* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
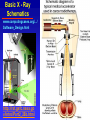
Density Labels: X-ray & Ultrasound While Mass Spectroscopy is not covered in our texts, other mass/density dependent technologies including X-ray Spectroscopy, Gamma Spectroscopy, & Ultrasound Analysis are covered in Guy & ffytche, An Introduction to The Principles of Medical Imaging, Imperial College Press, 2000, Chapters 4,5 & 7. Other coverage is also found in Shung, Chapters 1, X-ray, & 2, Ultrasound, in Shung, Smith, Tsui, Principles of Medical Imaging, Academic Press, 1992. X- ray Here a collimated beam of X-rays generated by a radioactive or electronically excited filament source is used to probe the density of objects placed between the source & a detector (film, fluorescent screen, storage phosphor, photodiode array). Absorbance of the x-ray energy by the medium or reflection or refraction of the beam will alter the exposure of the detector. Distance of the detector from the source will limit detector exposure, so object thickness decreases beam strength automatically. Internal reflections “fuzz” the sample image. Imaging improvements help correct such abberation. Reconstruction of images requires Fourier & triangulation deconvolution as in MRI. Heavy atoms yield higher X- ray absorbances than light atoms so they can be used as opaque markers or “contrast agents.” Basic X - Ray Schematics www.computingcases.org/.../ Software_Design.html http://rst.gsfc.nasa.go v/Intro/Part2_26b.html X-ray Basics & Theory Principles of Radiography: www.kodak.com/.../kpro/radiography/ W37_03.shtml http://learntech.uwe.ac.uk/radiography/RScience/imaging _principles_d/diagimage1.htm www.thejcdp.com/.../williamson/ 03williamson.htm Atomic physics principles: www.hmi.de/people/schiwietz/ links.html History of radiology: www.xray.hmc.psu.edu/ rci/ss9/ss9_15.html Digital X-ray background: www.gemedicalsystems.com/.../ dig_xray_intro.html Medical Imaging: www.csmt.ewu.edu/csmt/phys/ bhouser/medim.htm www.qdixray.com.au/ GeneralXray.htm astro.ocis.temple.edu/.../ PrinRad1.htm X-ray crystallographic technology: www.chemistry.ucsc.edu/.../ chem200a/schedule.html sharp-world.com/corporate/ news/030930-2.html Validation Issues Calibration for accuracy, sensitivity, precision & specificity requires examination of phantoms, objects, or crystals with known composition, architecture & structure. Imaging may be limited by the amount of time a subject can be exposed without doing damage by exposing them/it to xray bombardment. Most modern techniques have attempted to minimize exposures by maximizing the information collected in a given time. Flat panel electronics & digitizing approaches have helped as have the use of highly dense contrast agents. But computer analysis of image data combined with Fourier transform techniques have greatly speeded the process & made it safer. It is now possible to do computed tomographic imaging to high resolutions. www.aps.anl.gov/ald/grafgal2/ digital/reserch.htm X-ray Contrast Media: http://www.xray2000.f9.co.uk/Site3/contrast_media/contrast _media_introduction.htm www.amershamhealth.com/medcyclopaedia/ Volume%... www.ferringfertility.com/.../ uterine.htm More Advanced Treatments of X-ray Computed Tomography: rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/Intro/ Part2_26c.html Radiology & Ultrasonography links: www.nyerrn.com/ x/xray.htm Ultrasound This method uses piezoelectric transducers to produce ultrasonic pulses that reflect & refract off structures in the beam path. The amount of wave energy absorption, the reflection angles, & the distance from the transducer to the tissue & back to the probe determine the amount & location of the energy delivered back to the probe. The perceived energy & direction is delivered to the instrument electronics & displayed as an image. Soft tissues with contrasting contents of water & fat are well imaged by this technique. Contrast agents for ultrasound incorporate small bubbles that introduce air (gas) into the imaged system. Ultrasound Basics & Theory Ultrasound Basics & Theory: http://www.drgdiaz.com/intro.shtml www.cyberphysics.pwp.blueyonder.co.uk/ topics/... www.stfx.ca/.../teachersworkshops/ sld038.htm Ultrasound in obstetrics: www.ob-ultrasound.net/ Ultrasonography in ophthalmology www.jhu.edu/wctb/coms/ patient/echo/echo.htm Carotid Artery Plaque and 3D Ultrasound Ulf Schminke, MD; Christof Kessler, MD; Lillian Motsch, MD; Lutz Hilker, MD Neurosonology Lab, Dept. of Neurology, Ernst Moritz Arndt University Greifswald, Greifswald, Germany More Advanced Treatments of Ultrasound A simple quiz: mark.asci.ncsu.edu/.../rtu/ rtuquiz/rtuquizc.htm 3D Reconstruction & validation: www.fac.org.ar/.../stroke/ schminke/sld004.htm Ultrasonography of the thyroid: http://www.thyroidmanager.org/ FunctionTests/ultra-frame.htm Ultrasound contrast agents: www.ultrasonic.meng.ucl.ac.uk/ mbubble.html Harmonic imaging: www.medison.com/english/ pd/pd_07a.asp