSIDERATIONS Same principles of ALARA Change techniques if using grid – 3-5 times more if using grid – Body parts larger than 12cm SID – – VERY IMPORTANT TO MEASURE – Chest usually done at 63-72” – All others done at 40” DEDICATED UNIT- CYSTO RM Cystoscopic Studies for Foreign Objects Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Laparoscopic Cholecystecomy . Be careful not to hit laparoscopic instruments Cholangiogram – Sterile lead drape used – Contrast used Operative cholangiogram Op CHOLE Digital can reverse images Hickman Catheter placement Starts at upper thorax and ends in heart Catheter In Jugular Upper Extremity Arteriogram Bypass Surgery Cervical Spine Shoulder pull down Boost mode Magnification mode HIGHER DOSE Scout placement – Checks placement Sequential imaging – Watches placement of screws and pins – Final image for documentation Print a hard copy Lateral projection of the cervical spine with patient supine. Done to verify the correct position of instruments before continuing surgery. Often a spinal needle is placed in the disc space to show position. USE OF PORTABLE CROSS TABLE LATERAL C.SPINE Discectomy Lateral Lumbar Drape C-arm with sterile plastic conver to protect patient and equipment PA Lumbar AP or PA to lateral – Caution not to hit patient or equipment – KEEP STERILE Familiarize yourself with locks – PRACTICE WITH CI, RT’S X-table Lateral Lumbar Spine Challenges ? Positioning CR ? Hip Pinning Lateral Hip Field of View smaller with C-arm Rod Placement in Femur II parallel with long axis of leg Image of tibial nail screw holes perfectly round, and magnified to assist proper alignment. Image of tibial nail screw holes in incorrect alignment and oblong in shape. Image of tibial nail screw holes perfectly round, and magnified to assist proper alignment. Image of tibial nail screw holes in incorrect alignment and oblong in shape. NOTE THE POSITION OF THE II AND TUBE KEEP II CLOSE TO PATIENT KEEP TUBE AS FAR AWAY AS POSSIBLE MUST BE AT LEAST ________ INCHES FROM PT DSA A subtraction mask is taken before contrast injected Each of digitized image is from the mask Images acquired form – 1 image every 2-3 sec – Up to 30 images per sec 91 Three Dimensional (3-D) Intraarterial Angiography 92 RAD PROTECTION in the O.R. It’s your duty to protect the patient, yourself and others (healthcare professional) Politely ask whoever can, to move back from the area Provide aprons to those who cannot leave Announce your intent to make an exposure and give time for others to move back IF personnel are in sterile drape – may not be able to put on apron RAD PROTECTION in the OR C-ARM = HIGHER DOSE STAND BEHIND C-ARM UNIT WHEN POSSIBLE RAD PROTECTION RULES OF GOOD PRACTICE Never place your hand or other body part in primary beam Provide gonadal protection for the patient if possible FOR C-ARM – IF BEAM FROM BELOW – PLACE APRON ON TABLE BEFORE PATIENT IS ON TABLE Achieve maximum distance from the patient and tube (stand 90° from the patient) Minimum 6 foot exposure cord for radiography Label and handle cassettes carefully RADIATION PROTECTION Remember the “Cardinal Rules” RADIOGRAPHIC 6 ‘ exposure cord Minimum source to skin distance = 12” Preferred SID of 40”to 72”+ ( mag detail) Distance from tube and patient At least .25mm lead apron FLUOROSCOPIC Minimum source to skin distance = 12” Preferred SSD OF 18” Distance from tube and patient 5 min Audible Alarm At least .25mm lead apron to be worn 5 R/min - 10 R/min Post operative Portables Post operative images taken in recovery room All hardware must be included in the image Pre-op Post-OP How were these images taken? The Recovery Room and good Radiation Safety Practices Medical errors & Foreign Bodies How to avoid them Medical errors & imaging IT STARTS WITH YOU •CORRECT MARKER •On the correct side of the patients body There are many Opportunities For mistakes And safeguards to Prevent medical errors About 1,500 people Small amount considering about 28.4 million operations Yet this is no consolation for the people who've had it happen to them. Sponges Most common Sponges fill up with blood and can resemble parts of the body Common medical devices left inside patients Eyebrow Tweezer Tissue expander Retractor Syringe Purple Latex Gloves Sharpie Speculum Mouth gag, Hemostat Chest Spreader Nail in femoral artery Chicken bone Did you lose something? A few more examples of OR Peds images www.hawaii.edu/medicine/pediatrics Don’t get yourself in trouble… Portable and Mobile Competencies YOU MUST ALWAYS HAVE SUPERVISION EVEN AFTER COMPETENCY IS DONE per JRCERT DO NOT PUT YOURSELF IN A SITUATION WHERE YOU DO NOT HAVE APPROIATE SUPERVISION ! OR / PORT COMPS Still need direct supervisioneven after you have a competency Must have “DIRECT” supervision for portables and C-arm at ALL times PORTABLE & C- ARM COMPETENCIES Must first C- do a Pre-Portable check –off Arm check off Must do more than 3 exams of each area – portable – before attempting competency ?