* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AMT – 101 General Aircraft Technology Drawings
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
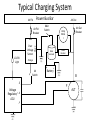
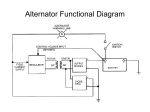
Troubleshooting Aircraft Charging Systems (Alternators/Reciprocating Engines) by Herb Spenner Troubleshooting Steps 1. 2. 3. 4. Setup Connections Electrical Components Finish Up Setup • Avionic must be turned off – Protects them from damage • Master switch – On – when checking voltage • Master switch – Off – when checking resistance • Select multi-meter range before measuring • Secure item before running engine Connections • Check circuit breakers – If tripped, find out why – Remind customer of Special Airworthiness Information Bulletin (SIAB) CE 11-10 • Electrical: Fire Hazard in Resetting Circuit Breakers • Check grounding straps – Refer to AC 43.13-1B – 11-188 – Use Low Ohm Meter (LMO) to check connections • Standard multi-meter not sensitive enough • See Practical Low Resistance Measurement – Bob Neckolls Connections • • • • Check all mechanical connections are tight Cleanup all corrosion Check for damaged insulation Recommend customer replace old aluminum battery cable – Better cold starts – Save money through longer component life • Check alternator belt • Insure alternator bearings work smoothly Typical Charging System Power Bus Bar Alt Fld Alt Fld Breaker Main Switch Black Main Solenoid Shunt Resister Orange + Alt Switch - LO/OV Light Alt Out Breaker Amp Mete r Red Over Voltage Sensor Alt Out Battery B I S Voltage Regulator/ ACU A F F ALT Electrical Components • Voltage Testing Setup (Voltage On) – Master switch (Bat & Alt) - On – Alternator field switch – On – Alternator field and Main alternator breaker – On – To generate a load, turn landing lights on • Check Amp Meter with load on – If needle deflects, it is OK – If no deflection plus voltage on connections and shunt resistor, replace meter Voltage Regulator • With Voltage On, check voltage regulator pins – All pins should be close to Power Bus Bar voltage • If Pin S is low, check Over Voltage Sensor (OVS) connections – If OVS connections are good, OVS is bad • If Pin F is low – Disconnect Pin F to alternator lead – If Pin F is still low, replace Voltage Regulator • Regulator is shorted, also check if alternator field shorted – If Pin F is high, check alternator Voltage Regulator • If Pin A is low – Usually a connection problem • If Pin I is high and LV/OV light is out – Check bulb and wiring Alternator • Disconnect alternator leads and check alternator – voltage off • Check resistance between F (field lead) and ground connection – Range – 3 to 6 ohms – If low, field coil is shorted - replace alternator – If high • Service brushes and clean commutator • Resistance still high, field coil is broken - replace alternator Alternator • Check for open Stator by measuring resistance between B (battery lead) and ground – If high, stator is open and alternator needs to be replaced • Check for shorted diode bridge – Place a multi-meter in series with alternator B lead to measure leakage current – If leakage current is over 0.5 ma, bridge is bad – replace alternator Alternator • Check for open diode bridge – Power on, engine at 1500 RPM and lights on – Check AC voltage on B lead • If over 0.5 V, bridge is bad – replace alternator Alternator • Check alternator output – Install multi-meter to measure current in to F lead – If current is 3.5 A or higher and alternator output is still low, replace alternator • If still unable to determine problem, run external regulator test outlined in Alternator Test Regulator handout Finish Up • Do a final complete system test with engine running and lights on • Charge/test battery – Remember Diamond DA42 crash • Reinstall and tighten all components • Clean aircraft – Return aircraft in as-good or better shape than you received it • Complete logbook entry and work order Troubleshooting Steps 1. 2. 3. 4. Setup Connections Electrical Components Finish Up Topic • Solid State Voltage Regulators and Alternators – Most common solution – Piston engine • Not covered (because of time limitations) – Battery problems – Generators – Mechanical regulators – Turbine charging systems – Rebuild alternator