* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
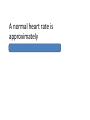
The blood receiving chambers of the heart are the atria. The pumping chambers of the heart are the ventricles. Blood returns to the heart from the lungs by means of the pulmonary veins. The large artery carrying blood from the left ventricle of the heart is the aorta. Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are arteries. Blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart are veins. On the right side of the heart, the valve between the right atrium and right ventricle is the Right AV valve (or tricuspid valve). The flaps of the heart valves are anchored to the wall of the ventricles by tissue chords known as Chordae Tendinae. Arteries that supply blood to the tissue of the heart itself are the coronary arteries. The sinoatrial (SA) node of the heart is found in the wall of the right atrium. The second major node of the heart that receives signals from the SA node is called the AV node. Heart contraction is also known by the term Systole. Heart muscle relaxation is also known by the term Diastole. A normal heart rate is approximately 60-100 beats per minute. Unusual heart sounds, such as those emitted by poorly functioning valves, are called Heart murmurs. The smallest vessels, which carry blood to the cells of the tissues are the capillaries. The inner layer of the vein often folds inward to form valves. Dilated veins with pooled blood cause a condition known as varicose veins. A typical blood pressure reading contains two numbers of which the first number is the systolic pressure and the second number is the diastolic pressue. The only arteries of the body that carries oxygen-poor blood are the pulmonary arteries. The only veins of the body that carry oxygen-rich blood are the pulmonary veins. The fluid portion of the blood is the plasma. The major molecule that transports oxygen within red blood cells is hemoglobin. Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow through a process known as hematopoiesis. Red blood cells survive and circulate in the human blood stream for approximately 100-120 days. The production of red blood cells is regulated by a hormone known as Erythropoietin or EPO. Antibodies are produced by white blood cells known as B cells. A mass of platelets that patch a hole in a blood vessel is known as a platelet plug. The two major types of cells in your lymph nodes are T-lymphocytes (T cells) and B-lymphocytes (B cells). Substances capable of stimulating the immune system are known as antigens. Foreign organisms are engulfed by macrophages in a process known as phagocytosis. The cells needed to activate both Bcells and Killer T-cells are called Helper T-cells. Cells that kill virus-infected cells are known as Killer T cells (or Cytotoxic Tlymphocytes, CTLs). The purpose of the eye is to gather light from the environment and form an image on cells of the retina. The nerve that carries impulses from the eye to the brain is the optic nerve. The inner coat of the posterior wall of the eye is composed of the retina (or rods and cones). The outer wall of the eye consists of the cornea and the sclera. The thin, watery fluid in the anterior chamber of the eye is aqueous humor. The jellylike substance that fills the posterior chamber of the eye is called vitreous humor. The pupil of the eye is an opening in the portion of the eye known as the iris. The eyelids are covered on their surfaces by the mucous membrane called the conjunctiva. Tears that bathe the eyeball and keep it moist are produced by the lacrimal glands. Twilight (dim light) vision is concerned with those retinal cells known as rods. Daylight vision and close, detailed vision are permitted by those retinal cells known as cones. The place where most cones are concentrated is the fovea. The optic disc contains no visual receptors and is therefore called the blind spot. The lobe of the brain where visual patterns are interpreted is the occipital lobe. The change of the lens shape to focus objects at various distances is under the control of a muscle called the ciliary muscle. The middle ear bones, which transmit sound to the inner ear, are known as the ossicles. The long, slender tube leading from the pharynx (throat) to the middle ear is the Eustachian tube. The snail-like structure of the inner ear is called the cochlea. Sound-induced nerve impulses are transmitted to the brain for interpretation over the cochlear branch of the nerve called the vestibulocochlear nerve. The five primary tastes are sweet, sour, salty, umami, and bitter.