* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download T5 Blood Pressure
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
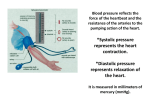
8/04/2013 SHMD 139 Pg 34 Blood pressure is the pressure the blood exerts on the artery walls Blood pressure (BP) is the result of the heart contracting and forcing blood into the blood vessels BP is necessary in order for blood to flow around the body Pg 34 Typical BP for the average person: 120 80 Systolic:When the heart is contracting Diastolic: When the heart is relaxing BP unit of measurement: milligrams of mercury (mmHg) Pg 33 Cardiac Output: the amount of blood pumped from the heart every minute Stroke Volume: The amount of blood pumped by the left ventricle of the heart in one contraction. Heart Rate: the number of times the heart beats in 1 minute, measured in beats per minute (bpm) Pg 34 Cardiac Output (litres per minute) = heart rate (bpm) x Stroke volume (litres) Thus, Q = HR x SV The average stroke volume is 70 – 90 millilitres (ml) The fitter you are, the larger your SV is At rest, your cardiac output (Q) is ± 5 litres per minute (L/m), while during exercise it can increase to as much as 30 L/m Pg 34 Blood Pressure (mmHg) = Cardiac Output (litres per minute) x Resistance to flow (R) Thus, BP = Q x R Resistance to blood flow is caused by: 1. Size of the blood vessels. i.e. The smaller the blood vessel, the greater the resistance 2. Thickness of the blood. i.e. The thicker the blood, the greater the resistance. If heart rate = 72 bpm & stroke volume = 85ml Cardiac output? 85ml ÷ 1000 = 0.085L Thus, Q = HR x SV = 72 x 0.085 = 6.12 L/m Round off = 6 L/m If heart rate = 68 bpm & stroke volume = 80ml Cardiac output? Diastolic R = 14 Systolic R = 22 Blood Pressure? 80ml ÷ 1000 = 0.080L Thus, Q = HR x SV = 68 x 0.08 = 5.44 L/m Systolic BP =QxR = 5 x 22 = 110 mmHg Thus BP = 110 mmHg 70 Diastolic BP =QxR = 5 x 14 = 70 mmHg Pg 34 Exercise increases heart rate, which will result in an increased cardiac output, which will increase blood pressure Q = HR x SV BP = Q x R If Q is increased, and R does not change, then BP will automatically increase Exercise raises systolic BP, but there is usually only a slight change in diastolic BP Pg 132 Is a repeatedly elevated blood pressure exceeding 140 over 90 mmHg, and means high pressure (tension) in the arteries. If a person with high blood pressure does not reduce their BP, they are more at risk of suffering a stroke or heart attack . Pg 35 Used by heavy weightlifters Process of breathing against a closed glottis or against a closed mouth & nose The valsalva maneouvre helps stabilise the shoulder girdle and torso while lifting heavy weights. This helps the lifter to move the weight more efficiently. Pg 36 The valsalva maneouvre causes BP to increase, and reduces blood flow to the thoracic cavity Thoracic cavity: part of the body that is enclosed by the ribcage and the diaphragm, containing the heart and lungs Therefore anyone suffering from hypertension or heart problems should avoid this move, as it could cause a stroke or heart attack. Pg 167 It is vital to measure BP before a client exercises, as it will tell you if they are at risk of having a heart attack. BP is measured with a blood pressure meter and stethoscope. Pg 167 1. The client should be seated and relaxed for 5 minutes 2. Ask the client to rest their left arm on the arm of the chair. Their elbow should be at 45 degrees, with the palm of the hand facing up. 3. Find the brachial pulse – it should be on the inner side of the arm, just under the biceps muscle. 4. Place the cuff just clear of the elbow (about 2-3cm above the elbow). The bladder of the cuff (The part which inflates) should be directly over the pulse. 5. Place the earpieces of the stethoscope in your ears and place the microphone over the brachial pulse. Pg 167 6. Inflate the cuff up to 200mmHg. 7. Slowly open the valve by turning it anti-clockwise and release the pressure. 8. Listen out for the first time you hear the thud of the heart beat and make a mental note of it. This is the systolic blood pressure reading. 9. Keep deflating the cuff, and when the heart beat becomes muffled or disappears, this is your diastolic reading. 10. Keep deflating the cuff and, if necessary, repeat after around 30 seconds. Classification of blood pressure for adults Category Systolic (mmHg) Diastolic (mmHg) Desirable 90 – 119 60 – 79 Prehypertension 120 – 139 80 – 89 Stage 1 Hypertension 140 – 159 90 – 99 Stage 2 Hypertension 160 – 179 100 - 109 ≥180 ≥ 110 Hypertensive Crises