* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File 3 middle ages ppt
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
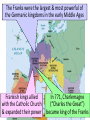
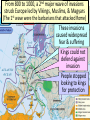
■Essential Question: – I will distinguish between the major characteristics of feudalism, manorialism, chivalry, and faith in the middle ages by completing a circle graph. ■Warm-Up QUIZ: – What two groups settled together to make Russia? – What was Kiev? – Name 2 ways the Byzantine Empire influenced Russia Quick Review: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire? In the East, the Byzantine Empire became a center for trade & Greco-Roman culture the West, Europe grew weak The In Middle Ages & fell into the Middle Ages from 500 to 1300 Also known as the “Dark Ages” or “Medieval” era WhenEurope barbarianAfter kingdoms that conquered Rome, the Fall of Rome Europe was plagued by constant warfare Warfare disrupted trade, Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten Europe lost a common language; Latin mixed with local languages to form Spanish, French, Italian Without the unity of the Roman Empire, Europe Germanic Tribes in the Middle Ages became divided into a series of Germanic kingdoms Germanic people lived in small communities led by chiefs & his loyal warriors Family ties & loyalty were more important than citizenship During theSpread early Middle Ages, the Germanic The of Christianity kingdoms were slowly converted to Christianity Question: Should the Pope be involved in secular issues? Why or Why Not? The Catholic Pope became involved in secular (non-religious) issues like road repair, aiding the poor, & helping Christian kings expand their power The Franks the largest & most powerful of Thewere Spread of Christianity the Germanic kingdoms in the early Middle Ages Frankish kings allied with the Catholic Church & expanded their power In 771, Charlemagne (“Charles the Great”) became king of the Franks Charlemagne was greatest Medieval king Charlemagne &the the Frankish Empire because he did something no other king was able to do…create an organized empire He spread Christianity He created schools to train future priests Charlemagne expanded He valued learning & built the Frankish empire schools in his empire Charlemagne & the Frankish Empire After Charlemagne’s death …This was the last in 814, his Frankish Empire opportunity to provide was divided & lost power… unity in medieval Europe From 800 to 1000, a 2nd major wave of invasions struck Europe led by Vikings, Muslims, & Magyars (The 1st wave were the barbarians that attacked Rome) ■ Text These invasions caused widespread fear & suffering Kings could not defend against invasion People stopped looking to kings for protection Feudalism ■ Feudalism began in Europe as a way to offer protection: –Feudalism is based on land & loyalty –Land-owning lords offer land (called a fief) to knights in exchange for their loyalty & promise to protect the lord’s land Feudal Structure Knights were specially trained soldiers who protect the lords & peasants Some peasants were serfs & could not leave the lord’s estate Kings had land but very little power Lords (also called Nobles) were the upper-class landowners; they had inherited titles (“Duke,” “Earl,” “Sir”) Lords built castles to protect their territory from outside invasions The Manorial System During the Middle Ages, the manorial system was the way in which people survived The lord’s land was called a manor The lord provided peasants with housing, farmland, & protection In exchange, peasants repaid the lord by working his land & providing a portion of the food they produced Peasant life was hard: They paid taxes to use the lord’s mill, had to get permission to get married, & life expectancy was about 35 years old Manors were self-sufficient communities; Everything that was needed was produced on the manor 1. Christianity as a Create this chart in your unifying force notes leaving room for the 2. Government based on information with the landholding numbers. 3. Got involved in political affairs 4. Devotion to feudal lord and heavenly Lord Economic 5. Set of rights and System: Manors obligations 3 between peasants and lords Code of Belief 6. Alliances Behavior: System: between lords Chivalry The Church and vassals 3 3 7. Loyalty in exchange for land Put the correct numbers and military in the right circles. service 8. Ranking of power and authority 9. Respect towards women 10. Lord’s estate 11. Power over people’s everyday lives 12. Displays courage and valor in battle 13. Selfsufficient community producing a variety of goods. Feudalism Manors The Church Chivalry 2. Government based on landholding 5. Set of rights and obligations between peasants and lords 1. Christianity as a unifying force 4. Devotion to feudal lord and heavenly Lord 6. Alliances between lords and vassals 10. Lord’s estate 3. Got involved in political affairs 9. Respect towards women 7. Loyalty in exchange for land and military service 13. Selfsufficient community producing a variety of goods. 11. Power over people’s everyday lives 12. Displays courage and valor in battle 8. Ranking of power and authority