* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4 Like Father, Like Son
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Literary Welsh morphology wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish pronouns wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Danish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
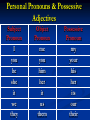
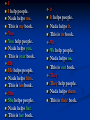
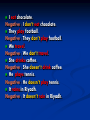
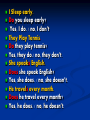
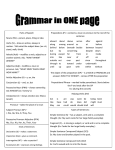
Unit 4 Like Father, Like Son Possessive Case ‘s is used with singular nouns : A man’s job A child’s voice A simple apostrophe(‘) is used with plural nouns ending in s: The girls’ school The students’ class We add ‘s to the last noun of phrase to show possession: This is Ahmed and Ali’s father 1. This is my son’s/sons bicycle. son’s 2. This is Jenny/Jenny’s desk. Jenny’s 3. That is Tony and Pam's/ Tony's and Pam house. Tony and Pam's 4. Those are Bob/Bob’s shoes. Bob’s 5. These are the boys/boys’ bicycles. boys’ Personal Pronouns & Possessive Adjectives Subject Pronoun I you he she it we they Object Pronoun me you him her it us them Possessive Pronoun my your his her its our their I I help people. Nada helps me. This is my book. You You help people. Nada helps you. This is your book. He He helps people. Nada helps him. This is his book. She She helps people. Nada helps her. This is her book. it It helps people. Nada helps it. This is its book. We We help people. Nada helps us. This is our book. They They help people. Nada helps them. This is their book. Who’s/Whose Who’s = Who is Who’s is used to ask about a person. “Who’s Ahmed?” “He is my brother” “Who’s your teacher?” “Sahar” Whose Whose is used to ask about an entity possessor (Owner). “Whose book is this?” “Maha’s” “Whose brother is Ahmed?” ”Ali’s” Excersise: “---------- mother is Nourah?” ” Hala’s” Whose “---------- sheet is this?” “Sarah’s” Whose “---------- Nourah?” ” she is Hala’s mother” Who is (who’s) “---------- Sarah’s sister?” ” Amal” Who is (who’s) “---------- bag is this?” ” Nada’s” Whose “---------- your father?” ” Omar” Who is (who’s) Possessive Adjective & Possessive Pronoun Possesive adjective Possessive pronoun my your his her its our your their mine yours his hers -----ours yours theirs Possessive Pronoun Possessive adjectives come before a noun. It’s my dog. It’s our dog. It’s his dog. It’s their dog. Possessive Pronouns don’t take a noun after them. This dog is mine. This dog is ours. This dog is his. This dog is theirs. “Who’s/Whose is Ann” ”She’s my/mine sister”. Who’s my “Is this bag your/yours?” “No, it’s Sheila’s/Sheila” yours Sheila’s “Who/Whose dog is that?” ”it’s their/theirs” Whose theirs “Are those balls your/yours” ”yes, they’re our/ours” yours ours “Who’s he?” ”Tom’s and Julie’s/Tom and Julie’s father Tom and Julie’s Possessive Adjective & Possessive Pronoun Possessive adjective This is my Possessive pronoun house It’s mine your yours his his her hers its ------ our ours your yours their theirs Present Simple Affirmative (Positive) Subject I We You They He She It Simple present live in Riyadh lives in Riyadh Present Simple Present Simple tense is used to express Permanent states , repeated actions and daily routines. Examples: I live in Riyadh ----> Permanent States She goes to the park every Friday ----> repeated actions He Smokes ----> daily routines. Most verbs take –s with (he, she, it) He sings , She plays , It speaks loudly With (he, she, it) We add –es to verbs ending in -sh, -ch, -ss,-x , -o He teaches English , She kisses the baby. Ahmed Fixes the car , Nada does the job With (he, she, it) if the verb ends with a consonant +y , we drop the y and add –ies Study ----> He studies English. fly ----> He flies to London. Present Simple Negative Subject I We You They He She It do not (don’t) does not (doesn't) Simple present live in Riyadh I eat chocolate. Negative : I don’t eat chocolate. They play football. Negative : They don’t play football. We travel. Negative : We don’t travel. She drinks coffee. Negative : She doesn’t drink coffee. He plays tennis. Negative : He doesn’t play tennis. It rains in Riyadh. Negative : It doesn’t rain in Riyadh. Interrogative (Question) Subject Do Does I We You They He She It Simple present live in Riyadh ? I Sleep early. Do you sleep early? Yes, I do. / no, I don’t They Play Tennis. Do they play tennis? Yes, they do./ no, they don’t. She speaks English. Does she speak English? Yes, she does. / no, she doesn’t. He travels every month. Does he travel every month? Yes, he does. / no, he doesn’t.