* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download middleages
England in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Open-field system wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Medievalism wikipedia , lookup
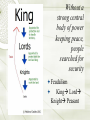
Medieval Europe 500-1500 Russell’s Rule to the Middle Ages: Major questions about the Middle Ages (according to the regents) deal with: 1) 2) 3) Feudalism (weak central gov’t) Rise and power of Catholic Church The Crusades and the increase in trade The Good and the Bad Results of the Fall of Rome Germanic invasions lead to fall of Roman Empire which also led to: 1) Breakdown of trade Fear of bandits and without someone to “police” people stopped trading = Less money, Less power, more isolation 2) Cities destroyed 3) Population Shift People move out of “center” of Civilization and begin moving to North and Countryside QuickTime™ and a TIF F (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 4) Learning decreased a. Germanic invaders were not educated leaving only priest and other high officials educated b. People could not read ancient texts of Greeks or Romans (culture lost) 5) Loss of common language a. Germanic people spoke different language leading to Latin changing in to different dialects such as Spanish and French b. DIFFERENT LANGUAGES SEPARATE PEOPLE Homer says” Latin, who needs Latin? I’m never going to use Latin” After the Fall of Rome, many people went searching for stability in everyday life, Where do people search for stability? - Individually Society 6) THE CHURCH!!!!!! Increase in power of RCC! Life began to surround itself around the Church Going to Church Holidays Behaviors Education Roman Catholic Church became source of education for many The Arts Mostly church related Gothic Architecture Flying Buttresses Stained Glass THE MEDIEVAL CHURCH Age of Faith: Gothic Architecture Economy: Monasteries and churches often had their own lands and produced food and wine with the help of the peasants. Tithe Tax by the Church, each person must give 1/10 income to Church Another example of RCC increase in power. This left Europe weak for many years until… Life became chaos Nothing was stable Charlemagne (Charles the Great) united Europe 771 ad -created greatest empire since Ancient Rome -Frank (German) King, 6’4 -Spread Christianity -Pope crowned him Emperor signifying alliance between Germans, Church, and former Roman Empire Created Holy Roman Empire 1st Reich Died in 814 So what happened after Charlemagne? WEAK RULERS Divided Empire amongst sons…too weak Rulers that followed Charlemagne were weak and empire would be divided in 3 parts -This lack of strong leadership lead to Feudalism in Europe o Nobles often fought over power with one another o Viking invasions also helped weaken rulers and villages Political Systems of the Middle Ages People searched for safety Answer: Feudalism Remember Feudalism is the political term Manor system or manorialism is the economic term for this system Without a strong central body of power keeping peace, people searched for security Feudalism King Lord Knight Peasant OATH OF FEALTY VASSALS (lesser lords and knights) pledged their loyalty. THE BASIS OF MEDIEVAL ECONOMY WAS THE FIEF, OR PARCEL OF LAND GIVEN AFTER AN OATH OF LOYALTY IN EXCHANGE FOR SERVICES. FEUDALISM Kings were Relatively Weak Decentralized political system LORDS, LAND, AND LOYALTY Isolated, Self-Sufficient Manors Lords and Nobles control the domain or fief Oaths of Fealty to one’s liege lord Land was the basis of wealth Protection was exchanged for loyalty and land QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. SERFS AND SERFDOM Serfs were tied to the land. They could not leave, marry, etc. without the lord’s permission. A serf was at the bottom of the manor system. They worked the lord’s land, and often the church estates, and then could tend their own small plot of land they received in exchange for these services. LABOR!! LAND! SERFS ALSO GOT PROTECTION ! Feudal Society KING NOBLES LESSER LORDS KNIGHTS SERFS Economics: MANORIALISM AGRARIAN TRADITIONAL ECONOMY AGRARIAN MANORIALISM A SELF-SUFFICIENT ECONOMY BASED ON AGRICULTURE THE MANOR HOUSE THE LORD’S HOUSE WAS THE BIGGEST ONE BUT OFTEN NOT VERY SANITARY. IF HE LIVED IN A CASTLE, IT WAS COLD AND DAMP. THE LORD HAD CONTROL OF ALL OF THOSE IN HIS DESMESNE (domain). THEY WORKED OR PROVIDE MILITARY SERVICES FOR HIM. HE PROTECTED THEM IN HIS CASTLE IN TIMES OF DANGER. THE MANOR SYSTEM ANYTHING NOT PRODUCED ON THE LORD’S MANOR COULD BE BARTERED. MONEY WAS RARELY USED AFTER ROME’S EMPIRE COLLAPSED. MEDIEVAL FARM TOOLS THE AX THE RAKE THE FLAIL MEDIEVAL FARM TOOLS LONG HANDLED SCYTHE AND THE SICKLE MEDIEVAL FARM TOOLS HAYMAKING FORK AND SPADE THE 3 FIELD SYSTEM Gray - Woodlands; the building blocks of the manor. Green - The 3 Fields; crops were rotated each season on land owned by the Lord and worked by the serfs. Purple - The Lord's house, land and pond. Burnt Orange - The villager's homes. Yellow - Small plots of land serfs could work themselves for their own benefit. Blue - the stream used by all. THE PLOUGH (PLOW) In the Middle Ages, three inventions would help increase food production: HORSE HARNESS The Ox was a slow animal, but the ox harness was lethal to the horse. Once a new harness was designed, “horse power” was used. WINDMILL WATERMILLS KEPT PEASANTS NEAR RIVERS. BUT THE WINDMILL EXPANDED WHERE GRAIN COULD BE GROUND. What do these inventions mean Increase food production Increase population Less people needed to farm KNIGHTS Knights Soldiers of the Middle Ages For a Fief, would pledge loyalty to defend Lords/Kings lands MEDIEVAL TOURNAMENT Soldiers mounted on horseback Protect nobles or kings possessions IN THE LATER MIDDLE AGES, THERE WERE FEWER INVADERS SO KNIGHTS WOULD FIGHT IN ENTERTAINMENT CALLED TOURNAMENTS. CHIVALRY WAS THE IDEAL CODE OF HONOR THAT A KNIGHT SHOULD FIGHT, LIVE, AND DIE BY. Code of Chivalry Moral/ethical code of the knights Behaviors of what is right/wrong Tournaments: when knights were not at war. (just like in A Knight’s Tale) - Jousting sword fighting MEDIEVAL WEAPONS LONG BOW CROSS BOW SWORD Trebuchet Medieval Women Role of Women in Feudal society - little or no power - could inherit land - home activities or convent Rise of the Guild System: -people, especially the poor, without education were unsure of how to better their lives. -What is the guild system? Page 388 in text take notes Question to answer 1) What is a guild? 2) What is the purpose of the guild system? 3) What are the different levels of the guild system? 4) What are some examples of guilds? Guild system – organization of individuals in the same business or occupation working together to improve economic and social conditions Apprentice journeyman. Master Guilds Middle Age living conditions Small damp homes Dirt Floors 2 or 3 baths a year Garbage in streets Fecal matter in streets Dead bodies Very few had hot water What is a castle for? Wars Numerous Wars (Hundred Years war between France and Britain and pillaging by Vikings and barbarians of lands) Hundred Years War: 1337 -1453 VS England vs. France -Fought over who was heir to French throne when King died -English ruler Edward III believed it was him because he was the grandson of Philip IV of France -Joan of Arc - France eventually gets England off soil Increase nationalistic feelings Black Death Also known as the Bubonic Plague People thought the apocalypse was coming people were scared that God was punishing them Black Death 1/3 of Europe’s population gone Workers decrease Productivity decrease Trade decrease Middle Ages: Good or bad Good 3 field system Horse harness Iron Plow Guild System Chivalry Results of Crusades Commercial Revolution Bad -Feudalism -Education -Living Conditions -War (100 years war, Crusades -Disease black death -Life of a serf