* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECGs MADE EASY
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
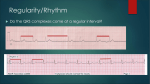
BASIC ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Dr. Riko Prima Putra, SpJP ELECTROCARDIOGRAM The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic recording of the electrical potentials produced by the cardiac tissue. Electrical impulse formation occurs within the conduction system of the heart. Excitation of the muscle fibers throughout the myocardium results in cardiac contraction. The ECG is recorded by applying electrodes to various locations on the body surface and connecting them to a recording apparatus. Sinus Rhythms Normal Sinus Rhythm Rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS 60-100 beats per minute Atrial regular Ventricular regular Uniform in appearance, upright, normal shape, one preceding each QRS complex 0.12-0.20 second 0.10 second or less. If greater than 0.10 second in duration, the QRS is termed “wide” since the existence of a bundle branch block or other intraventricular conduction defect cannot be accurately detected in a single-lead. Sinus Rhythms Sinus Bradycardia Rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS Less than 60 beats per minute Atrial regular Ventricular regular Uniform in appearance, upright, normal shape, one preceding each QRS complex 0.12-0.20 second Usually 0.10 second or less Sinus Rhythms Sinus Tachycardia Rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS Usually 100-160 beats per minute Atrial regular Ventricular regular Uniform in appearance, upright, normal shape, one preceding each QRS complex 0.12-0.20 second Usually 0.10 second or less Sinus Rhythms Sinus Dysrhythmia (Arrhythmia) Rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS Usually 100-160 beats per minute but may be faster or slower Irregular (R-R intervals shorten during inspiration and lengthen during expiration) Uniform in appearance, upright, normal shape, one preceding each QRS complex 0.12-0.20 second Usually 0.10 second or less Atrial Rhythms Premature Atrial Complexes Early (premature) P waves Upright P waves that differ in shape from normal sinus P waves in Lead II 1. 2. • 3. P waves may be biphasic (partly positive, partly negative), flattened, notched or pointed The early P wave may or may not be followed by a QRS complex Atrial Rhythms Premature Atrial Complexes (PACs) Rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS Usually normal but depends on underlying rhythm Essentially regular with premature beats Premature Differ from sinus P waves – may be flattened, notched, pointed, biphasic, or lost in the preceding T wave Varies from 0.12-0.20 second when the pacemaker site is near the SA node; 0.12 second when the pacemaker site is nearer the AV junction Usually less than 0.10 second but may be prolonged. The QRS of the PAC is similar to those of the underlying rhythm unless the PAC is abnormally conducted. Atrial Rhythms Supraventricular Tachycardia Rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS 150-250 beats per minute Regular Atrial P waves may be seen which differ from sinus P waves (may be flattened, notched, pointed, or biphasic). P waves are usually identifiable at the lower end of the rate range but are seldom identifiable at rates above 200. May be lost in the preceding T wave. Usually not measurable because the P wave is difficult to distinguish from the preceding T wave. If P waves are seen, the RR interval will usually measure 0.120.20 second. Less than 0.10 second unless an intraventricular conduction defect exists. Atrial Rhythms The Unstable Patient Signs and Symptoms Shock Chest pain Hypotension Shortness of breath Pulmonary congestion Congestive heart failure Acute myocardial infarction Decreased level of consciousness Atrial Rhythms ELECTRICAL THERAPY – Synchronized Countershock Description and Purpose Synchronized countershock reduces the potential for delivery of energy during the vulnerable period of the T wave (relative refractory period). A synchronizing circuit allows the delivery of a countershock to be “programmed”. The machine searches for the peak of the QRS complex (R wave deflection) and delivers the shock a few milliseconds after the highest part of the R wave. Indications: Supraventricular tachycardia Atrial fibrillation Atrial flutter Unstable ventricular tachycardia with pause Atrial Rhythms Atrial Flutter Rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS Atrial rate 250-350 beats per minute; ventricular rate variable – determined by AV blockade. The ventricular rate will usually not exceed 180 beats per minute due to the intrinsic conduction rate of the AV junction. Atrial regular Ventricular may be regular or irregular Not identifiable P waves; saw-toothed “flutter waves” Not measurable Usually less than 0.10 second but may be widened if flutter waves are buried in the QRS complex or if an intraventricular conduction defect exists. Atrial Rhythms Atrial Fribrillation Rate Atrial rate usually greater than 350-400 beats per minute; ventricular rate variable Rhythm Ventricular rhythms usually very irregular; a regular ventricular rhythm may occur because of digitalis toxicity. P waves No identifiable P waves; fibrillatory waves present. Erratic wavy baseline. PR interval Not measurable QRS Usually less than 0.10 second but may be widened if an intraventricular conduction defect exists. Ventricular Rhythms Premature Ventricular Complexes Rate Usually normal but depends on the underlying rhythm Rhythm Essentially regular with premature beats. If the PVC is an interpolated PVC, the rhythm will be regular. P waves There is no P wave associated with the PVC PR interval None with the PVCs because the ectopic beat originates in the ventricle QRS Greater than 0.12 second. Wide and bizarre. T wave frequently in opposite direction of the QRS complex. Ventricular Rhythms Patterns of PVCs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Pairs (couplets) – two sequential PVCs Runs or bursts – three or more sequential PVCs are called vntricular tachycardia (VT) Bigeminal PVCs (ventricular bigeminy) – every other beat is a PVC Trigeminal PVCs (ventricular trigeminy) – every third beat is a PVC Quadrigeminal PVCs (ventricular quadrigeminy) – every fourth beat is a PVC Ventricular Rhythms Common Causes of PVCs Normal variant Anxiety Exercise Hypoxia Digitalis toxicity Acid-base imbalance Myocardial ischemia Electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypercalcemia, hypomagnesemia) Congestive heart failure Increased sympathetic tone Acute myocardial infarction Stimulants (alcohol, caffeine, tobacco) Drugs (sympathomimetics, cyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines) Ventricular Rhythms Warning Dysrhythmias Six or more PVCs per minute PVCs that occurred in pairs (couplets) or in runs or three or more (ventricular tachycardia) PVCs that fell on the T wave of the preceding beat (R-on T phenomenon) PVCs that differed in shape (multiformed PVCs) Ventricular Rhythms Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) Rate Atrial rate not discernible, ventricular rate 100250 beats per minute Rhythm Atrial rhythm not discernible Ventricular rhythm is essentially regular P waves May be present or absent; if present they have no set relationship to the QRS complexes – appearing between the QRS’s at a rate different from that of the VT. PR interval None QRS Greater than 0.12 second. Often difficult to differentiate between the QRS and the T wave. Ventricular Rhythms VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA - CAUSES Hypoxia Exercise R-on T PVCs Catecholamines Digitalis toxicity Myocardial ischemia Acid-base imbalance Electrolyte imbalance Ventricular aneurysm Coronary artery disease Rheumatic heart disease Acute myocardial infarction CNS stimulants (cocaine, amphetamines) Ventricular Rhythms Ventricular Fibrillation Rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS Cannot be determined since there are no discernible waves or complexes to measure Rapid and chaotic with no pattern or regularity Not discernible Not discernible Not discernible Ventricular Rhythms Defibrillation (Unsynchronized Countershock) Description and Purpose: The purpose of defibrillation is to produce momentary asystole. The shock attempts to completely depolarize the myocardium and provide an opportunity for the natural pacemaker centers of the heart to resume normal activity. Defibrillation is a random delivery of energy – there is no relation of the discharge of energy to the cardiac cycle. Indications: Unstable ventricular tachycardia with a pulse Pulseless ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation Sustained Torsades de Pointes Ventricular Rhythms Asystole Rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS Ventricular usually indiscernible but may see some atrial activity. Atrial may be discernible. Ventricular indiscernible. Usually not discernible Not measurable Absent Ventricular Rhythms Causes of Pulseless Electrical Activity (MATCHx4ED) Myocardial infarction (massive acute) Acidosis Tension pneumothorax Cardiac tamponade Hypovolemia (most common cause) Hypoxia Hyperkalemia Hypothermia Embolus (massive pulmonary) Drug overdoses (cyclic antidepressants, calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, digitalis) “Bundle Branch” Blok Kanan (RBBB) Gangguan hantaran pada cabang kanan Bundle His Dapat diakibatkan adanya fibrosis atau kelainan bawaan Blok sempurna disebut RBBB komplit Blok tidak sempurna disebut RBBB inkomplit dan dapat terjadi pada orang normal RBBB Komplit Di lead V1 atau V2 - QRS intv > 0,12” (broad notched R, rsr, rsR’ atau rSR’ - Tipe QRS “M type” atau “ Shape” dimana R2 > R1 Gelombang S dalam, negatif di V5-V6, QRS > 0,12” Kadang ada kelainan repolarisasi RBBB Inkomplit Syaratnya sama dengan RBBB komplit tetapi QRS intv antara > 0,08” - < 0,12” RBBB Komplit “Bundle Branch” Blok Kiri (LBBB) Mempunyai arti klinis selalu patologis Terbagi atas blok komplit dan inkomplit LBBB Komplit: QRS intv 0,12” atau lebih 2. QS atau RS di V1, gelombang R melebar dengan ada lekuk di puncaknya (nothed) 3. Gelombang Q mengecil/hilang di lead I, aVL, V5,V6 4. Kelainan repolarisasi berupa ST depressi 1. LBBB inkomplit Sama dengan LBBB komplit tetapi QRS intv 0,08”- 0,11” LBBB Komplit THANK YOU