* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Mole
Two-body Dirac equations wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chaos wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Bose–Einstein statistics wikipedia , lookup
Quasi-set theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
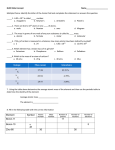
The Mole 23 6.02 X 10 The Mole • 1 pair = 2 representative particles • 1 dozen = 12 representative particles • 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 representative particles The Mole (mol): A unit to count numbers of particles – 1 dozen cookies = 12 cookies – 1 mole of cookies = 6.02 X 1023 cookies – 1 dozen Al atoms = 12 Al atoms – 1 mole of Al atoms = 6.02 X 1023 atoms Note that the NUMBER is always the same, but the MASS is very different! A Mole of Particles Contains 6.02 x 1023 particles • Representative Particle: – Refers to the species present. – Usually atoms, molecules, or formula units. – Example: • Atomic Nitrogen = N • Nitrogen gas = N2 1 mole of all of these = • Water = H2O 23 rep. particles 6.02 x 10 • Calcium ion = Ca2+ • Glucose = C6H12O6 Avogadro’s Number as Conversion Factor 6.02 x 1023 particles 1 mole or 1 mole 6.02 x 1023 particles Note that a particle could be an atom OR a molecule! Learning Check 1. Number of atoms in 0.500 mole of Al a) 0.500 mole of Al b) 6.02 x 1023 Al atoms in 1 mole c) So, in 0.5 mole, 3.01 x 1023 Al atoms 2.Number of moles of S in 1.8 x 1024 S atoms a) 6.02 x 1023 S atoms in 1.0 mole of S atom b) So, 3 x 6.02 x 1023 = 1.8 x 1024 S atoms in 3 x 1 mole= 3.0 mole S atoms c) 3.0 mole S atoms Gram Atomic Mass • Gram Atomic Mass – – Atomic mass of an element expressed in grams. – The gram atomic mass is the mass of 1 mol of atoms of any element. 1 mole of C atoms = 12.0 g 1 mole of Mg atoms = 24.3 g 1 mole of Cu atoms = 63.5 g # of C atoms in12.0 g of C atoms = # of Mg atoms in24.3 g of Mg atoms = # of O atoms in 16.0 g • How many is that? 6.02 x 1023!! Other Names • Gram Molecular Mass/Molecular Weight • Gram Formula Mass/Formula Weight • What is the gram atomic mass (GAM) of 1 mol of the following compounds? – Gram Molecular Mass of SO3 and H2O = ? • SO3 = 80.1g H2O = 18 g – Gram Formula Mass of NaCl and CaI2 = ? • NaCl = 58.5 g CaI2 = 293.9 g Molar Mass( atoms, molecules and compounds) Molar Mass: mass of one mol of any substance(usually we round to the tenths place). A. 1 mole of Br atoms = B. 1 mole of Sn atoms = 79.9 g/mole 118.7 g/mole Mass in grams of 1 mole equal numerically to the sum of the atomic masses 1 mole of CaCl2 = 111.1 g/mol 1 mole Ca x 40.1 g/mol + 2 moles Cl x 35.5 g/mol = 111.1 g/mol CaCl2 1 mole of N2O4 = 92.0 g/mol Learning Check! A. Molar Mass of K2O = ? Grams/mole B. Molar Mass of antacid Al(OH)3 = ? Grams/mole Example: 1. How many grams are in 9.45 mol dinitrogen trioxide? 718.20 g N2O3 2. How many moles are in 92.2 g iron (III) oxide? • 0.58 mol Fe2O3 What is the formula mass of Ca3(PO4)2 ? 1 formula unit of Ca3(PO4)2 3 Ca 3 x 40.08 2P 2 x 30.97 8O + 8 x 16.00 310.18 amu 10 Volume of a Mol • Standard temperature and pressure: – STP – 0°C and 101.3 kPa or 1 atm – At these conditions, 1 mol of any gas = 22.4 L • 1. What is the volume, in L, at 0.60 mol SO2 gas at STP? 13.44 L SO2 (g) • 2. The density of a gaseous compound containing carbon and oxygen is 1.964 g/L at STP. What is the molar mass? 43.99 g/mol Problems, cont. • 3. A gaseous compound composed of sulfur and oxygen is linked in the formation of acid rain and has a density of 3.58 g/L at STP. What is the molar mass? 80.19 g/mol • 4. What is the density of Kr gas at STP? 3.74 g/L Big Helper… 23 N =6.02 x 10 A Molar Mass Representative Grams moles particles Gram atomic mass/ Gram molecular mass/ (Molecules, formula mass Atoms, Molar 22.4 liters Ions, volume (STP) Formula units) Liters Converting Moles and Grams Aluminum is often used for the structure of light-weight bicycle frames. How many grams of Al are in 3.00 moles of Al? 3.00 moles Al ? g Al 1. Molar mass of Al 1 mole Al = 27.0 g Al 2. Conversion factors for Al 27.0g Al 1 mol Al or 1 mol Al 27.0 g Al 3. Setup 3.00 moles Al Answer x 27.0 g Al 1 mole Al = 81.0 g Al Atoms/Molecules and Grams • Since 6.02 X 1023 particles = 1 mole AND 1 mole = molar mass (grams) • You can convert atoms/molecules to moles and then moles to grams! (Two step process) • You can’t go directly from atoms to grams!!!! You MUST go thru MOLES. Calculations molar mass Grams Avogadro’s number Moles particles Everything must go through Moles!!! Atoms/Molecules and Grams How many atoms of Cu are present in 35.4 g of Cu? 35.4 g Cu 1 mol Cu 63.5 g Cu 6.02 X 1023 atoms Cu 1 mol Cu = 3.4 X 1023 atoms Cu Learning Check! How many atoms of K are present in 78.4 g of K? Learning Check! How many atoms of O are present in 78.1 g of oxygen? 78.1 g O2 1 mol O2 6.02 X 1023 molecules O2 2 atoms O 32.0 g O2 1 mol O2 1 molecule O2 Percent Composition • Percent composition: – The percent by mass of each element in a compound. X 100% % mass of element = grams of element grams of compound • 1. Calculate the percent composition of each element in propane, C3H8. • C = 81.82% • H = 18.18% Types of Formulas • Empirical Formula The formula of a compound that expresses the smallest whole number ratio of the atoms present. Ionic formula are always empirical formula • Molecular Formula The formula that states the actual number of each kind of atom found in one molecule of the compound. Empirical Formula • Empirical Formulas: • The lowest whole number ratio of atoms of the elements in a compound. – Example: CO (could be C2O2, C4O4, but not CO2) • *Empirical Formula may or may not be the molecular formula. • Examples: –Hydrogen Peroxide = H2O2 but the empirical formula is HO –Carbon dioxide = CO and it is the To obtain an Empirical Formula 1. Determine the mass in grams of each element present, if necessary. 2. Calculate the number of moles of each element. 3. Divide each by the smallest number of moles to obtain the simplest whole number ratio. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained* in step 3), multiply through by the smallest number that will give all whole numbers * Be careful! Do not round off numbers prematurely Empirical Problems • 1. What is the empirical formula of a compound that is 25.9% nitrogen and 74.1% oxygen? • Looks hard, but follow the three steps… Problem, cont. • Step 1: – Convert % to moles. • 1.85 mol N • 4.63 mol O • Step 2: – Divide both answers by the lowest one. • 1.85 mol N is lowest. 1 mol N –2.5 mol O Problem, cont. • Step 3: – If one answer is a decimal, multiply both by a number so it is converted to a whole number. • 2.5 mol O becomes 5 mol • 1 mol N becomes 2 mol • Answer: N2O5 Chemical Formulas of Compounds • Formulas give the relative numbers of atoms or moles of each element in a formula unit - always a whole number ratio (the law of definite proportions). NO2 2 atoms of O for every 1 atom of N 1 mole of NO2 : 2 moles of O atoms to every 1 mole of N atoms • If we know or can determine the relative number of moles of each element in a compound, we can determine a formula for the compound. A sample of a brown gas, a major air pollutant, is found to contain 2.34 g N and 5.34g O. Determine a formula for this substance. require mole ratios so convert grams to moles moles of N = 2.34g of N = 0.167 moles of N 14.01 g/mole moles of O = 5.34 g = 0.334 moles of O 16.00 g/mole N 0.167 O 0.334 NO 2 Formula: N O 0.167 0.334 0.167 0.167 Determine Empirical Formula 1. 75% carbon, 25% hydrogen 2. 52.7% potassium, 47.3% chlorine 3. 22.1% aluminium, 25.4% phosphorous, 52.5% oxygen 4. 13% magnesium, 87% bromine 5. 32.4% sodium, 22.5% sulfur, 45.1% oxygen Molecular Formulas • Molecular Formulas: – Either the same as the empirical formula or a simple whole number multiple of it. Known molar mass of molecule = Molar mass of empirical form. the number of empirical formula units needed (EFU). Multiply empirical formula with EFU to get the molecular formula Calculation of the Molecular Formula A compound has an empirical formula of NO2. The colourless liquid, used in rocket engines has a molar mass of 92.0 g/mole. What is the molecular formula of this substance?