* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download franks__feudalism_best
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Merovingian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
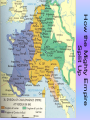
The Early Middle Ages: The Franks & Feudalism Or..were the Dark Ages really a dark as they seemed? Who sacked the city of Rome? The Franks • In the Roman province of Gaul (France) • No cities or written laws – 100s of tiny kingdoms – Farmers or herders • Swore loyalty to King – weapons & loot Clovis • Converts to Christianity after a battle • Roman Catholic Church welcomed & supports Clovis’s conquests • by 511 AD—united all of the Franks into one kingdom • two forces were now allied 1. Military (Franks) 2. Spiritual (Church) • Merovingian Dynasty Charles Martel • Mayor of the Palace • extended Frank’s reign to the north, south, and east • defeated Muslims at the Battle of Tours – Stopped the Muslim expansion into W. Europe – becomes a Christian hero Pepin the Short • son of Charles Martel • Fights the Lombards for the Church • pope declares him “king by the Grace of God” • this begins the Carolingian Dynasty Charlemagne • Greatest European empire since Rome • Summer military campaigns – Muslims in Spain and Germanic tribes • Spread Christianity by conquering the east and south • Holy Roman Emperor – joining of Germanic power, the Church, and the heritage of the Roman Empire Charlemagne’s Empire Included 2/3 of Italy, all of France, a small part of Spain, and Germany Charlemagne Cnt. • Encourages learning and law • Limits rule of the nobles • counts governed their counties justly • Visits whole kingdom – judges cases, settles disputes, and rewards faithful • Irish, English, German, Italian, and Spanish scholars – school for court children • Monasteries—trained monks – expanded libraries – handwritten copies of books After Charlemagne • Grandsons split empire in 843 AD – Louis the German – Lothair – Charles the Bald • Magyars—900 AD, cavalry from Hungary invade • Vikings—From Scandinavia, sailors – Raided and looted from Ireland to France How the Mighty Empire Split Up What is Feudalism? • Social Structure of the Middle Ages • Based on loyalty and importance of the Oath • Keep these words in mind while you are watching the film: – – – – – – – – Manor Lords Vassals Fief Knights Serf Peasants Self-Sufficiency Feudalism The Manor System • Self-Sufficient – All needs provided on estate • Controlled by Lord – (who was someone else’s Vassal) – Remember: Social Pyramid Gives Gets King/Lord Vassal Land (fief) Power/authority Collects Taxes Loyalty Military service Taxes Loyalty/Honor Military protection Land Power/Authority Right to collect taxes King Lords Lesser Nobles, Knights Gives Serfs • Cannot leave manor •Need permission to marry Gets Manor Lord Serf Small land Labor/taxes Protection Loyalty Basic needs Military service (sometimes) Labor Small tract of land Money Protection Loyalty Basic needs Peasants • Free Chivalry • Complex rules governing society • Three Masters: – Feudal Lord – Heavenly Lord – Chosen Lady • Knights usually wealthy – Education starts at 7 till 21 • Tournaments, troubadours, poetry – Real warfare brutal • Few women had authority Medieval Letter Writing: Take one of the following roles and write a letter to a family member in a different country. Tell them what your life is like on the manor, what rights you have, and the work you do. You may only use your notes from today. Make it at least 1 page: – Lord (Major Lord) – Vassal (Lesser Lord) – Knight – Serf – Peasant