* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 - pennsaukenchemistry2
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Rigid rotor wikipedia , lookup
Magnetorotational instability wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bose–Einstein condensate wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
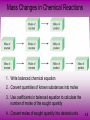
Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions Chapter 3 Natural lithium is: 7.42% 6Li (6.015 amu) 92.58% 7Li (7.016 amu) Average atomic mass of lithium: 100 = _______ amu 3.1 The mole (mol) is the amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in exactly ______ grams of 12C 1 mol = NA =____________________ ___________________ number (NA) 3.2 eggs Molar mass is the mass of 1 mole of shoes in grams marbles atoms 1 mole 12C atoms = ____________ atoms = ______ g 1 12C atom = 12.00 amu 1 mole 12C atoms = ___________ g 12C 1 mole lithium atoms = ___________ g of Li For any element ___________ (amu) = __________ (grams) 3.2 One Mole of: S C Hg Cu Fe 3.2 _____ g = ________________ amu 1 amu = ______________ g M = molar mass in g/mol NA = Avogadro’s number 3.2 Do You Understand Molar Mass? How many atoms are in 0.551 g of potassium (K) ? 3.2 Molecular mass (or molecular weight) is the sum of the atomic masses (in amu) in a molecule. SO2 1S 2O amu amu SO2 amu For any molecule ________ mass (amu) = ______ (grams) 1 molecule SO2 = _________ amu 1 mole SO2 = ________ g SO2 3.3 Do You Understand Molecular Mass? How many H atoms are in 72.5 g of C3H8O ? 3.3 Percent composition of an element in a compound = n x molar mass of element x 100% molar mass of compound n is the number of moles of the element in 1 mole of the compound C2H6O 3.5 Types of Formulas • ____________ Formula The formula of a compound that expresses the _________________ ratio of the atoms present. Ionic formula are always ____________ formula • _______ Formula The formula that states the _____ number of each kind of atom found in _________ of the compound. To obtain an Empirical Formula 1. Determine the _______________ of each element present, if necessary. 2. Calculate the number of _________ of each element. 3. Divide each by the smallest number of moles to obtain the_______________. 4. If _____numbers are not obtained* in step 3), multiply through by the _____ number that will give all whole numbers * Be careful! Do not round off numbers prematurely A sample of a brown gas, a major air pollutant, is found to contain 2.34 g N and 5.34g O. Determine a formula for this substance. require mole ratios so convert grams to moles Calculation of the Molecular Formula A compound has an empirical formula of NO2. The colourless liquid, used in rocket engines has a molar mass of 92.0 g/mole. What is the molecular formula of this substance? Empirical Formula from % Composition A substance has the following composition by mass: 60.80 % Na ; 28.60 % B ; 10.60 % H What is the empirical formula of the substance? Consider a sample size of _____ grams This will contain: _____ grams of Na, ______ grams of B, and _____ grams H Determine the number of ______ of each Determine the ________ number ratio Combust 11.5 g ethanol Collect 22.0 g CO2 and 13.5 g H2O g CO2 mol CO2 mol C gC 6.0 g C = 0.5 mol C g H2O mol H2O mol H gH 1.5 g H = 1.5 mol H g of O = g of sample – (g of C + g of H) 4.0 g O = 0.25 mol O Empirical formula C0.5H1.5O0.25 Divide by smallest subscript (0.25) Empirical formula C2H6O 3.6 Mass Changes in Chemical Reactions 1. Write balanced chemical equation 2. Convert quantities of known substances into moles 3. Use coefficients in balanced equation to calculate the number of moles of the sought quantity 4. Convert moles of sought quantity into desired units 3.8 Other units • Molarity – Moles solute / L solution • Gases – 22.4 L = 1 mole of ANY GAS at STP Methanol burns in air according to the equation 2CH3OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 4H2O If 209 g of methanol are used up in the combustion, what mass of water is produced? 3.8 Limiting Reagents 6 red green leftused overup 3.9 Method 1 • • • • Pick A Product ????? The ____ answer will be the correct answer The _____that gives the _____answer will be the _______ reactant Limiting Reactant: Method 1 • 10.0g of aluminum reacts with 35.0 grams of chlorine gas to produce aluminum chloride. Which reactant is limiting, which is in excess, and how much product is produced? 2 Al + 3 Cl2 2 AlCl3 • Start with Al: • Now Cl2: Method 2 • Convert one of the reactants to the _____ • See if there is enough _______ to use up the other ______ • If there is less than the ______amount, it is the ______ reactant • Then, you can find the desired species Do You Understand Limiting Reagents? In one process, 124 g of Al are reacted with 601 g of Fe2O3 2Al + Fe2O3 Al2O3 + 2Fe Calculate the mass of Al2O3 formed. 3.9 Use limiting reagent (Al) to calculate amount of product that can be formed. g Al mol Al mol Al2O3 g Al2O3 3.9 Finding Excess Practice • 10.0g of aluminum reacts with 35.0 grams of chlorine gas 2 Al + 3 Cl2 2 AlCl3 • We found that _______ is the limiting reactant, and _______ of aluminum chloride are produced. Given amount of excess reactant Amount of excess reactant actually used Note that we started with the limiting reactant! Once you determine the LR, you should only start with it! ___________ is the amount of product that would result if all the limiting reagent reacted. _________ is the amount of product actually obtained from a reaction. % Yield = _________Yield x 100 _________Yield 3.10