* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8 The Heart and Lungs at Work
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
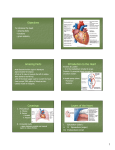
CHAPTER 8 Heart and Lungs at Work Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Cardiovascular Anatomy • Heart • Peripheral Circulatory System • Red Blood Cells Cardiovascular Physiology • Transport of Carbon Dioxide • Oxygen Uptake Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology • Structure • Function Exercise Effects on Cardiorespiratory System • Cardiac Output • Capillary Supply • Blood Volume • Ventilation Exercise and Environments • Altitude • Temperature Kinesiology Books Publisher 2 LESSON 1 CARDIOVASCULAR ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 1: THE LANGUAGE OF NATOMYand control of Explain theAfunction the cardiovascular system and the terms that are used to evaluate and describe its various components. Kinesiology Books Publisher 3 Cardiovascular system • Supplies muscles and organs with O2 • Removes metabolic by-products from tissues • Critical for performance 4 Kinesiology Books Publisher 4 CARDIOVASCULAR ANATOMY • Heart • Peripheral Circulatory System • Red Blood Cells Kinesiology Books Publisher 5 HEART • Pumps blood through the human body Kinesiology Books Publisher 6 STRUCTURE: MUSCLE CELLS 3 layers: 1. Endocardium (innermost) • Lines heart chambers • Allows smooth blood flow 2. Myocardium (middle) • Thick and muscular • Pumps blood 3. Epicardium (outer) • Thin • Protection • Pericardium • Protective sac • Loosely surrounds heart 7 Kinesiology Books Publisher 7 2. Myocardium Pericardial cavity Pericardium (outer) 1. Endocardium Pericardium (inner) 3. Epicardium 8 Kinesiology Books Publisher 8 STRUCTURE: CHAMBERS AND VESSELS Ventricles • Pump blood to the body • Right ventricle • Deoxygenated blood • To lungs • Via pulmonary artery • Left ventricle • Oxygenated blood • To body • Via aorta Right ventricle Left ventricle Kinesiology Books Publisher 9 Pulmonary vein STRUCTURE: CHAMBERS AND VESSELS Atria • Pump blood into ventricles • Right atrium • Deoxygenated blood • From body • Via superior/inferior vena cava • Left atrium • Oxygenated blood • From lungs • Via pulmonary vein Right atrium Left atrium Kinesiology Books Publisher 10 STRUCTURE: VALVES Semilunar valves • Open when ventricles contract to direct blood flow into arteries 1. Pulmonary valve: right ventricle pulmonary artery 2. Aortic valve: left ventricle aorta • Close when ventricles relax to prevent backflow 1 1 2 2 11 Kinesiology Books Publisher 11 STRUCTURE: VALVES Atrioventricular valves • Open when atria contract to direct blood flow into ventricles 1. Tricuspid valve: right atrium right ventricle 2. Bicuspid / mitral valve: left atrium left ventricle • Close when atria relax to prevent backflow 1 2 1 2 12 Kinesiology Books Publisher 12 1.Deoxygenated blood enters right atrium from body via superior/ inferior vena cava 2.Right atrium pumps deoxygenated blood to right ventricle through tricuspid valve 3.Right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood through pulmonary valve to lungs via pulmonary artery 1 3 1 3 2 2 1. Oxygenated blood enters left atrium from lungs via pulmonary vein 2. Left atrium pumps oxygenated blood to left ventricle through bicuspid valve 3. Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood through aortic valve to body via aorta Kinesiology Books Publisher 13 FUNCTION • Heart contracts in a constant rhythm • May speed up or slow down • Depending on the body’s blood and oxygen need • Sinus node • Bundle of nerve fibres that control heart rate • Located inside right atrium wall • Generate a nerve impulse (action potential) • Cause muscle walls to contract • Atria 1st,ventricles 2nd 14 Kinesiology Books Publisher 14 BLOOD PRESSURE • Important measure of cardiac function • Two components 1. Systolic BP • During ventricular contraction (systole) • How hard heart works • Strain against arterial walls during contraction • Normal: 120 mm Hg 2. Diastolic B • During heart relaxation (diastole) • Indicates peripheral BP (outside the heart) • Ease with which blood flows from arterioles to capillaries • Normal: 70-80 mm Hg 15 Kinesiology Books Publisher 15 16 Kinesiology Books Publisher 16 17 Kinesiology Books Publisher 17 CARDIAC OUTPUT • Amount of blood pumped by heart into aorta each minute • Quantity of blood that flows into peripheral circulation Stroke volume (ml/beat) Heart rate (beat/min) Cardiac output (ml/min) 18 Kinesiology Books Publisher 18 CARDIAC OUTPUT Stroke Volume • Amount of blood (ml) pumped out of left ventricle per heartbeat • Resting: 70 ml Heart rate • Rhythmical contraction of the heart walls (beats per minute, bpm) • Resting: 40-70 bpm • Maximum: 220 – age (years) Intensity of work • Estimated by measuring heart rate via carotid or radial pulse • Palpate with middle 2-3 fingers and count # beats per 10 sec x 6 19 Kinesiology Books Publisher 19 PERIPHERAL CIRCULATORY SYSTEM • Consists of blood vessels made up of layers of tissue • Smooth muscle cell layer allow vessels to contact • This regulates blood flow throughout the body Kinesiology Books Publisher 20 TGS 8.6 – Exit Card Make the Match Match the following terms with their corresponding function/characteristic. Kinesiology Books Publisher 21 D F E B C A 22 Kinesiology Books Publisher 22