* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture2
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Berkeley Software Distribution wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
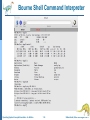
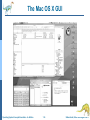
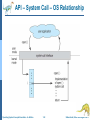
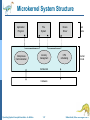
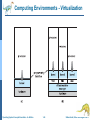
Lecture 2: Operating System Operations System Calls Operating System Structure Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating-System Operations Dual-mode operation allows OS to protect itself and other system components User mode and kernel mode Mode bit provided by hardware Provides ability to distinguish when system is running user code or kernel code Some instructions designated as privileged, only executable in kernel mode System call changes mode to kernel, return from call resets it to user Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.2 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating-System Operations (cont.) Benefits of Dual Mode: MSDOS for 8088 architecture had no mode bit—no dual mode An errant user program could wipe out the OS data Multiple programs are able to write to a device at the same time Current Intel CPUs have all mode bits Most contemporary operating systems, Windows, Unix, Linux, Solaris take advantage of this feature and provide greater protection of the OS. Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.3 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Process Management A process is a program in execution. It is a unit of work within the system. Program is a passive entity, process is an active entity. Process needs resources to accomplish its task CPU, memory, I/O, files Process termination requires reclaim of any reusable resources Single-threaded process has one program counter specifying location of next instruction to execute Process executes instructions sequentially, one at a time, until completion Typically system has many processes, some user, some operating system running concurrently on one or more CPUs Concurrency by multiplexing the CPUs among the processes Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.4 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Process Management Activities The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with process management: Creating and deleting both user and system processes Suspending and resuming processes Providing mechanisms for process synchronization Providing mechanisms for process communication Providing mechanisms for deadlock handling Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.5 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Memory Management To execute a program all (or part) of the instructions must be in memory All (or part) of the data that is needed by the program must be in memory. Memory management determines what is in memory and when Optimizing CPU utilization and computer response to users Memory management activities Keeping track of which parts of memory are currently being used and by whom Deciding which processes (or parts thereof) and data to move into and out of memory Allocating and deallocating memory space as needed Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.6 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Storage Management OS provides uniform, logical view of information storage Abstracts physical properties to logical storage unit - file OS maps files onto physical media and accesses these files via the storage devices (i.e., disk drive, tape drive) File-System management Files usually organized into directories Access control on most systems to determine who can access what (e.g. read/write/execute access) OS activities include Creating and deleting files and directories Primitives to manipulate files and directories Mapping files onto secondary storage Backup files onto stable (non-volatile) storage media Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.7 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 I/O Subsystem One purpose of OS is to hide peculiarities of hardware devices from the user I/O subsystem responsible for Memory management of I/O including buffering (storing data temporarily while it is being transferred), caching (storing parts of data in faster storage for performance), spooling (the overlapping of output of one job with input of other jobs) General device-driver interface Drivers for specific hardware devices Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.8 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Protection and Security Protection – any mechanism for controlling access of processes or users to resources defined by the OS Security – defense of the system against internal and external attacks Huge range of attacks: denial-of-service (using all resources and keeping legitimate users out of the system), worms, viruses, identity theft, theft of service (unauthorized use of a system) On some systems an OS function, while some leave it to additional software. Systems generally first distinguish among users, to determine who can do what User identities (user IDs--security IDs in Windows) include name and associated number, one per user User ID then associated with all files, processes of that user to determine access control Group identifier (group ID) allows set of users to be defined and controls managed, then also associated with each process, file Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.9 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Open-Source Operating Systems Operating systems made available in source-code (like Linux) format rather than just compiled binary code (like Windows) Mac OS X and iOS: hybrid, open-source kernel called Darwin, but also closed-source components. Interested programmers can freely debug, analyze, support and provide changes. Learning tool for students: modify, compile, run. Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.10 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Open-Source Operating Systems-History To counter the move to limit software use and redistribution In 1983, Richard Stallman started the GNU project to create a free, open- source Unix compatible OS. founded the Free Software Foundation (FSF), “copyleft” GNU Public License (GPL) requires source code to be distributed with binaries. Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.11 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Open-Source Operating Systems-History Examples include GNU/Linux Linus Torvalds originally Enhanced by several thousand programmers Spawned many distributions: RedHat, Fedora, Debian, Ubuntu BSD UNIX Distributions: FreeBSD, OpenBSD Darwin: core of Mac OS X Solaris: Commercial UNIX-based OS of Sun Microsystems partially open-sourced as some of the code is still owned by At&T. Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.12 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 User Operating System Interface - CLI Command-line interface (CLI) or command interpreter allows direct command entry Sometimes implemented in kernel, sometimes by systems program Sometimes multiple flavors implemented – shells Unix/Linux: Bourne Shell, C Shell, Korn Shell, etc. Primarily fetches a command from user and executes it Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.13 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Bourne Shell Command Interpreter Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.14 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 User Operating System Interface - GUI User-friendly desktop metaphor interface Usually mouse, keyboard, and monitor Icons represent files, programs, actions, etc Various mouse buttons over objects in the interface cause various actions (provide information, options, execute function, open directory (known as a folder) Invented at Xerox PARC Many systems now include both CLI and GUI interfaces Microsoft Windows is GUI with CLI “command” shell Apple Mac OS X is “Aqua” GUI interface with UNIX kernel underneath and shells available Unix and Linux have CLI with optional GUI interfaces (CDE, KDE, GNOME) Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.15 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 The Mac OS X GUI Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.16 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Touchscreen Interfaces Touchscreen devices require new interfaces Mouse not possible or not desired Actions and selection based on gestures Virtual keyboard for text entry Voice commands. Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.17 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 System Calls Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Programming Interface (API) Set of functions that are available to an application programmer, including their parameters, and return values Three most common APIs are Win32 API for Windows, POSIX API for POSIX-based systems (including virtually all versions of UNIX, Linux, and Mac OS X), and Java API for the Java virtual machine (JVM) A programmer accesses an API via a library of code E.g. libc in UNIX/Linux for C programmers Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.18 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Example of System Calls System call sequence to copy the contents of one file to another file Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.19 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Example of Standard API Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.20 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 System Call Interface Managed by run-time support library (set of functions built into libraries included with compiler) Intercepts API function calls Typically, a number associated with each system call System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface invokes the intended system call in OS kernel and returns status of the system call and any return values The caller need know nothing about how the system call is implemented Just needs to obey API and understand what OS will do as a result call Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.21 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 API – System Call – OS Relationship Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.22 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 System Call Parameter Passing Often, more information is required than simply identity of desired system call Exact type and amount of information vary according to OS and call Three general methods used to pass parameters to the OS Simplest: pass the parameters in registers In some cases, may be more parameters than registers Parameters stored in a block, or table, in memory, and address of block passed as a parameter in a register This approach taken by Linux and Solaris Parameters placed, or pushed, onto the stack by the program and popped off the stack by the operating system Block and stack methods do not limit the number or length of parameters being passed Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.23 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Parameter Passing via Table Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.24 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Types of System Calls Process control create process, terminate process get process attributes, set process attributes wait for time wait event, signal event allocate and free memory Locks for managing access to shared data between processes Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.25 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Types of System Calls File management create file, delete file open, close file read, write, reposition get and set file attributes Device management request device, release device read, write, reposition get device attributes, set device attributes logically attach or detach devices Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.26 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Types of System Calls (Cont.) Information maintenance get time or date, set time or date get system data, set system data get and set process, file, or device attributes Communications create, delete communication connection send, receive messages if message passing model to host name or process name From client to server Shared-memory model create and gain access to memory regions transfer status information Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.27 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Types of System Calls (Cont.) Protection Control access to resources Get and set permissions Allow and deny user access Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.28 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Examples of Windows and Unix System Calls Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.29 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Standard C Library Example C program invoking printf() library call, which calls write() system call Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.30 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Example: FreeBSD Unix variant Multitasking User login -> invoke user’s choice of shell Shell executes fork() system call to create process Executes exec() to load program into process Shell waits for process to terminate or continues with user commands Process exits with: code = 0 – no error code > 0 – error code Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.31 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Structure General-purpose OS is very large program Various ways to structure ones Monolithic Layered Microkernel Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.32 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Monolithic -- UNIX UNIX – limited by hardware functionality, the original UNIX operating system had limited structuring. The UNIX OS consists of two separable parts Systems programs (compilers, editors, system libraries, etc.) The kernel Consists of everything below the system-call interface and above the physical hardware Provides the file system, CPU scheduling, memory management, and other operating-system functions; Disadv: a large number of functions for one level – Difficult to implement and maintain Performance adv: minimum overhead for communication within the kernel Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.33 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Traditional UNIX System Structure Beyond simple but not fully layered Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.34 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Layered Approach The operating system is divided into a number of layers (levels), each built on top of lower layers. The bottom layer (layer 0), is the hardware; the highest (layer N) is the user interface. With modularity, layers are selected such that each uses functions (operations) and services of only lower-level layers Adv: Simplicity of construction and debugging Difficulty: appropriately defining various layers Disadv: added overhead by each layer Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.35 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Microkernel System Structure Nonessential components removed from the kernel and implemented as system or user programs. Kernel contains minimal process and memory management and communication facility. Mach example of microkernel Mac OS X kernel (Darwin) partly based on Mach Main function: provide communication between client programs and various services also running in user-space Communication takes place between user modules using message passing Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.36 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Microkernel System Structure Application Program File System messages Interprocess Communication Device Driver user mode messages memory managment CPU scheduling kernel mode microkernel hardware Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.37 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Microkernel System Structure Benefits: Easier to extend a microkernel, new services added to user space, no or minimal modification to the kernel More secure (less code is running in kernel mode) Detriments: Performance overhead of user space to kernel space communication Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.38 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Modules Many modern operating systems implement loadable kernel modules Has a set of core components Links in additional modules during boot time or runtime Dynamic linking as the kernel is running Each talks to the others over known interfaces Overall, similar to layered approach but with more flexible since each module can call each module Linux, Solaris, etc Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.39 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Hybrid Systems Most modern operating systems are actually not one pure model Hybrid combines multiple approaches to address performance, security, usability needs Linux and Solaris kernels in kernel address space, so monolithic, plus modular for dynamic loading of functionality Windows mostly monolithic, plus retains some microkernel behaviour providing support for user-space different subsystems Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.40 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Hybrid Systems Apple Mac OS X Somewhat layered and microkernel behaviour At the top: Aqua UI plus a set of application environments (such as Cocoa programming environment) Below is kernel consisting of Mach microkernel Memory management IPC (interprocess communication), message passing and BSD Unix kernel parts, Command-line interface Networking File system plus I/O kit and dynamically loadable modules (called kernel extensions) Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.41 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Mac OS X Structure graphical user interface Aqua application environments and services Java Cocoa Quicktime BSD kernel environment BSD Mach I/O kit Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition kernel extensions 1.42 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Virtual Machines (VM) Allows operating systems to run as applications within other operating systems. Vast and growing industry Virtualization – OS natively compiled for CPU, running guest OSes also natively compiled Several guest operating systems (execution environment) Giving the illusion that each guest execution environment is running its own private computer VMware application: ran one or more guest copies of Windows or other OSes, each running applications, all on native Windows host OS VMM (Virtual Machine Manager) runs the guest OSes, manages their resources and protects each guest from others. Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.43 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Computing Environments - Virtualization Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.44 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Computing Environments - Virtualization Use cases involve laptops and desktops running multiple OSes for exploration or compatibility Apple laptop running Mac OS X host, Windows as a guest Developing apps for multiple OSes without having multiple systems QA testing applications without having multiple systems Operating System Concepts Essentials – 9th Edition 1.45 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013