* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arrythmia 411
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
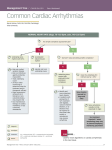
Cardiac Arrhythmias Dr. Ahmad Hersi Myocardium Muscle Action Potential Action Potential of a Myocardial Cell +25 1 Overshoot +10 mv Corresponding ECG Overlay 0 2 -25 -50 0 Active Transport Na+ out K+ back in -75 Resting Potential - 90 mv -100 4 RRP ARP K+ Na+ Ca++ SNP Normal Cardiac Cycle Systole Diastole Electrical Depolarization “activate” Repolarization “recovery” Mechanical Contract “empty” Relax “fill” What does it tell us? • • • • the electrical conduction through the heart areas of ischemia or myocardial damage LV Hypertrophy electrolyte disturbances / drug toxicity The Electrical System of the Heart SA Node AV Node Bundle of HIS Right Bundle Branch Inter- nodal Tracts Left Bundle Branch Anterior Superior Fascicle Posterior Inferior Fascicle Septal Depolarization Fibers Purkinjie Fibers Conduction System of the Heart: A Conceptual Model for Illustration SA Node Inter-nodal Tract Left Bundle Branch AV Node Bundle of HIS James Fibers Right Bundle Branch Bundle of Kent Septal Depolarization Fibers Anterior Superior Fascicle Posterior Inferior Fascicle SA SA Node – “pacemaker” of Node the heart (60-100bpm) AV Node AV Node – junction of the atria and ventricles (40-60bpm) Bundles – Bundle of His connects the AV node to the bundle branches (20-40bpm) Bundle of HIS Inter- nodal Tracts What Is In Each Beat? (the cardiac cycle in waves, complexes, and intervals) • P Wave – atrial contraction or depolarization, (usually upright) • QRS Complex – time for ventricular contraction or depolarization (usually upright) (0.04 - 0.12sec) (delays in the bundle branches will widen the QRS) • T Wave – ventricular repolarization “recharging” (usually upright) • PR Interval – time between atrial depolarization to ventricular depolarization (beginning of P wave to beginning of QRS)(0.12 - 0.20sec) (prolonged PR = delays in the AV node conduction) • QT Interval – represents one complete ventricular depolarization and repolarization (beginning of QRS to the end of the T wave) (0.32 – 0.44sec) (disturbances are usually due to electrolyte disturbances or drug effects) The ECG Complex with Interval and Segment Measurements ECG Paper and related Heart Rate & Voltage Computations Memor ize Reading a Rhythm Strip What Do I Look For? ► Regularity - What is the R – R Interval? ► Rate - Is the rate normal (60-100), slow, or fast? ***Six-second strip method - (30 big boxes) & multiply times ten ► P Wave – Is there a P wave before every QRS? Is it upright? ► QRS Complex – Is there a normal QRS complex following each P wave? Wide or normal? ► T wave – How does your T wave look? Upright? ► Measure your intervals – PR Interval, QRS, QT Pacemakers of the Heart • SA Node - Dominant pacemaker with an intrinsic rate of 60 - 100 beats/minute. • AV Node - Back-up pacemaker with an intrinsic rate of 40 - 60 beats/minute. • Ventricular cells - Back-up pacemaker with an intrinsic rate of 20 - 45 bpm. Tehran Arrhythmia Center Rhythm Analysis • • • • • Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Step 4: Step 5: Calculate rate. Determine regularity. Assess the P waves. Determine PR interval. Determine QRS duration. Tehran Arrhythmia Center Step 1: Calculate Rate 3 sec 3 sec Option 1 – Count the # of R waves in a 6 second rhythm strip, then multiply by 10. Interpretation? 9 x 10 = 90 bpm Tehran Arrhythmia Center Step 1: Calculate Rate R wave • Option 2 – Find a R wave that lands on a bold line. – Count the # of large boxes to the next R wave. If the second R wave is 1 large box away the rate is 300, 2 boxes - 150, 3 boxes - 100, 4 boxes - 75, etc. (cont) Tehran Arrhythmia Center Step 1: Calculate Rate 3 1 1 0 5 0 7 6 5 0 0 0 5 0 0 • Option 2 (cont) – Memorize the sequence: 300 - 150 - 100 - 75 - 60 - 50 Interpretation? Approx. 1 box less than 100 = 95 bpm Tehran Arrhythmia Center Step 2: Determine regularity R R • Look at the R-R distances (using a caliper or markings on a pen or paper). • Regular (are they equidistant apart)? Occasionally irregular? Regularly irregular? Irregularly irregular? Interpretation? Regular Tehran Arrhythmia Center Step 3: Assess the P waves • Are there P waves? • Do the P waves all look alike? • Do the P waves occur at a regular rate? • Is there one P wave before each QRS? Interpretation? Normal P waves with 1 P wave for every QRS Tehran Arrhythmia Center Step 4: Determine PR interval • Normal: 0.12 - 0.20 seconds. (3 - 5 boxes) Interpretation? 0.12 seconds Tehran Arrhythmia Center Step 5: QRS duration • Normal: 0.04 - 0.12 seconds. (1 - 3 boxes) Interpretation? 0.08 seconds Tehran Arrhythmia Center Rhythm Summary • Rate • Regularity • P waves • PR interval • QRS duration Interpretation? 90-95 bpm Regular Normal 0.12 s 0.08 s Normal Sinus Rhythm Tehran Arrhythmia Center Normal Sinus Rhythm • Normal and constant P wave contours • Normal P wave axis • Rate between 60 and 100 bpm Tehran Arrhythmia Center Anatomical Aspects of Normal Sinus Node • Located at the superior anterolateral portion of right atrium near its border with the superior vena cava • It is an epicardial structure near sulcus terminalis • From endocardial approach the closest approach is near the superior end of crista terminalis Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Node Function • • • • • The dominant cardiac pacemaker Highly responsive to autonomic influences Decreasing rate with vagal stimulation Increasing rate with sympathetic activity Normal sinus rate under basal conditions is 60-100 bpm. Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Tachycardia • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 130 bpm Regular Normal 0.16 s 0.08 s Interpretation? Sinus Tachycardia Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Tachycardia • Sinus rhythm exceeding 100 bpm in adults • Usually between 100 and 180 bpm but may be higher with extreme exertion • Maximum heart arte decreases wit age from near 200 bpm to less than 140 bpm • Gradual onset and termination Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Tachycardia Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Tachycardia Causes • Common in infancy and childhood • Normal response to a variety of physiological and pathological stresses – – – – – – Exertion, anxiety Hypovolemia, anemia Fever Congestive heart failure Myocardial ischemia Thyrotoxicosis • Drugs • Inflammation Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Bradycardia • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 30 bpm Regular normal 0.12 s 0.10 s Interpretation? Sinus Bradycardia Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Bradycardia • Sinus rhythm at a rate less than 60 bpm • Can result from excessive vagal or decreased sympathetic tone as well as anatomic changes in sinus node • Frequently occurs in healthy young adults, particularly well-trained athletes • Sinus arrhythmia often coexists Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Bradycardia Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Bradycardia Junctional Escape Beats Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Bradycardia Causes • • • • • • • Hypothyroidism Drugs During vomiting or vasovagal syncope Increased intracranial pressure Hypoxia, hypothermia Depression Jaundice Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Arrhythmia • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 50-75 bpm Phasic variations normal 0.12 s 0.10 s Interpretation? Sinus Arrhythmia Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sinus Pause Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sick Sinus Syndrome • A combination of symptoms (dizziness, fatigue, confusion, syncope and congestive heart failure) caused by sinus node dysfunction • Atrial tachyarrhythmias may accompany sinus node dysfunction <bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome> Tehran Arrhythmia Center AV Block Types • First degree AV block • Second degree AV block – Mobitz type I (Wenckebach) – Mobitz type II • Third degree AV block (Complete heart block) • High degree (advanced) AV block Tehran Arrhythmia Center First Degree AV Block • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 60 bpm Regular Normal 0.36 s 0.08 s Interpretation? 1st Degree AV Block Tehran Arrhythmia Center PR Interval PR interval < 0.12 s 0.12-0.20 s > 0.20 s High catecholamine states Wolff-Parkinson-White Normal AV nodal blocks Wolff-Parkinson-White 1st Degree AV Block Tehran Arrhythmia Center First Degree AV Block • Conduction time is prolonged but all impulses are conducted. • PR interval exceeds 0.2 sec in adults • Site of conduction delay may be in the AV node (most commonly), in the His-Purkinje system or both. Tehran Arrhythmia Center First Degree AV Block Tehran Arrhythmia Center Wenckebach AV Block • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 50 bpm Regularly irregular Nl, but 4th no QRS Lengthens 0.08 s Interpretation? 2nd Degree AV Block, Type I Tehran Arrhythmia Center Mobitz Type I Second Degree AV Block • Also called Wenckebach block • Typical type characterized by progressive PR prolongation culminating in a nonconducted P wave • Narrow QRS in most cases Tehran Arrhythmia Center WB Tehran Arrhythmia Center Tehran Arrhythmia Center Wenckebach Block • Atypical pattern in over half the cases • The site of block is almost always in the AV node. • Generally benign and does not advance to more advanced AV block • Can occur in normal children and welltrained athletes Tehran Arrhythmia Center Mobitz Type II AV Block • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 40 bpm Regular Nl, 5th P no QRS 0.18 s 0.11 s Interpretation? 2nd Degree AV Block, Type II Tehran Arrhythmia Center Mobitz Type II Second Degree AV Block • PR interval remains constant prior to the blocked P wave • Commonly associated with bundle branch blocks Tehran Arrhythmia Center Tehran Arrhythmia Center Tehran Arrhythmia Center Tehran Arrhythmia Center 2:1 AV Block Tehran Arrhythmia Center 2:1 AV Block AV Nodal Level Tehran Arrhythmia Center 2:1 AV Block Infra-nodal Level Tehran Arrhythmia Center 2:1 AV block Infra-nodal Level Tehran Arrhythmia Center Complete Heart Block • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 40 bpm Regular No relation to QRS None Wide (> 0.12 s) Interpretation? 3rd Degree AV Block Tehran Arrhythmia Center Complete AV block • No atrial activity conducts to the ventricles • AV dissociation is present. The atria and ventricles are controlled by independent pacemakers. • Ventricular focus is usually located just below the site of block. • Higher sites are more stable with a more faster escape rate. Tehran Arrhythmia Center Complete AV block Tehran Arrhythmia Center Remember • When an impulse originates in a ventricle, conduction through the ventricles will be inefficient and the QRS will be wide and bizarre. Tehran Arrhythmia Center Tehran Arrhythmia Center AV Conduction Disturbances Etiology • Degenerative diseases are the most common causes • A variety of other diseases may be responsible: myocardial infarction, drugs, acute infections, infiltrative diseases, neoplasms, etc. • Hypervagotonia Tehran Arrhythmia Center Tehran Arrhythmia Center Tehran Arrhythmia Center Premature Beats • Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs) • Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Tehran Arrhythmia Center PAC • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? Interpretation? 70 bpm Occasionally irreg. 2/7 different contour 0.14 s (except 2/7) 0.08 s NSR with Premature Atrial Contractions Tehran Arrhythmia Center Narrow QRS Beats • When an impulse originates anywhere in the atria (SA node, atrial cells, AV node, Bundle of His) and then is conducted normally through the ventricles, the QRS will be narrow (0.04 - 0.12 s). Tehran Arrhythmia Center PVC • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 60 bpm Occasionally irreg. None for 7th QRS 0.14 s 0.08 s (7th wide) Interpretation? Sinus Rhythm with 1 PVC Tehran Arrhythmia Center Wide QRS Beats • When an impulse originates in a ventricle, conduction through the ventricles will be inefficient and the QRS will be wide and bizarre. Tehran Arrhythmia Center Ventricular Conduction Normal Signal moves rapidly through the ventricles Abnormal Signal moves slowly through the ventricles Tehran Arrhythmia Center Ventricular Premature Complexes Compensatory Pause Interpolated VPC Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Fibrillation • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 100 bpm Irregularly irregular None None 0.06 s Interpretation? Atrial Fibrillation Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Fibrillation Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Fibrillation • • • • • The most common sustained arrhythmia Incidence increases progressively with age. Prevalence: 0.4% of overall population Mortality rate double that of control AF is characterized by disorganized atrial activity without discrete P waves Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Fibrillation • Undulating baseline or atrial deflections of varying amplitude and frequency ranging from 350 to 600 bpm. • Irregularly irregular ventricular response. Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Fibrillation • Morbidity related to: – – – – – – Excessive ventricular rate Pause following cessation of AF Systemic embolization Loss of atrial kick Anxiety secondary to palpitations Irregular ventricular rate Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Fibrillation • Persistent AF usually in patients with cardiovascular disease – Valvular heart disease – Hypertensive heart disease – Congenital heart disease • Paroxysmal AF may occur with acute hypoxia, hypercapnia or metabolic or hemodynamic derangements • Normal people with emotional stress or surgery or acute alcoholic intoxication • Lone AF Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Fibrillation • Therapeutic Goals: – Control of ventricular rate – Restoration and maintenance of sinus rhythm – Prevention of thromboembolism Tehran Arrhythmia Center CHADS2 Score and Risk of Stroke JAMA 2001;285:2864 Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Flutter • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 70 bpm Regular Flutter waves None 0.06 s Interpretation? Atrial Flutter Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Flutter • Regular atrial tachyarrhythmia with atrial rate between 250-350 bpm. • Flutter waves are seen as saw-tooth like atrial activity Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Flutter • Atrial Flutter is a form of atrial reentry localized to right atrium. • Typically the ventricular rate is half the atrial rate, but the ventricular response may be 4:1, 2:1, 1:1 etc. Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Flutter Circuit Tehran Arrhythmia Center Atrial Flutter • Most often in patients with organic heart disease • Usually less long-lived than AF and may convert to AF. • Control of ventricular rate is difficult in atrial flutter • The most effective treatment is DC cardioversion Tehran Arrhythmia Center PSVT • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? Interpretation? 74 148 bpm Regular regular Normal none 0.16 s none 0.08 s Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Tehran Arrhythmia Center Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT) • Usually at a rate of 150-250 bpm • No organic heart disease in the majority • Presentations – Palpitations – Chest discomfort,dyspnea, lightheadedness – Frank syncope – SCD Tehran Arrhythmia Center Preexcitation Tehran Arrhythmia Center VT • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? 160 bpm Regular None None Wide (> 0.12 sec) Interpretation? Ventricular Tachycardia Tehran Arrhythmia Center Ventricular Arrhythmias Definitions • Premature Ventricular beats – Single beats – Ventricular Bigeminy, the appearance of one PVC after each sinus beat – Couplets, two consecutive premature beats – Triplets, three consecutive premature beats – Salvos, runs of 3-10 premature beats • Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm (Slow VT), rate 60100 bpm • Ventricular Tachycardia (VT), rate over 100 bpm • Ventricular Flutter, regular large oscillations at a rate of 150-300 bpm • Ventricular Fibrillation (VF), irregular undulations of varying contour and amplitude Tehran Arrhythmia Center Ventricular Tachycardia Classification • Duration – Sustained VT defined as VT that persists for than 30 s or requires termination because of hemodynamic collapse – Nonsustained VT, 3 beats to 30 s • Morphology – Monomorphic – Polymorphic Tehran Arrhythmia Center Salvos Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sustained Monomorphic VT Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sustained Polymorphic VT Tehran Arrhythmia Center VT Etiology • VT generally accompanies some form of structural heart disease most commonly: – Ischemic heart disease – Cardiomyopathies • Primary electrical abnormalities – Long QT syndromes – Brugada syndrome • Idiopathic VT Tehran Arrhythmia Center VF • • • • • Rate? Regularity? P waves? PR interval? QRS duration? None Irregularly irreg. None None Wide, if recognizable Interpretation? Ventricular Fibrillation Tehran Arrhythmia Center Sudden Death Syndrome • Incidence – 400,000 - 500,000/year in U.S. – Only 2% - 15% reach the hospital – Half of these die before discharge • High recurrence rate Tehran Arrhythmia Center Clinical Substrates Associated with VF Arrest • • • • • • Coronary artery disease Idiopathic cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Long QT syndrome RV dysplasia Rarely: WPW syndrome Tehran Arrhythmia Center