* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
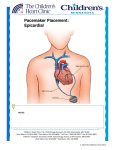
16 Pacemakers and Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators Fast & Easy ECGs, 2nd E – A SelfPaced Learning Program Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 1 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Artificial Pacemakers • Medical devices used to generate and deliver electrical impulses to the myocardium to stimulate a normal heartbeat • Some are external to the body and provide temporary treatment, others are permanently implanted in the chest Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 2 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Artificial Pacemakers • One type of temporary pacemaker is the transcutaneous pacemaker – It delivers electrical impulses through lead wires to electrode pads that are applied to the surface of the patient’s chest • Permanent pacemakers are implanted in a surgically created pocket beneath the skin in the patient’s chest wall just below the clavicle Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 3 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Permanent Pacemakers • Consist of: – A generator – One or more lead wires – A power source (often a lithium battery) – Logic circuits that detect cardiac electrical activity and determine the appropriate response I Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 4 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Permanent Pacemakers • May be used to: – Symptomatic bradycardia – Sick sinus syndrome – Atrial fibrillation with bradycardia – 3rd-degree (complete) AV heart block – Symptomatic 2nd-degree AV heart block, particularly type II – The sudden development of various combinations of AV heart block and bundle branch block in patients experiencing acute MI – Recurrent tachycardias that can be overdriven and thereby terminated by pacemaker activity – Synchronization of the heart beat in heart failure (cardiac resynchronization therapy) Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 5 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Pacemaker Electrodes • Are either positioned in the atrium or ventricle alone (single-chamber pacemakers) or, more often, in both chambers (dualchamber pacemakers or AV sequential pacemakers) Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 6 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Permanent Pacemakers • Are programmable – Receive and transmit data/programming instructions through the skin using electromagnetic waves • Adjustments can be made to: – Output – Sensitivity – Refractory period – Rate adaption Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 7 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Pacing Modes • Single-chamber – One pacing lead is inserted into either the right atrium or right ventricle but not both • Dual-chamber – Electrodes are placed into two chambers of the heart – One lead paces the atrium while the other paces the ventricle – By assisting the heart in coordinating the function between the atria and ventricles, this type of pacemaker acts similarly to how the heart naturally paces itself – Also referred to as an AV sequential pacemaker – Most can be programmed to a single chamber mode, which can be useful if the atrial lead wire fails Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 8 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Pacing Modes • Fixed-rate – Paces the heart at a single, preset rate • Rate-responsive – Has sensors that identify increases or decreases in the patient’s physical activity and automatically adjusts base pacing rate to meet the body’s metabolic needs – Can boost the heart rate in response to motion or increased respirations for those patients whose body cannot appropriately increase the heart rate during activity Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 9 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Pacing Modes • Demand – Most common type used – Fires only when the patient’s intrinsic heart rate falls below a given threshold level • i.e., if the pacemaker is set at 60 beats per minute it remains inactive until there is a pause between beats that translates into a rate below 60, then the pacemaker fires Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 10 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Coding System • Pacemaker mode and function described by a five letter coding system – in practice, only three to four are commonly used Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 11 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Coding System • First letter represents the heart chamber being paced. This letter may be – – – – O = none A = atrium V = ventricle D = dual (ventricle and atrium) • Second letter represents the chamber of the heart being sensed by the pacemaker. This letter may be – – – – O = none A = atrium V = ventricle D = dual (ventricle and atrium) Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 12 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Coding System • Third letter indicates how the pacemaker generator responds to sensing. This letter may be – – – – O = none T = triggers pacing I = inhibits pacing D = dual (triggers and inhibits pacing) • Fourth letter has to do with adjustment of the pacing rate in response to exercise – If pacemaker is rate responsive, it is denoted with the letter “R” – If there is none, it is denoted as “O” Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 13 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Coding System • The fifth letter indicates multisite pacing. This letter may be – O = none – A = atrium – V = ventricle – D = dual (ventricle and atrium) Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 14 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Coding System Examples • VOO – In this mode, the ventricle is paced and there is no sensing function • AAI – Pacemaker paces and senses in the atrium – When it senses atrial activity, pacing is inhibited • VVI – Ventricle is paced and sensed – If spontaneous cardiac output is detected, then the device is inhibited Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 15 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Coding System Examples • VDD – Here the pacemaker paces the ventricle and senses both the atrium and ventricle – On sensing intrinsic atrial activity, the pacemaker triggers ventricular pacing; on sensing ventricular activity, the pacemaker inhibits pacing – It is also known as a P-synchronous pacer Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 16 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Coding System Examples • DVI – Pacemaker can pace in the atrium, the ventricle, or both – Sensing takes place only in the ventricle – When the pacemaker senses intrinsic ventricular activity, it inhibits pacing • DDD – Pacemaker paces and senses in the atrium, the ventricle, or both – On sensing activity in either chamber, the pacemaker inhibits pacing in that chamber – Or, on sensing atrial activity, the pacemaker may trigger ventricular pacing Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 17 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) • Used to resynchronize a heart that does not beat in synchrony, a common problem in patients with heart failure • Employs three leads: – one is placed in right atrium – one is located in right ventricle – last one is inserted through the coronary sinus to pace the free wall of the left ventricle – These three wires are connected to a CRT generator and programmed so that the two ventricular wires are activated simultaneously I Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 18 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Unipolar and Bipolar Systems • Unipolar – positive electrode is positioned in the heart tissue and the negative electrode is connected to the pulse generator – produces tall pacing spikes on the ECG • In a bipolar system, – electrodes are only millimeters apart in the cardiac tissue – produces short pacemaker spikes Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E I 19 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. ECG Features of a Pacemaker • Depending on how many chambers are paced, the firing of a pacemaker produces one or two narrow pacemaker spikes on the ECG Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 20 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. ECG Features of a Pacemaker • A paced ECG complex shows two features: (a) a narrow “pacing spike,” which reflects the impulse depolarizing the paced chamber and (b) a P wave or QRS complex that immediately follows the pacing spike I Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 21 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Pacemaker Failure • Pacemakers may not work properly for a number of reasons, including a failure to capture, a failure to pace, a failure to sense, oversensing, and pacemaker-mediated tachycardia Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 22 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Pacemaker Failure • Failure to capture is seen as the presence of pacemaker spikes that are not followed by a P wave or broad QRS complex Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 23 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Pacemaker Failure • Failure of the pacemaker to sense is seen as the presence of ECG pacemaker spikes that fall where they shouldn’t Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 24 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Pacemaker Failure • Oversensing is seen as an absence of pacemaker spikes in the presence of a heart rate that is slower than the rate set for the pacemaker Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 25 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Pacemaker Failure • Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia is seen as a fast heart rate with a pacemaker spike preceding each QRS complex on EGG. Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 26 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) • Is implanted in patients who are at risk of sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 27 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator • Is programmed to detect cardiac dysrhythmias and correct them by delivering paced beats, cardioversion, or defibrillation Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 28 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Therapies Provided by the ICD Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 29 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Practice Makes Perfect • Analyze this ECG tracing I Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 30 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Practice Makes Perfect • Analyze this ECG tracing I Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 31 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Practice Makes Perfect • Analyze this ECG tracing I Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 32 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Practice Makes Perfect • Analyze this ECG tracing I Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 33 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.