* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1st Semester Exam Review2
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Surface wave inversion wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
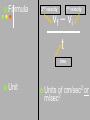
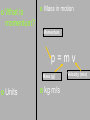
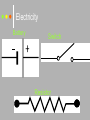
st 1 Semester Exam Review Lab Equipment Test tubes Watch glass Erlenmeyer flask Beakers Graduated cylinder Triple beam balance Lab Equipment Which of the following measure volume? Lab Equipment Measuring First Volume read the liquid at eye level Second, read the volume at the curve of the meniscus. MEASUREMENTS What is this measuring device called? Graduated Cylinder What is it used to measure? Volume of liquids What is the curved line called? Meniscus What is the measurement? 50 .0 mL Which is more precise: a graduated cylinder or a beaker? Why? Graduated cylinder is more precise because it measures in smaller intervals. Lab Equipment Which of the following measure mass? MEASUREMENTS 1. What is this measuring device called? _______________ Triple Beam Balance 2. What is it used to measure? Mass of solids _________________ 3. What is the measurement below? ___________ 365.4 grams 4. What are the correct units? ________________ Grams (g) Precision vs Accuracy What is precision? Precision indicates how close together or how repeatable the results are. A precise measuring instrument will give very nearly the same result each time it is used. What is accuracy? Accuracy indicates how close a measurement is to the accepted value. For example, we'd expect a balance to read 100.00 grams if we placed a standard100.00 g weight on the balance. If it does not, then the balance is inaccurate. MEASUREMENTS 1. Which of the following is more precise? Why? The first one is more precise because it measures in smaller intervals. A student measured the length of a piece of string that was 64.34 cm long. Her measurements were 64.32 cm, 64.34 cm, 64.35 cm, and 64.34 cm. Which of the following statements is true? The measurements were accurate but not precise. The measurements were precise but not accurate. The measurements were both precise and accurate. The measurements were neither accurate nor precise. Lab Safety General guidelines Safety first! Your main responsibility in lab is to prevent injuries of yourself and your partners!! Never work alone. Always read the directions before starting the lab. Know where all safety equipment is located and emergency contact numbers. No eating and drinking in lab (or tasting the chemicals!) Report ALL accidents to teacher. Lab Safety continued…. Eye protection and Clothing Before starting lab, tie back long hair, roll up sleeves. Put on any protective equipment that teacher requires: • Ex: apron, lab coat, goggles, gloves, closed-toe shoes, etc.) Always wear approved GOGGLES while in lab…**even if you are NOT conducting an experiment at the time. No contact lenses in lab The eyewash is available to rinse out hazardous chemicals in the eye. Disposal Safety AVOID Use HAZARDS caution when handling hot glassware. When diluting acid, always add acid slowly to water. Never add water to acid. Always read the directions or consult your MSDS when disposing chemicals!! During a lab activity, isopropyl alcohol is splashed into a student’s eyes. What should the student do? A Run to the nurse’s office B Put on safety goggles C Flush eyes with water D Wipe eyes with a cloth Scientific Method How many Data Trends How many students do you predict will have a cell phone by the year 2009? 15 thousand 18 thousand 19 thousand 20 thousand Hypothesis What is a hypothesis? A hypothesis is an educated guess that can be tested by experimentation. Theory What is a theory? An explanation of things or events based on many observations. Can it be changed? • YES!! It can be changed as new data uncovers new information. Which statement is true about a theory? A. A theory can not be changed according to new data. B. A theory does not have to be repeated, because it based on only one observation. C. A theory is an explanation of things and events based on many observations. D. A theory is can never become a Speed is how fast you are going. Units: meters per sec (m/s) Position vs time graph The position vs time graph shows where things are at different times Speed is the slope of the position vs time graph 5 secs 275 m 150m / 5 sec =30 m/sec speed time position 14 m 14 m / 4 sec = 3.5 m/s speed speed B A Acceleration & Momentum rate at which speed changes What is acceleration? Rate of change means the ratio of the amount of change divided by how much time it took to change Formula 2nd velocity 1st velocity vf – vi t time Unit 2 or of cm/sec m/sec2 Units Positive acceleration (speeding up) Deceleration (slowing down) Zero acceleration (constant speed) Acceleration is the slope of the speed vs. time graph DON’T WRITE What is momentum? Mass in motion Momentum p=mv Mass (g) Units kg m/s Velocity (m/s) A force is a push or a pull What is force? F = ma Force (N) Mass (g) Acceleration (m/s2) Acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/sec2) Weight Force (N) Fw = m g Mass (kg) • Gravity (g) is a force that pulls every mass toward the Earth; its different depending on your planet. • Earth g=9.8 m/sec2 (ALWAYS!!!) • Mars g=3.8 m/sec2 (ALWAYS!!!) Kinetic Energy What is kinetic energy? Energy of motion Potential Energy What is potential energy? Stored energy ? ? ? Law of Conservation of Energy What does the Law of Conservation of Energy state? Energy can never be created or destroyed – it can only be turned into another form. Electricity A circuit is a continuous loop that provides a pathway for electricity to travel through. There are 2 types: Open circuits: an open circuit is a circuit that has a break in it. • An open circuit is said to be ‘turned off.’ Closed circuits: a closed circuit has no breaks in it and therefore the electrical current is flowing in a closed circuit. • A closed circuit is said to be ‘turned on.’ Electricity Battery Switch Resistor Electricity In a series circuit there is only one path for the current. If a light burns out in a series circuit all the lights will go out. In a parallel circuit the current can flow in more than one path. If a light burns out in a parallel circuit the others will not go out. Electricity Law of Conservation of Energy Energy can never be created or destroyed – it can only be turned into another form. How much current would be measured in the circuit below if each resistor had a resistance of 5 ohms? I=V/R I= 6v/ 2* 5 Ω I= 0.6 amps Heat Transfer Three mechanisms for heat transfer • Conduction • Convection • Radiation Heat transfer Conduction – heat transfer by direct contact of particles EX.- Spoon in hot cup of coffee Convection – transfer of heat by bulk movement of fluid and gases EX- radiator, sea breeze Radiation – heat transfer in the form of waves EX.- Light, microwaves, radio waves, x-rays Thermal Energy is the total energy of the particles in a material – both kinetic and potential Greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is the warming of Earth due to carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere. Warming occurs as sunlight strikes the Earth. Much of the sunlight is reflected back into space. But Earth's atmosphere absorbs much of the heat and slows its escape from Earth. In this way, the Earth is like a greenhouse. The atmosphere encloses the Earth just as panes of glass enclose a greenhouse. transverse Transverse Waves Transverse wave: has its oscillations perpendicular to the direction of the wave. The wave moves left to right and the oscillation moves up and down Ocean waves are transverse waves longitudinal Longitudinal Wave Longitudinal wave: has oscillations in the same direction the wave moves. Sound is a longitudinal wave Parts of a Transverse Wave What are the parts of a transverse waves? Crest • The highest point of a wave CREST Trough • The lowest point of a wave REST POSITION TROUGH Rest Position • The resting position from which other things are measured Speed Speed describes how fast the wave moves Speed is frequency (f) times wavelength (l) v fl Speed (m/sec) Wavelength (m) Frequency (hz) Reflection: bounce off and goes in a new direction. Refraction: bends as it crosses the edge Ripple Tank Diffraction: bends as it goes around a corner or through an opening Absorption: amplitude gets smaller and smaller as it passes through the material Tacoma Resonance Resonance occurs when a force exerted on an object exactly matches the natural frequency of the object When resonance occurs only a small force is needed to get a large response. If you shake a string at the right frequency, if makes a big wave motion. If your frequency is not just right, the string will not make a wave pattern at all Formula Cheat Sheet