* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circulatory System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
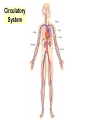
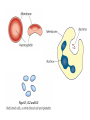
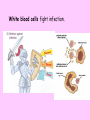
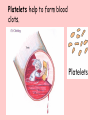
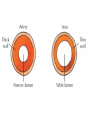
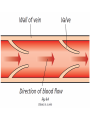
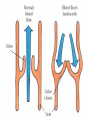
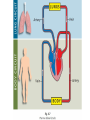
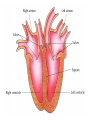
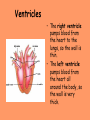
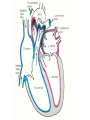
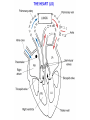
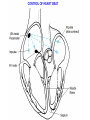
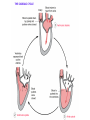
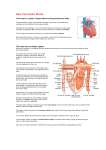
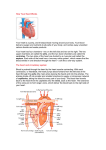
The Circulatory System Circulatory System Structure of Blood Blood is made of: • Plasma • Red blood cells • White blood cells • platelets 3 Types of Blood Cell Plasma is the liquid part of blood and it transports chemicals (e.g. food, hormones, carbon dioxide, salts and urea) and heat around the body. Red blood cells contain a red pigment called haemoglobin which transports oxygen around the body. White blood cells fight infection. Platelets help to form blood clots. Functions of the Blood Transports chemicals such as food, wastes, and hormones Maintains body temperature Transports oxygen Fights infection Forms blood clots Blood Vessels Arteries • Arteries carry blood away from the heart • They have a strong flow of blood that is under high pressure • The walls are strong and thick • They have no valves Veins • Veins carry blood to the heart • The blood flow or pressure is low • They have thinner, weaker walls • They have valves • Capillaries are tiny blood vessels • They connect arteries to veins • Their walls are very thin • They allow materials to pass in and out of the blood stream Capillaries Arteries and Veins. The arteries and veins carry the blood through the heart and all the organs of the body. The Heart The heart pumps blood around the body. Structure of the Heart •The heart contains four chambers. •The top two are the right and left atrium. •The bottom two are the right and left ventricle. • The heart is made of Cardiac Muscle which never gets tired. It is supplied with oxygen rich blood from the coronary artery Ventricles • The right ventricle pumps blood from the heart to the lungs, so the wall is thin. • The left ventricle pumps blood from the heart all around the body, so the wall is very thick. Blood Vessels of Heart •Vena cava – bring blood from body to right hand side of heart. •Pulmonary artery - bring blood from right hand side of heart to lungs. •Pulmonary vein – brings blood to left hand side of heart from lungs. •Aorta brings blood from left hand side of heart to body. • Oxygenated blood: Is blood in which oxygen is attached to the haemoglobin molecules in the red blood cells. It is bright red because the attached oxygen makes the normally blue haemoglobin molecules turn red. • Deoxygenated blood: When blood has delivered oxygen to the cells, it is described as deoxygenated. It now looks a very dark red because so many of the haemoglobin molecules have turned blue again. The mixture of blue and red molecules looks dark red to our eyes. Heartbeat •At rest the average rate of an adult’s heartbeat is 70 beats per minute (b.p.m.). •Each heartbeat causes a pulse of blood in the arteries. •Exercise, stress, excitement and smoking can increase the heartbeat. Exp: To demonstrate the effect of exercise on the rate of `breathing Method: 1. Count your breaths per minute at rest. 2. Repeat step one three times, get an average reading. 3. Exercise vigorously for two mintues. 4. Immediately after exercising count the breaths per minute. 5. Continue to record the breaths per minute until it returns to the average resting rate. Results: Conclusion: Exercise and the Heartbeat • When we exercise the cells in the body need more food and oxygen. • The cells also need to get rid of carbon dioxide and heat. • This causes the heart to beat faster and our pulse rate increases. 1 Exercise • It increases not only the muscles of the arms and legs but also the muscles of the heart. • It reduces weight. • A good balance between exercise and rest is needed for a health heart and lungs. Body Temperature • The normal temperature of the human body is 37 °C. • When we are ill our body temperature may rise, this helps to destroy the bacteria and viruses that cause us to become ill.