* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart - SD57 Mail
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
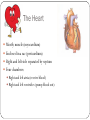
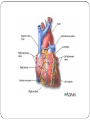
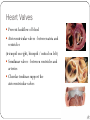
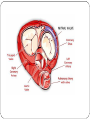
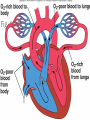
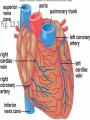
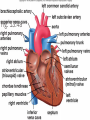
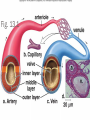
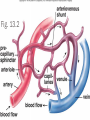
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM THE HEART AND BLOODVESSELS Learning Outcomes: C3 – Describe the interrelationships of the structures of the heart Identify structures diagrams and give functions and direction of blood flow C5 – analyze the functional interrelationships of the vessels of the circulatory system Describe the 5 types of blood vessels in terms of structure and function Identify and give the function of the blood vessels of the body The Heart Mostly muscle (myocardium) Enclosed in a sac (pericardium) Right and left side separated by septum Four chambers: Right and left atria (receive blood) Right and left ventricles (pump blood out) Heart Valves Prevent backflow of blood Atrioventricular valves - between atria and ventricles (tricuspid on right, bicuspid / mitral on left) Semilunar valves - between ventricles and arteries Chordae tendinae support the atrioventricular valves A Double Pump Right: receives blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs Left: receives blood from the lungs and pumps it to the body Fig. 13.4b Blood Vessels of the Heart Superior and inferior vena cava - from upper and lower body to the right atrium Pulmonary trunk - branches into R and L pulmonary arteries - to the lungs Pulmonary veins - from lungs to heart Aorta - from left ventricle, branches to all parts of the body Coronary arteries - supply the heart muscle Fig. 13.3b Fig. 13.4a BLOOD VESSELS 5 types arteries - carry blood away from the heart; thick, muscular walls arterioles – smaller branches of the arteries veins – carry blood toward the heart; thinner walls, have valves to prevent backflow venules – smaller branches of veins capillaries – networks of microscopic vessels in all tissues; walls are very thin (one cell thick); connect veins and arteries; supply cells with nutrients Fig. 13.1 Fig. 13.2 Assignment Draw arrows in red and blue on your diagram to show the flow of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood through the heart List in order all the structures blood would flow through as it passes through the heart and lungs, starting with the vena cava and ending with the aorta