* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 12a
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
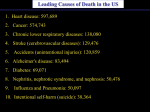
Chapter 12a Cardiovascular Disease Lecture Presentation Betty McGuire Cornell University Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Cardiovascular Disease The prevalence of cardiovascular diseases High blood pressure Atherosclerosis Coronary artery disease Heart attack Cardiovascular disease and cigarette smoking Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. The Prevalence of Cardiovascular Diseases Cardiovascular disease is the single biggest killer of men and women in the U.S. Affects slightly more men than women However, women who have heart attacks are more likely than men to die in the subsequent weeks Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. High Blood Pressure Blood pressure (review) The pressure exerted by blood on the walls of the vessels Systolic value is the pressure when the heart is contracting Diastolic value is the pressure when the heart is relaxing Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. High Blood Pressure Hypertension = high blood pressure Silent killer No symptoms Can cause fatal problems of the following: Heart (made to work harder, so enlarges) Kidneys (in response to reduced blood flow, release renin, which further increases blood pressure) Brain Blood vessels Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. High Blood Pressure Most physicians consider a blood pressure of 160/90 to be high and to require treatment Treatment may involve: Medication Diuretics to reduce blood volume Drugs that cause blood vessels to dilate Lifestyle changes Weight control Regular exercise No smoking Limit dietary salt Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis A buildup of fatty deposits in the walls of arteries Fueled by an inflammatory response May narrow the artery, which reduces blood flow Can be fatal if this occurs in the heart (heart attack) or brain (stroke) Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Atherosclerosis Treating atherosclerosis may include: Healthy lifestyle Control weight Engage in regular aerobic exercise Eat a heart-healthy diet Medications Lower blood pressure Reduce blood cholesterol levels Prevent formation of unwanted clots Daily low-dose aspirin therapy Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Coronary Artery Disease Coronary artery disease Fatty deposits of atherosclerosis occur in the coronary arteries (nourish heart muscle) Underlying cause of most heart attacks Angina pectoris (chest pain) serves as a warning that the heart muscle is not receiving sufficient oxygen Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Coronary Artery Disease Coronary angiography Diagnostic procedure in which high-speed x-rays are taken as a contrast dye moves through the coronary arteries Can show coronary artery blockage Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Coronary Artery Disease Treating coronary artery blockage may include: Medications (some dilate blood vessels) Surgical procedures Angioplasty A balloon is used to widen the lumen of the artery; stents may be inserted to keep the treated artery open Coronary bypass surgery A section of a leg vein is used to provide an alternate pathway, bypassing a blockage between the aorta and a coronary artery Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Heart Attack Heart attack = myocardial infarction Part of the heart muscle dies because of an insufficient blood supply If the individual survives, the dead cardiac muscle is replaced by scar tissue, which cannot contract, so part of the heart permanently loses its pumping ability Commonly caused by a blood clot blocking a coronary artery Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Heart Attack Heart failure Condition in which the heart becomes an inefficient pump Leads to shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid accumulation Can result if a large enough section of heart muscle is damaged by a heart attack Symptoms can be treated with drugs Digitalis increases strength of heart contractions Diuretics reduce fluid accumulation Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Heart Attack PLAY | Vioxx Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Cardiovascular Disease and Cigarette Smoking Cigarette smoking Each year cardiovascular disease kills many more people than does lung cancer Smokers have a twofold to threefold increase in the risk of heart disease Components of smoke produce immediate effects on the cardiovascular system Over the long term, smoking increases atherosclerosis Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Cardiovascular Disease and Cigarette Smoking Components of cigarette smoke Nicotine Increases heart rate Constricts blood vessels, so raises blood pressure Increases stickiness of platelets, so increases the risk of abnormal clots Carbon monoxide Prevents RBCs from transporting oxygen Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.