* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Base e and Natural Logarithms 10.5
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Function (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
History of the function concept wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
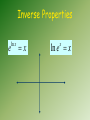
Base e and Natural Logarithms E.Q: How do I use logarithms to solve exponential equations? How do I use the properties of exponents to simplify logarithmic expressions and solve logarithmic equation? CCSS: F.IF.7e; F.LE.3; F.IF.5; F.BF.5 CCSS: F.IF.7e; F.IL.3 • GRAPH exponential and logarithmic functions, showing intercepts and end behavior. • OBSERVE using graphs and tables that a quantity increasing exponentially eventually EXCEEDS a quantity increasing linearly, quadratically, or (more generally) as a polynomial function. CCSS: F.IF.5; F.BF.5 • RELATE the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship it describes. For example, if the function h(n) gives the number of person-hours it takes to assemble n engines in a factory, then the positive integers would be an appropriate domain for the function.* Emphasize the selection of a model function based on behavior of data and context • Understand the inverse relationship between exponents and logarithms and use this relationship to solve problems involving logarithms and exponents. Standards for Mathematical Practice 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. History The number e is a famous irrational number, and is one of the most important numbers in mathematics. The first few digits are 2.7182818284590452353602874713527... It is often called Euler's number after Leonhard Euler. e is the base of the natural logarithms (invented by John Napier). Calculating The value of (1 + 1/n)n approaches e as n gets bigger and bigger: (1 + 1/n)n n 1 2.00000 2 2.25000 5 2.48832 10 2.59374 100 2.70481 1,000 2.71692 10,000 2.71815 100,000 2.71827 Vocabulary natural base: the number e, which is found using 1 1 n n • the base rate of growth shared by all continually growing processes • Used heavily in science to model quantities that grow & decay continuously natural base exponential function: an exponential function with base e Vocabulary natural logarithm: a logarithm with base e The natural log gives you the time needed to reach a certain level of growth. natural logarithmic function: the inverse of the natural base exponential function Ex 1 e 0.5 Use a calculator to estimate to four decimal places. Ex 2 e 8 Ex 3 Ex 4 ln 3 1 ln 4 Writing Equivalent Expressions Exponential logarithmic Write an equivalent equation in the other form. Ex 5 Ex 6 e x 23 e 6 x Ex 7 Ex 8 ln x 1.2528 ln x 2.25 Inverse Properties e ln x x ln e x x Writing Equivalent Expressions Ex 9 Evaluate Ex 10 e ln 21 Ex 11 Evaluate ln e x2 1 Evaluate e ln x 3 Ex 12 Evaluate ln e 7 Solving Equations Ex 13 Solve the following equations. 3e2 x 4 10 Ex 14 2 x 2e 5 15 Solving Equations Ex 15 Solve the following equations. ln 3x 0.5 Ex 16 ln x 3 3