* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 Intro to Middle Ages Feudalism 2007
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
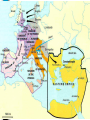
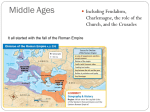
The Middle Ages The Decline of the Roman Empire & the Rise of Feudalism Barbarians Ruled Western Europe By 500 A.D. Western Roman Empire fell to barbarian tribes: –Visigoths controlled Spain –Ostrogoths controlled Italy –Franks controlled Gaul (France) –Vandals controlled North Africa –Angles, Saxons, Jutes battled for Britannia –Celts ruled Ireland & Scotland The Middle Ages After the fall of Rome, Western Europe entered the Middle Ages from 500-1500 A.D. Latin barbarianAges: Reasons for blended the risewith of Middle languages to make Italian, The “Dark Ages” The “Medieval” era –No Roman emperor to make rules 500 –French, 1000 Spanish, etc. –No Roman army to protect people –No common language to unite them –No longer citizens of a common empire; people now loyal to family members (clan) or feudalism Decline of Civilization Constant warfare among the barbarian tribes & the Romans made it too dangerous to trade: –With no trade, towns & cities became useless –People built to farming villages to make food & find protection –Priests became the only people who could read & write No Roman Government? Without the Roman Government, how are things different in Western Europe: –Trade? No more trade –Food? Self-sufficient farmers –Safety? Dangerous fighting –Leadership? No emperors –Language? Different languages –Religion? Polytheism Feudalism Feudalism began in Europe as a way to offer protection: –Feudalism is a series of agreements between lords & knights in which lords offer land in exchange for loyalty & military protection from knights –Lords built castles to protect peasants from outside invasions Feudal Structure Knights were specially trained soldiers who protect the lords & peasants Some peasants were serfs & could not leave the lord’s estate Kings had land but very little power Lords (also called Nobles) were the upper-class landowners; they had inherited titles (“Duke,” “Earl,” “Sir”) Manorial System The manorial system produced the food for people to eat: –Lords allowed peasants to live on their land in exchange for a portion of the food they grew –Peasants agreed to pay “rent” to the nobles in exchange for shelter & protection Peasant life was difficult: they were dependent upon the lords & got lots of diseases I am the King!! I have so much land!! I think I’ll build myself a castle, but I have no power so maybe I should give fiefs to some lords Thank you king for this fief. As your loyal lords we will oversee this land We will fight for the king and provide him with food from our lands, but this territory to too large. Let’s pick the best land to build our homes on, then let’s give fiefs to some vassals!! Thank you lords for this fief. We promise loyalty, military service, & a portion of our food Let’s pick the best land to build our homes on!! Aren’t we going to need protection, too? Oh yeah, let’s give fiefs to some knights also! Let’s allow serfs to do all the work & provide us with food! We will gain their work & loyalty Thank you vassals for allowing us to live on this land. We provide you loyalty, military service, & a portion of our food According to the code of Chivalry, I will forever protect my lord & vassal, my God, and my sweetie-pie at home! The Power of the Christian Church Many people in Western Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire were polytheistic but Christians converted many “barbarians” In this time of chaos, the Christian church emerged as a stable & unifying force in Western Europe The Power of the Christian Church Catholicism became the dominant religion in Western Europe: –Without a common government to hold everyone together, the Church filled an important role in peoples’ lives –The Catholic Pope became the strongest political leader in Western Europe The Power of the Christian Church Each territory in Western Europe had a monastery (where monks lived) & provided order for the feudal manors: –Local priests were important because the church taught that all people are sinners & need God’s forgiveness –Christians paid a tithe (percentage of their food as a tax to the church)