* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DC Circuits
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
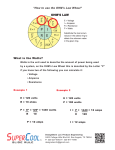
DC Circuit – Practice Problems Problem 1 – Parallel bulbs, ceiling lamps and you. Problem 2 – The Current Issue of Powerful Computing? Problem 3 – If a voltmeter were a car it would park like this? Problem 4 – It costs how much? You’ve got to be kidding! Summary - What did I learn? Here is what you should learn! Click on this icon to return to the this slide. Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer P r o b l e m 1 Consider a ceiling lamp made from 3 bulbs wired in parallel. The bulbs are rated 100, 75 and 60 watts respectively and operate at 120 volts. A. Clearly Sketch and label a circuit diagram modeling the ceiling lamp. The lamps are the only elements using energy in the circuit . The circuit is protected by a 15 amp circuit breaker. B. Calculate the current through each individual bulb. C. Discuss relationships that exists between individual bulb currents, total lamp current & the circuit breaker. Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer A n s w e r 1 A P r o b l e m 1 P r o b l e m 1 The current through each individual bulb depends on the power rating of the bulb. The power rating on each bulb measures the rate of which the bulb can transform electrical energy into heat and light energy: the greater the power, the greater the current. The greatest current is through the 100 watt bulb and least through the 60 watt bulb. The sum of individual bulb currents add to equal the total lamp current. If the lamp current exceeds the limit set by the circuit breaker the circuit will open resulting in no current flow. I = 0 amps. Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer Answer 1B P r o b l e m 1 P r o b l e m 1 60 w R1 120 V 75 w R2 100 w R3 Power is the product of current and voltage therefore, current is the ratio of power to voltage. In parallel each bulb has the same voltage across it. P IV I P V P1 I1 V I1 = 0.5 amps P2 I2 V I2 = 0.625 amps P3 I3 V I3 = 0.833 amps Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer Problem 2 Monitor 2.2 amps Lamp 1 .2 amps Speakers 1.5 amps How much power is used to operate this computer workstation? Each device operates at 120 volts. Computer 4.0 amps Video Camera .375 amps Scanner .52 amps Printer .667 amps Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer Answer 2 Lamp 144 watts Video Camera 45 watts Scanner 62.4 watts Computer 480 watts Speakers 180 watts Monitor 264 watts Printer 80 watts TOTAL CURRENT = 10.46 AMPS TOTAL POWER = 1255 WATTS (1.26 kW) Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer If Voltmeter Were a Car It Would Park In Parallel! V Consider the adjacent Series Circuit: R1 15 V R2 A R3 V R1=4.5 Ohms V 1) Draw an equivalent circuit and calculate the equivalent resistance. 2) Calculate the current reading on the ammeter. 3) Calculate the voltage drop across each Resistor. R2=7.5 Ohms R3=8 Ohms Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer Answer 3 15 V Req A V 1) The equivalent resistance is Req = 20 Ohms. 2) The current in the circuit is I = 0.75 Ampere. 3) The Voltage Drops across: VR1 = 3.375 Volts VR2 = 5.625 Volts VR3 = 6.0 Volts Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer P r o b l e m 4 Scanner 62.4 watts Speakers 180 watts Computer 480 watts Monitor 264 watts Lamp 144 watts Calculate the cost of operating Video Camera 48 watts this computer system for 1 month at $ 0.10 per kwh. (24 hours x 30 days.) Printer 80 watts Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer Answer 4 $ 90.36 per month Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer Summary of DC Circuits Parallel Circuits 1) The voltage is constant across circuit elements in parallel. 2) The current through circuit elements in parallel can change. 3) The sum of individual currents add to equal the total system current. 4) The sum of the individual element’s power add to equal the total system power. 5) Power = Energy / Time = I x V = V2/R = I2 x R Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer Summary of DC Circuits Series Circuits 1) The current circuit elements wired in series is constant. 2) The voltage can change across a circuit element wired in series. 3) The sum of voltage drops across individual circuit elements equals the voltage of the power supply. 4) The equivalent resistance of a circuit with more than one circuit element wired in series is equal to the sum of the individual circuit element’s resistance. Copyright - Adam Randall & Ann Roemer