* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Maths EYFS Parents Meeting
Survey
Document related concepts
Philosophy of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and art wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Secondary School Mathematics Curriculum Improvement Study wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
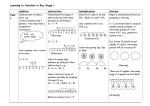
Maths Parents’ Meeting Wednesday 4th February 2015 WELCOME ‘ Mathematics is a creative and highly inter-connected discipline that has developed over centuries, providing the solution to some of history’s most intriguing problems.’ (National Curriculum in England, Sept. 2013) Today’s Meeting • To help you to understand the Maths curriculum for EYFS and KS1. • To understand how we teach in order to cover the requirements of the curriculum. • To identify the key ways in which you can help your child at home and in school. What is the Early Years Foundation Stage? • The Early Years Foundation Stage (E.Y.F.S.) is the stage of education for children from birth to the end of the Reception year. • It is based on the recognition that children learn best through play and active learning. E.Y.F.S Framework • • Your child will be learning skills, acquiring new knowledge and demonstrating their understanding through 7 areas of learning and development 3 prime areas: – Personal, Social and Emotional Development – Communication and Language – Physical Development These prime areas are those most essential for your child’s healthy development and future learning. 4 specific areas: – Literacy – Mathematics – Understanding the Words – Expressive Arts and Design As children grow, the prime areas will help them to develop skills in these areas Mathematics in E.Y.F.S ‘A unique child’ EYFS Curriculum.docx In the Classroom ‘Positive relationships and enabling environments’ •Maths rich learning environment •Rich learning opportunities •Adult-led activities •Free flow and child-initiated learning •Exploration and play •Stimulating resources •Active learning •Adult intervention and interaction In and Out of the Classroom • • • • • • • • • • Number, shape and treasure hunts Ball/ring games Bikes and Scooters Washing line numbers Chalk, printing,playdough Sand and water trays – finding objects, measuring and comparing volume Role play areas including shopping, cooking, sorting and packing Stories and rhymes Using a balance to compare objects Counting and dice games Counting - as easy as 1,2,3!! • • • • • Knowing number names in order 1 to 1 correspondence Keeping track of objects counted Last number is total of set Recognising small numbers of objects without counting them • Counting objects that you can’t move, touch or see • Knowing when to stop when counting out objects from larger set • Conservation • Knowing that if an object is added or removed then the number changes Identifying and writing numbers New Curriculum Aims: Become fluent in the fundamentals Reason mathematically Solve problems by applying their mathematics Depth of understanding before acceleration through new content Challenge will be through the use of rich and sophisticated challenges focussing on the application of knowledge Curriculum content divided into domains Number – place value, addition and subtraction, multiplication and division, fractions Measurement Geometry – properties of shapes, position and direction Statistics (Y2 onwards) Ratio and Proportion (Y6) Algebra (Y6) Investigations and problem solving to promote inter-connections used throughout. Key Stage 1 and the New Curriculum Number and Place Value • Place value is central to mathematics. Recognising that the digit ‘5’ in the number 54 has a different value from the number 5 or the ‘5’ in 504 is an important step in mathematical understanding. • Count, both forwards and backwards, from any number, including past 100 • Read and write numbers up to 100 as digits • Count in 2s, 5s and 10s • Find ‘one more’ or ‘one less’ than a number • Use mathematical language such as ‘more’, ‘less’, ‘most’, ‘least’ and ‘equal’ Key Stage 1 and the New Curriculum Calculation • Use the +, -– and = symbols to write and understand simple number calculations • Represent and use number bonds and related subtraction facts within 20 • Add and subtract one- and two-digit numbers, up to 20 • Solve missing number problems, such as 10 – ? = 6 • Begin to use simple multiplication by organising and counting objects Fractions • Understand 1/ 4 and 1/2 to explain parts of an object or number of objects Key Stage 1 and the New Curriculum Measurement • • • • • Use practical apparatus to explore different lengths, weights and volumes Use language such as ‘heavier’, ‘shorter’ and ‘empty’ to compare things they have measured Recognise the different coins and notes of British currency Use language of time, such as ‘yesterday’, ‘before’, days of the week and months of the year Tell the time to the hour and half-hour, including drawing clock faces Shape • • • Recognise and name some common 2-d shapes, such as squares, rectangles and triangles Recognise and name some common 3-d shapes, such as cubes, cuboids and spheres Describe movements, including quarter turns Calculation methods Concrete objects • Pictorial representations Mental methods Written methods Experience maths using concrete objects. Physically move objects to ‘carry out’ operation • Use Numicon and Diennes to help understanding of number, relative size and how operations link together. • Draw pictures and symbols to represent numbers. • Mental methods – securing children’s fluency, enabling them to use numbers efficiently. Ensure a good understanding of place value. • Use number tracks, number lines and 100 square • Written methods – progressive approach. Initially using expanded method. • Mental v’s written – choosing and using appropriate methods for the question asked Addition and Subtraction 2+3= I buy 2 cakes and my friend buys 3 cakes. How many cakes did we buy altogether? (Children could draw a picture to help them work out the answer) pictures symbols 8+5= 8 people are on the bus. 5 more get on at the next stop. How many people are on the bus now? (Children could use dots or tally marks to represent objects – quicker than drawing a picture) 5–2= I have five cakes. I eat two of them. How many do I have left? (Take away) Drawing a picture helps children to visualise the problem A teddy bear costs £5 and a doll costs £2. How much more does the bear cost? (Find the difference) 13 – 5 = Mum baked 13 biscuits. I ate 5. How many were left? (Take away) Lisa has 13 felt tip pens and Tom has 5. How many more does Lisa have? (Find the difference) Using dots or tally marks is quicker than drawing a detailed picture Addition and Subtraction • Counting on 18 + 5 = +1 18 +1 19 +1 20 +2 18 +1 21 +1 22 23 +3 20 23 24 Addition • 47 + 35 = 82 +10 47 40 +10 57 8 +10 +3 67 30 77 6 +2 80 82 40 8 30 6 70 14 + 70 + 14 = 84 Subtraction 43 – 20 3 43 – 20 = 23 23 – 3 = 20 43 – 20 7 43 – 20 = 2 3 23 – 7= 16 Multiplication Counting in steps of ……. 0 Using pictures and symbols 5 10 15 20 3x2=6 2x4=8 Knowing multiplication facts 25 Multiplication Repeated addition 2+2+2+2=8 4x2=8 2 multiplied by 4 4 lots of 2 14 x 2 = 28 Rectangular array 5 x 3 or 3 x 5 Division Sharing or grouping? 6 cakes shared between 2 6÷2=3 6 cakes put into groups of 2 Division 15 – I wonder how many 5’s? 15 ÷ 5 = 3 0 5 Linking an array to division 10 15